
Agriculture & Smart Farming
Revolutionize farming using IoT, AI, and robotics for precision crops, healthier soils, and automated irrigation.
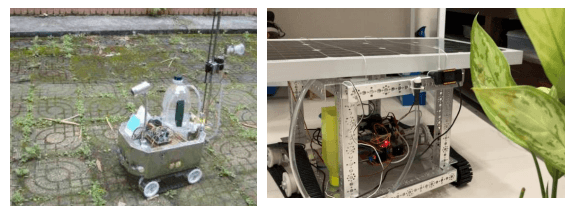
Smart Robotic Pythomedic and Pesticide Sprayer using Image Processing and machine learning
Plant diseases pose a significant global and Indian agricultural challenge, resulting in crop yield reduction and financial losses for farmers. While existing solutions like smart disease detection using machine learning offer promise, they often present cost or implementation barriers. Our solution introduces a user-friendly Smart Spraying robot equipped with a front camera and machine learning algorithm to identify and address plant diseases efficiently. Tested with over 3000 images across three vegetable plants, the model demonstrates 100% accuracy in detecting specific leaf diseases. However, its applicability is currently limited to these plants. Future iterations can expand its scope to encompass a broader range of crops.

Smart Robotic Pythomedic and Pesticide Sprayer using Image Processing and machine learning
Plant diseases pose a significant global and Indian agricultural challenge, resulting in crop yield reduction and financial losses for farmers. While existing solutions like smart disease detection using machine learning offer promise, they often present cost or implementation barriers. Our solution introduces a user-friendly Smart Spraying robot equipped with a front camera and machine learning algorithm to identify and address plant diseases efficiently. Tested with over 3000 images across three vegetable plants, the model demonstrates 100% accuracy in detecting specific leaf diseases. However, its applicability is currently limited to these plants. Future iterations can expand its scope to encompass a broader range of crops.

Smart Robotic Pythomedic and Pesticide Sprayer using Image Processing and machine learning
Plant diseases pose a significant global and Indian agricultural challenge, resulting in crop yield reduction and financial losses for farmers. While existing solutions like smart disease detection using machine learning offer promise, they often present cost or implementation barriers. Our solution introduces a user-friendly Smart Spraying robot equipped with a front camera and machine learning algorithm to identify and address plant diseases efficiently. Tested with over 3000 images across three vegetable plants, the model demonstrates 100% accuracy in detecting specific leaf diseases. However, its applicability is currently limited to these plants. Future iterations can expand its scope to encompass a broader range of crops.
Examination of NPK Values and Their Effects on Soil
Soil health and soil quality are defined as the ability of the soil to perform as an essential living system under the restrictions of land use. This activity maintains the biological productivity of the soil, which benefits both the environment and human health. Soil quality is linked to soil function, whereas soil health portrays the soil as a finite, non-renewable, and dynamic living resource. The notion of soil health, which encompasses interactions between plant inputs and soil in creating a healthy environment, is discussed in this paper.

Examination of NPK Values and Their Effects on Soil
Soil health and soil quality are defined as the ability of the soil to perform as an essential living system under the restrictions of land use. This activity maintains the biological productivity of the soil, which benefits both the environment and human health. Soil quality is linked to soil function, whereas soil health portrays the soil as a finite, non-renewable, and dynamic living resource. The notion of soil health, which encompasses interactions between plant inputs and soil in creating a healthy environment, is discussed in this paper.

Examination of NPK Values and Their Effects on Soil
Soil health and soil quality are defined as the ability of the soil to perform as an essential living system under the restrictions of land use. This activity maintains the biological productivity of the soil, which benefits both the environment and human health. Soil quality is linked to soil function, whereas soil health portrays the soil as a finite, non-renewable, and dynamic living resource. The notion of soil health, which encompasses interactions between plant inputs and soil in creating a healthy environment, is discussed in this paper.
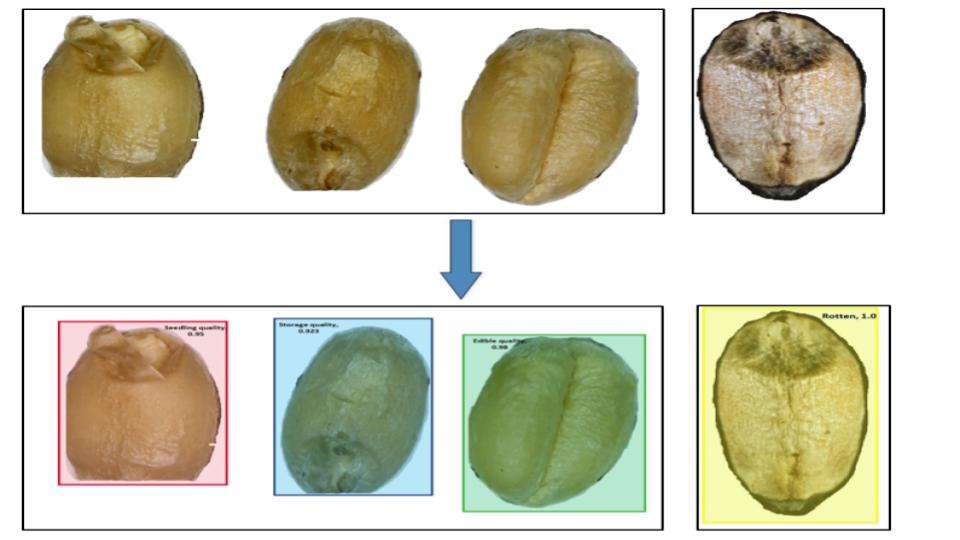
Assessment of Quality of The Wheat Grain Using Image Processing and Mask R-CNN
The study develops a Mask Regional Convolutional Neural Network (Mask RCNN) model to classify the quality of wheat grains into four categories: storage quality, edible, seeding quality, or rotten. The model is trained on 122 images created from 2,000 grains, using image processing to extract grain texture. The wheat grains are annotated with VGG Image Annotator, and the JSON files are used for training and testing the Mask RCNN model. The trained model achieves low training and validation losses and demonstrates high accuracy in classifying the grain quality when tested on a new image with all four classes.

Assessment of Quality of The Wheat Grain Using Image Processing and Mask R-CNN
The study develops a Mask Regional Convolutional Neural Network (Mask RCNN) model to classify the quality of wheat grains into four categories: storage quality, edible, seeding quality, or rotten. The model is trained on 122 images created from 2,000 grains, using image processing to extract grain texture. The wheat grains are annotated with VGG Image Annotator, and the JSON files are used for training and testing the Mask RCNN model. The trained model achieves low training and validation losses and demonstrates high accuracy in classifying the grain quality when tested on a new image with all four classes.

Assessment of Quality of The Wheat Grain Using Image Processing and Mask R-CNN
The study develops a Mask Regional Convolutional Neural Network (Mask RCNN) model to classify the quality of wheat grains into four categories: storage quality, edible, seeding quality, or rotten. The model is trained on 122 images created from 2,000 grains, using image processing to extract grain texture. The wheat grains are annotated with VGG Image Annotator, and the JSON files are used for training and testing the Mask RCNN model. The trained model achieves low training and validation losses and demonstrates high accuracy in classifying the grain quality when tested on a new image with all four classes.

Application of Data Analysis and Soft Computation to Model the Need of Crop Insurance for the Indian Farmers
A very high level of uncertainty is associated with agriculture in the form of natural, social, and human-related actions. Farmers incur heavy losses whenever their farmlands are affected. Crop insurance is the answer to such losses that existed as an institutional response to nature-induced risk. Hence, there is a demand to model the need for crop insurance for Indian Farmers. The first part involves applying exploratory data analysis (EDA) to correlate the factors with the farmers' responses. A correlational analysis is also conducted to study the relationship between different factors. The second part involves the application of three machine learning (ML) algorithms, namely, Logistic Regression (LR), Random Forest (RF), and Gradient Boost classifier (GB) to meet the aims and objectives of the paper.

Application of Data Analysis and Soft Computation to Model the Need of Crop Insurance for the Indian Farmers
A very high level of uncertainty is associated with agriculture in the form of natural, social, and human-related actions. Farmers incur heavy losses whenever their farmlands are affected. Crop insurance is the answer to such losses that existed as an institutional response to nature-induced risk. Hence, there is a demand to model the need for crop insurance for Indian Farmers. The first part involves applying exploratory data analysis (EDA) to correlate the factors with the farmers' responses. A correlational analysis is also conducted to study the relationship between different factors. The second part involves the application of three machine learning (ML) algorithms, namely, Logistic Regression (LR), Random Forest (RF), and Gradient Boost classifier (GB) to meet the aims and objectives of the paper.

Application of Data Analysis and Soft Computation to Model the Need of Crop Insurance for the Indian Farmers
A very high level of uncertainty is associated with agriculture in the form of natural, social, and human-related actions. Farmers incur heavy losses whenever their farmlands are affected. Crop insurance is the answer to such losses that existed as an institutional response to nature-induced risk. Hence, there is a demand to model the need for crop insurance for Indian Farmers. The first part involves applying exploratory data analysis (EDA) to correlate the factors with the farmers' responses. A correlational analysis is also conducted to study the relationship between different factors. The second part involves the application of three machine learning (ML) algorithms, namely, Logistic Regression (LR), Random Forest (RF), and Gradient Boost classifier (GB) to meet the aims and objectives of the paper.

Rapid Approach to Quantify the Industrial Pollution in The Water Bodies Using Machine Learning and Satellite Imaging
Chemical industries often pollute nearby water bodies, affecting water quality and groundwater, which impacts agriculture. There is a need for rapid testing of water from such polluted sources near industries. Our solution tackles this by assessing water quality using satellite images. We collected images of Pune city via the Mapbox API and developed a machine learning model to detect water bodies and assess their quality using image processing. Clean and polluted water bodies are segregated. Polluted bodies are further tested using a sensing device that measures pH and TDS of water samples. The convolutional neural network model achieves over 95% accuracy in water body detection. This solution provides a reliable and rapid method for checking water quality and evaluating the impact of nearby industries on water bodies.

Rapid Approach to Quantify the Industrial Pollution in The Water Bodies Using Machine Learning and Satellite Imaging
Chemical industries often pollute nearby water bodies, affecting water quality and groundwater, which impacts agriculture. There is a need for rapid testing of water from such polluted sources near industries. Our solution tackles this by assessing water quality using satellite images. We collected images of Pune city via the Mapbox API and developed a machine learning model to detect water bodies and assess their quality using image processing. Clean and polluted water bodies are segregated. Polluted bodies are further tested using a sensing device that measures pH and TDS of water samples. The convolutional neural network model achieves over 95% accuracy in water body detection. This solution provides a reliable and rapid method for checking water quality and evaluating the impact of nearby industries on water bodies.

Rapid Approach to Quantify the Industrial Pollution in The Water Bodies Using Machine Learning and Satellite Imaging
Chemical industries often pollute nearby water bodies, affecting water quality and groundwater, which impacts agriculture. There is a need for rapid testing of water from such polluted sources near industries. Our solution tackles this by assessing water quality using satellite images. We collected images of Pune city via the Mapbox API and developed a machine learning model to detect water bodies and assess their quality using image processing. Clean and polluted water bodies are segregated. Polluted bodies are further tested using a sensing device that measures pH and TDS of water samples. The convolutional neural network model achieves over 95% accuracy in water body detection. This solution provides a reliable and rapid method for checking water quality and evaluating the impact of nearby industries on water bodies.
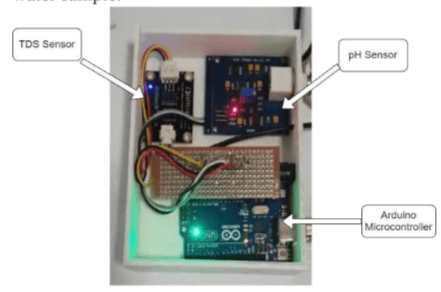
A Novel Approach Towards Calculating The Reusability Coefficient Of Water From Nearby Water Bodies Using Artificial Intelligence
Most water bodies are polluted, but there is limited data on the level of pollution. This project proposes a solution to assess water quality by collecting samples from various sources like sewage, rivers, and farms. The solution has three parts: 1) detecting turbidity using image processing, 2) measuring TDS and pH using an Arduino-based prototype, and 3) determining a quality coefficient through machine learning. All components are integrated into a 3D-printed device. The model achieves an accuracy of 89% in estimating water quality, while the circuit accurately measures TDS and pH. This real-time solution enables the detection of water body quality and potential usage after appropriate treatment

A Novel Approach Towards Calculating The Reusability Coefficient Of Water From Nearby Water Bodies Using Artificial Intelligence
Most water bodies are polluted, but there is limited data on the level of pollution. This project proposes a solution to assess water quality by collecting samples from various sources like sewage, rivers, and farms. The solution has three parts: 1) detecting turbidity using image processing, 2) measuring TDS and pH using an Arduino-based prototype, and 3) determining a quality coefficient through machine learning. All components are integrated into a 3D-printed device. The model achieves an accuracy of 89% in estimating water quality, while the circuit accurately measures TDS and pH. This real-time solution enables the detection of water body quality and potential usage after appropriate treatment

A Novel Approach Towards Calculating The Reusability Coefficient Of Water From Nearby Water Bodies Using Artificial Intelligence
Most water bodies are polluted, but there is limited data on the level of pollution. This project proposes a solution to assess water quality by collecting samples from various sources like sewage, rivers, and farms. The solution has three parts: 1) detecting turbidity using image processing, 2) measuring TDS and pH using an Arduino-based prototype, and 3) determining a quality coefficient through machine learning. All components are integrated into a 3D-printed device. The model achieves an accuracy of 89% in estimating water quality, while the circuit accurately measures TDS and pH. This real-time solution enables the detection of water body quality and potential usage after appropriate treatment
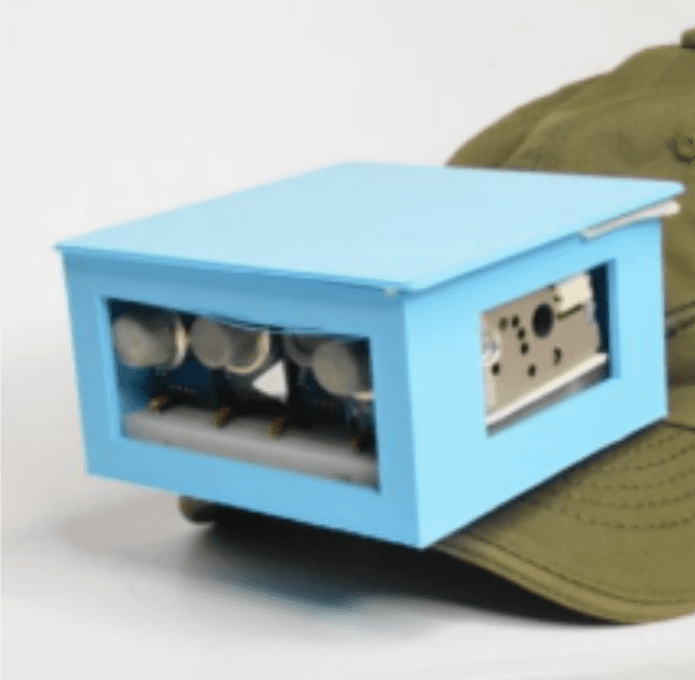

Environmental Technology or Environmental Safety
Sewage disposal cleanup is a hazardous job, exposing workers to harmful gases, infections, and health risks like musculoskeletal disorders and respiratory problems. SEWER GUARD is a project aimed at developing an information and communication ecosystem to monitor and alert workers about dangerous gas levels in sewers. It uses MQ series sensors to measure gas levels and sends alerts if they exceed safe thresholds. The system correlates gas intensity, depth, and exposure time, enabling workers to evacuate before conditions become life-threatening. An Android app and cloud storage are integrated for monitoring and data storage. Authorities can also be notified via SMS if sewage overflow is likely. SEWER GUARD aims to improve the safety and working conditions of sanitary workers engaged in sewer cleanup operations.

Environmental Technology or Environmental Safety
The research presented here looks into the vibration properties of 3D-printed airless tires, which have the potential to revolutionize tire design and transportation efficiency. Through extensive experimentation and vibration research, three distinct tire constructions were investigated. Because of its good damping and deformation qualities, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) was chosen as the 3D printing material. The experimental arrangement was designed to simulate real-world road conditions, and an MPU6050 sensor captured tire vibrations in three axes. The vibrational properties of the tire structures were revealed using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) analysis, allowing for a comparative assessment of their stability. Structure 1 was found to be the most vibration-stable, followed by Structures 3 and 2.

Environmental Technology or Environmental Safety
Sewage disposal cleanup is a hazardous job, exposing workers to harmful gases, infections, and health risks like musculoskeletal disorders and respiratory problems. SEWER GUARD is a project aimed at developing an information and communication ecosystem to monitor and alert workers about dangerous gas levels in sewers. It uses MQ series sensors to measure gas levels and sends alerts if they exceed safe thresholds. The system correlates gas intensity, depth, and exposure time, enabling workers to evacuate before conditions become life-threatening. An Android app and cloud storage are integrated for monitoring and data storage. Authorities can also be notified via SMS if sewage overflow is likely. SEWER GUARD aims to improve the safety and working conditions of sanitary workers engaged in sewer cleanup operations.
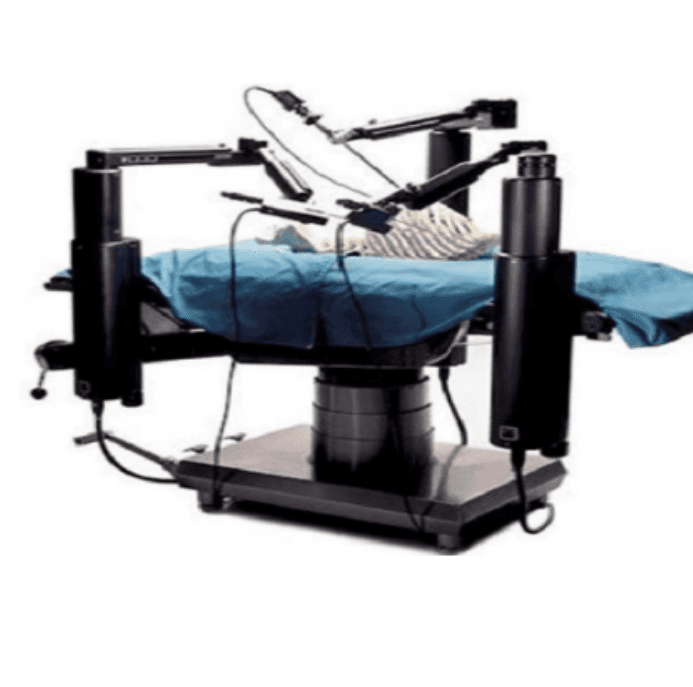
A Review on RoboticsA Review on Robotics Used in Biomedical Surgery
In terms of advancing surgical techniques, robotic surgery, which has been around for more than 20 years is a revolutionary development. The last ten years have seen a rise in the usage of robotics in medical treatments. In an effort to develop smaller, more effective, and less expensive equipment, researchers are ready to achieve record heights as robotic surgery becomes more and more common. Robotic surgery has been successfully used in many hospitals throughout the world and is gaining recognition on a global scale. In this article, we examine robotic surgery's development and progression, current robotic systems, limitations as well as current statistics, and current roles of robotics in surgery, and finally, we discuss the possible roles of robotic surgery in the future.

A Review on RoboticsA Review on Robotics Used in Biomedical Surgery
In terms of advancing surgical techniques, robotic surgery, which has been around for more than 20 years is a revolutionary development. The last ten years have seen a rise in the usage of robotics in medical treatments. In an effort to develop smaller, more effective, and less expensive equipment, researchers are ready to achieve record heights as robotic surgery becomes more and more common. Robotic surgery has been successfully used in many hospitals throughout the world and is gaining recognition on a global scale. In this article, we examine robotic surgery's development and progression, current robotic systems, limitations as well as current statistics, and current roles of robotics in surgery, and finally, we discuss the possible roles of robotic surgery in the future.

A Review on RoboticsA Review on Robotics Used in Biomedical Surgery
In terms of advancing surgical techniques, robotic surgery, which has been around for more than 20 years is a revolutionary development. The last ten years have seen a rise in the usage of robotics in medical treatments. In an effort to develop smaller, more effective, and less expensive equipment, researchers are ready to achieve record heights as robotic surgery becomes more and more common. Robotic surgery has been successfully used in many hospitals throughout the world and is gaining recognition on a global scale. In this article, we examine robotic surgery's development and progression, current robotic systems, limitations as well as current statistics, and current roles of robotics in surgery, and finally, we discuss the possible roles of robotic surgery in the future.
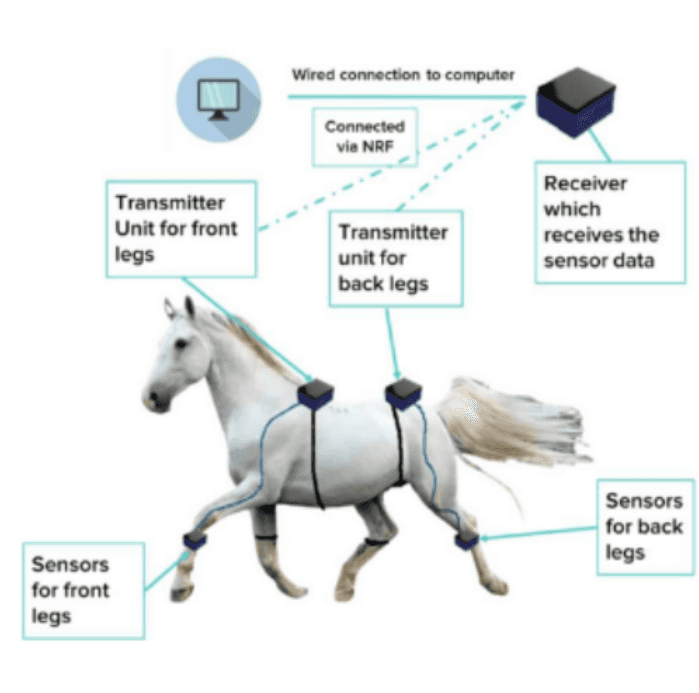
A Novel Approach to Quantify and Compute Gait Analysis Parameters of Quadrupeds
Gait analysis is the study of human and animal locomotion. Analysis of gait is particularly prevalent in developed countries, owing to extensive capital and resources. However, in developing countries such as India, gait analysis devices and instruments are restricted solely to metropolitan cities. Even in Metropolitan Cities, the analysis of human gait is costly. An analysis of quadruped gait is notably absent in developing countries and, if present, is extremely expensive. This creates a financial disparity, in which those in poverty are unable to have a veterinarian kinematically check their Quadruped's gait, while the wealthy are able to do so. The solution presented aims to analyze the gait of all quadrupeds. This mechanism correlates the usage of a Gyroscope, 3-axis accelerometer, and Digital Motion Processor along with graphs plotted using Python's MatPlotLib Library and three-dimensional simulations with an AutoCAD model and simulated using the library Panda3D in a portable, wearable device.

A Novel Approach to Quantify and Compute Gait Analysis Parameters of Quadrupeds
Gait analysis is the study of human and animal locomotion. Analysis of gait is particularly prevalent in developed countries, owing to extensive capital and resources. However, in developing countries such as India, gait analysis devices and instruments are restricted solely to metropolitan cities. Even in Metropolitan Cities, the analysis of human gait is costly. An analysis of quadruped gait is notably absent in developing countries and, if present, is extremely expensive. This creates a financial disparity, in which those in poverty are unable to have a veterinarian kinematically check their Quadruped's gait, while the wealthy are able to do so. The solution presented aims to analyze the gait of all quadrupeds. This mechanism correlates the usage of a Gyroscope, 3-axis accelerometer, and Digital Motion Processor along with graphs plotted using Python's MatPlotLib Library and three-dimensional simulations with an AutoCAD model and simulated using the library Panda3D in a portable, wearable device.

A Novel Approach to Quantify and Compute Gait Analysis Parameters of Quadrupeds
Gait analysis is the study of human and animal locomotion. Analysis of gait is particularly prevalent in developed countries, owing to extensive capital and resources. However, in developing countries such as India, gait analysis devices and instruments are restricted solely to metropolitan cities. Even in Metropolitan Cities, the analysis of human gait is costly. An analysis of quadruped gait is notably absent in developing countries and, if present, is extremely expensive. This creates a financial disparity, in which those in poverty are unable to have a veterinarian kinematically check their Quadruped's gait, while the wealthy are able to do so. The solution presented aims to analyze the gait of all quadrupeds. This mechanism correlates the usage of a Gyroscope, 3-axis accelerometer, and Digital Motion Processor along with graphs plotted using Python's MatPlotLib Library and three-dimensional simulations with an AutoCAD model and simulated using the library Panda3D in a portable, wearable device.
Development of a Robust Model to Predict the Sales of Tickets Employing Fuzzy IF- THEN Rules Based Algorithm
This study presents a robust model for predicting ticket sales of football matches based on game demand using a fuzzy IF-THEN rules-based algorithm. The proposed two-level simulation model first simulates the demand for a football match, and then simulates ticket sales by computing the Multi-Point Characteristics Index (MPCI) value. Factors influencing demand are categorized and expressed as linguistic terms, with uncertainties modeled using triangular fuzzy numbers (TFNs). The TFNs are converted to crisp values using the center of gravity method, and the properties and operations of TFNs are defined. The developed fuzzy IF-THEN rules-based algorithm, built on TFNs, provides an effective approach to forecasting ticket sales in the sports industry, considering the complex dynamics of game demand.

Development of a Robust Model to Predict the Sales of Tickets Employing Fuzzy IF- THEN Rules Based Algorithm
This study presents a robust model for predicting ticket sales of football matches based on game demand using a fuzzy IF-THEN rules-based algorithm. The proposed two-level simulation model first simulates the demand for a football match, and then simulates ticket sales by computing the Multi-Point Characteristics Index (MPCI) value. Factors influencing demand are categorized and expressed as linguistic terms, with uncertainties modeled using triangular fuzzy numbers (TFNs). The TFNs are converted to crisp values using the center of gravity method, and the properties and operations of TFNs are defined. The developed fuzzy IF-THEN rules-based algorithm, built on TFNs, provides an effective approach to forecasting ticket sales in the sports industry, considering the complex dynamics of game demand.

Development of a Robust Model to Predict the Sales of Tickets Employing Fuzzy IF- THEN Rules Based Algorithm
This study presents a robust model for predicting ticket sales of football matches based on game demand using a fuzzy IF-THEN rules-based algorithm. The proposed two-level simulation model first simulates the demand for a football match, and then simulates ticket sales by computing the Multi-Point Characteristics Index (MPCI) value. Factors influencing demand are categorized and expressed as linguistic terms, with uncertainties modeled using triangular fuzzy numbers (TFNs). The TFNs are converted to crisp values using the center of gravity method, and the properties and operations of TFNs are defined. The developed fuzzy IF-THEN rules-based algorithm, built on TFNs, provides an effective approach to forecasting ticket sales in the sports industry, considering the complex dynamics of game demand.

An Artificial Intelligence Integrated Technique for Screening
Neurological Diseases with Sound as a Biomarker
This project aims to develop a machine learning-based system for detecting neurological disorders like Parkinson's disease (PD) and paralysis through voice analysis. Researchers recorded speech samples from patients and healthy individuals, extracting features using Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC). K-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) models were trained on this dataset to classify voices into PD, paralysis, or normal categories. With an overall accuracy rate comparable to human laryngologists (60.1% and 56.1%), this system can assist clinicians in accurately identifying the presence and stage of neurological disorders, enabling appropriate treatment recommendations through therapy, medication, or a combination thereof

An Artificial Intelligence Integrated Technique for Screening
Neurological Diseases with Sound as a Biomarker
This project aims to develop a machine learning-based system for detecting neurological disorders like Parkinson's disease (PD) and paralysis through voice analysis. Researchers recorded speech samples from patients and healthy individuals, extracting features using Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC). K-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) models were trained on this dataset to classify voices into PD, paralysis, or normal categories. With an overall accuracy rate comparable to human laryngologists (60.1% and 56.1%), this system can assist clinicians in accurately identifying the presence and stage of neurological disorders, enabling appropriate treatment recommendations through therapy, medication, or a combination thereof

An Artificial Intelligence Integrated Technique for Screening
Neurological Diseases with Sound as a Biomarker
This project aims to develop a machine learning-based system for detecting neurological disorders like Parkinson's disease (PD) and paralysis through voice analysis. Researchers recorded speech samples from patients and healthy individuals, extracting features using Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC). K-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) models were trained on this dataset to classify voices into PD, paralysis, or normal categories. With an overall accuracy rate comparable to human laryngologists (60.1% and 56.1%), this system can assist clinicians in accurately identifying the presence and stage of neurological disorders, enabling appropriate treatment recommendations through therapy, medication, or a combination thereof
Statistical Scrutiny of the Prediction Capability of Different Time Series Machine Learning Models in Forecasting Bitcoin Prices
Cryptocurrencies (CTC) are decentralised digital currency. In the past decade, there has been a massive increase in its usage due to the advancement made in the field of blockchain. Bitcoin (BTC) is the first decentralised CTC which garnered a lot of attention from the media as well as the public due to its ability to sustain the momentum in the market. However, investing in BTC is not the first choice of the investor due to the market's erratic behaviour, price volatility and lack of a model that could be used to predict its price. For this purpose three machine learning (ML) models namely Long Short Term Memory (LSTM), Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average method (ARIMA) and Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated MovingAverage method (SARIMA) models have been employed which are statistically scrutinised on the basis of the performance metrics namely Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) and coefficient of determination (R2 ).

Statistical Scrutiny of the Prediction Capability of Different Time Series Machine Learning Models in Forecasting Bitcoin Prices
Cryptocurrencies (CTC) are decentralised digital currency. In the past decade, there has been a massive increase in its usage due to the advancement made in the field of blockchain. Bitcoin (BTC) is the first decentralised CTC which garnered a lot of attention from the media as well as the public due to its ability to sustain the momentum in the market. However, investing in BTC is not the first choice of the investor due to the market's erratic behaviour, price volatility and lack of a model that could be used to predict its price. For this purpose three machine learning (ML) models namely Long Short Term Memory (LSTM), Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average method (ARIMA) and Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated MovingAverage method (SARIMA) models have been employed which are statistically scrutinised on the basis of the performance metrics namely Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) and coefficient of determination (R2 ).

Statistical Scrutiny of the Prediction Capability of Different Time Series Machine Learning Models in Forecasting Bitcoin Prices
Cryptocurrencies (CTC) are decentralised digital currency. In the past decade, there has been a massive increase in its usage due to the advancement made in the field of blockchain. Bitcoin (BTC) is the first decentralised CTC which garnered a lot of attention from the media as well as the public due to its ability to sustain the momentum in the market. However, investing in BTC is not the first choice of the investor due to the market's erratic behaviour, price volatility and lack of a model that could be used to predict its price. For this purpose three machine learning (ML) models namely Long Short Term Memory (LSTM), Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average method (ARIMA) and Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated MovingAverage method (SARIMA) models have been employed which are statistically scrutinised on the basis of the performance metrics namely Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) and coefficient of determination (R2 ).
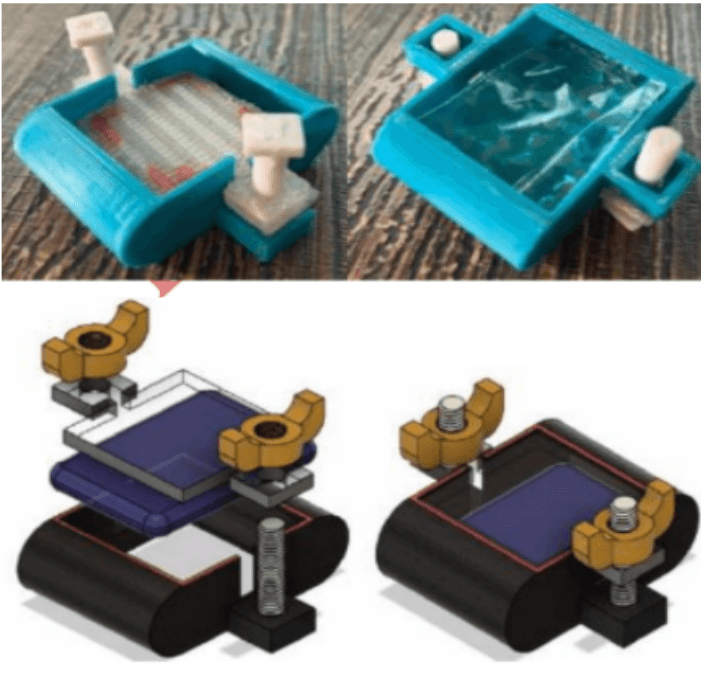
Creating a Haptic 4D Model Along With Machine Learning Analysis by Developing a Non- Invasive Pressure
Mapping Method to Screen for Genital Skin Cancer
Early detection of genital skin cancer is hindered by factors such as privacy concerns, social barriers, and discomfort. Traditional biopsy methods, though accurate, can cause pain and infection in the genital region. Our engineering objective is to develop a non-invasive screening method using machine learning. We created a mobile app that processes lesion images through a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN), achieving an 83% accuracy in classifying malignant lesions. Additionally, we employ a pressure mapping kit to create a 3D flexible printing file, providing tactile feedback for accurate diagnosis.

Creating a Haptic 4D Model Along With Machine Learning Analysis by Developing a Non- Invasive Pressure
Mapping Method to Screen for Genital Skin Cancer
Early detection of genital skin cancer is hindered by factors such as privacy concerns, social barriers, and discomfort. Traditional biopsy methods, though accurate, can cause pain and infection in the genital region. Our engineering objective is to develop a non-invasive screening method using machine learning. We created a mobile app that processes lesion images through a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN), achieving an 83% accuracy in classifying malignant lesions. Additionally, we employ a pressure mapping kit to create a 3D flexible printing file, providing tactile feedback for accurate diagnosis.

Creating a Haptic 4D Model Along With Machine Learning Analysis by Developing a Non- Invasive Pressure
Mapping Method to Screen for Genital Skin Cancer
Early detection of genital skin cancer is hindered by factors such as privacy concerns, social barriers, and discomfort. Traditional biopsy methods, though accurate, can cause pain and infection in the genital region. Our engineering objective is to develop a non-invasive screening method using machine learning. We created a mobile app that processes lesion images through a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN), achieving an 83% accuracy in classifying malignant lesions. Additionally, we employ a pressure mapping kit to create a 3D flexible printing file, providing tactile feedback for accurate diagnosis.
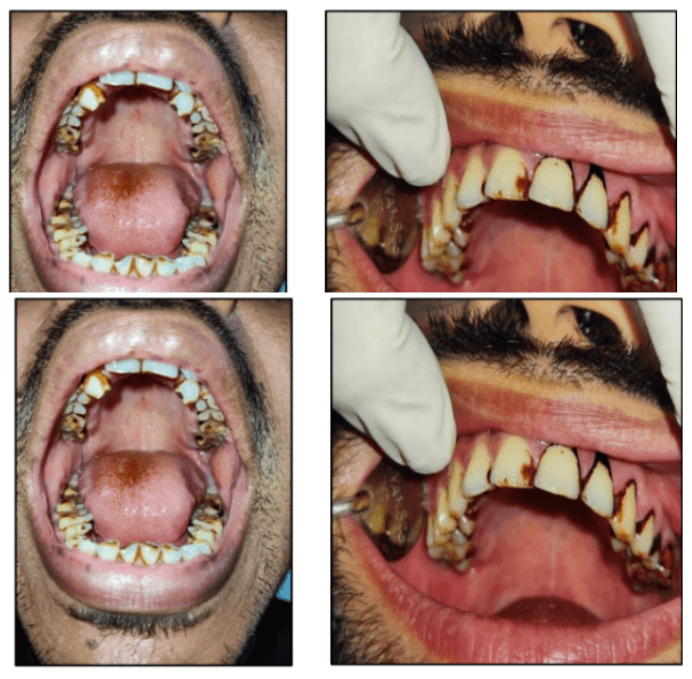
A Model to Identify the Impairment Caused by Smoking to the Oral Cavity
This project addresses the detection and classification of oral mucosal impairments caused by smoking or other factors using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). The CNN model is trained and tested on a dataset of 1,788 images categorized into three classes: healthy mucosa, impairments due to smoking, and impairments due to other factors. The dataset is split into 70% for training and 30% for validation. The developed CNN model achieves remarkable training and test accuracies of 99.95% and 100%, respectively, with training and test loss values of 0.0151 and 0.0023. This intelligent system enables accurate detection and differentiation of oral mucosal impairments, providing valuable diagnostic support for healthcare professionals.

A Model to Identify the Impairment Caused by Smoking to the Oral Cavity
This project addresses the detection and classification of oral mucosal impairments caused by smoking or other factors using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). The CNN model is trained and tested on a dataset of 1,788 images categorized into three classes: healthy mucosa, impairments due to smoking, and impairments due to other factors. The dataset is split into 70% for training and 30% for validation. The developed CNN model achieves remarkable training and test accuracies of 99.95% and 100%, respectively, with training and test loss values of 0.0151 and 0.0023. This intelligent system enables accurate detection and differentiation of oral mucosal impairments, providing valuable diagnostic support for healthcare professionals.

A Model to Identify the Impairment Caused by Smoking to the Oral Cavity
This project addresses the detection and classification of oral mucosal impairments caused by smoking or other factors using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). The CNN model is trained and tested on a dataset of 1,788 images categorized into three classes: healthy mucosa, impairments due to smoking, and impairments due to other factors. The dataset is split into 70% for training and 30% for validation. The developed CNN model achieves remarkable training and test accuracies of 99.95% and 100%, respectively, with training and test loss values of 0.0151 and 0.0023. This intelligent system enables accurate detection and differentiation of oral mucosal impairments, providing valuable diagnostic support for healthcare professionals.
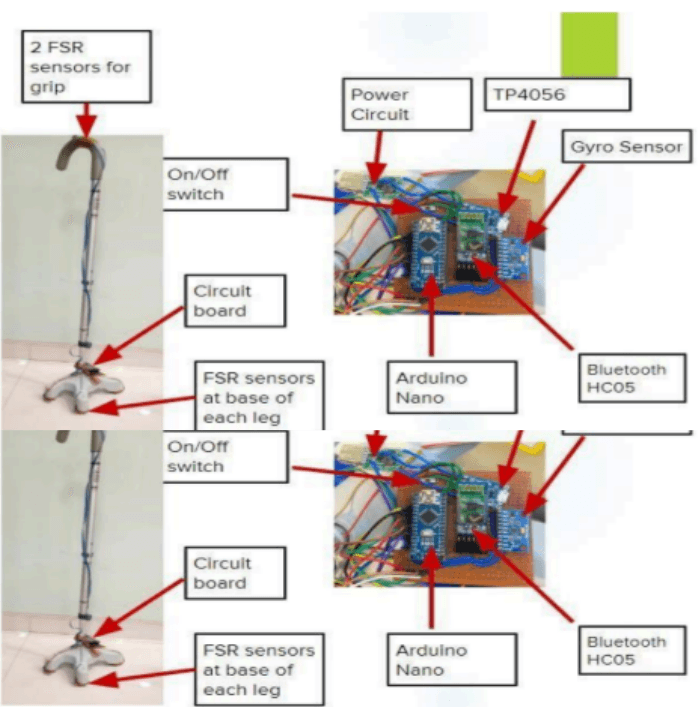
WalkFit
This project presents a smart walking stick designed to improve safety for the elderly by predicting fall risks. The lightweight, user-friendly prototype integrates sensors to monitor tilt angles and pressure distribution in real-time. By collaborating with physiotherapists and leveraging machine learning algorithms, the system analyzes the collected data to anticipate potential falls. This innovative solution provides valuable insights for families and healthcare professionals, demonstrating applications in physiology, neurology, and orthopedics. With its comprehensive approach and adaptability, the smart walking stick offers a promising avenue to enhance the well-being and overall safety of the aging population.

WalkFit
This project presents a smart walking stick designed to improve safety for the elderly by predicting fall risks. The lightweight, user-friendly prototype integrates sensors to monitor tilt angles and pressure distribution in real-time. By collaborating with physiotherapists and leveraging machine learning algorithms, the system analyzes the collected data to anticipate potential falls. This innovative solution provides valuable insights for families and healthcare professionals, demonstrating applications in physiology, neurology, and orthopedics. With its comprehensive approach and adaptability, the smart walking stick offers a promising avenue to enhance the well-being and overall safety of the aging population.

WalkFit
This project presents a smart walking stick designed to improve safety for the elderly by predicting fall risks. The lightweight, user-friendly prototype integrates sensors to monitor tilt angles and pressure distribution in real-time. By collaborating with physiotherapists and leveraging machine learning algorithms, the system analyzes the collected data to anticipate potential falls. This innovative solution provides valuable insights for families and healthcare professionals, demonstrating applications in physiology, neurology, and orthopedics. With its comprehensive approach and adaptability, the smart walking stick offers a promising avenue to enhance the well-being and overall safety of the aging population.
Find your nearest innovation lab
These awards reflect projects that pushed my boundaries, told deeper stories, and caught the attention of people who care about what visuals can say.
Find your nearest innovation lab
These awards reflect projects that pushed my boundaries, told deeper stories, and caught the attention of people who care about what visuals can say.