
Biotechnology & AI
Reimagine healthcare, genetics, and bioinformatics with cutting-edge tech and intelligent innovation.
Biotechnology & AI
Reimagine healthcare, genetics, and bioinformatics with cutting-edge tech and intelligent innovation.
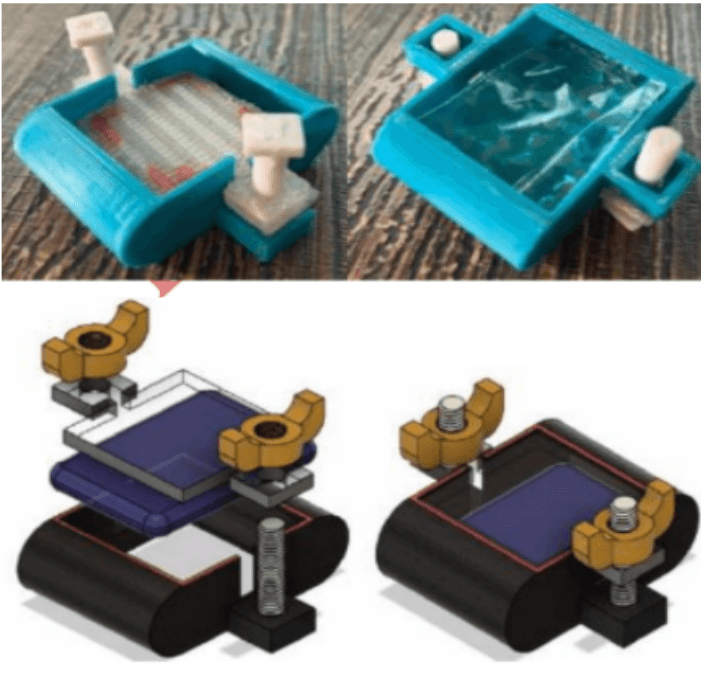
Creating a Haptic 4D Model Along With Machine Learning Analysis by Developing a Non- Invasive Pressure Mapping Method to Screen for Genital Skin Cancer
Early detection of genital skin cancer is hindered by factors such as privacy concerns, social barriers, and discomfort. Traditional biopsy methods, though accurate, can cause pain and infection in the genital region. Our engineering objective is to develop a non-invasive screening method using machine learning. We created a mobile app that processes lesion images through a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN), achieving an 83% accuracy in classifying malignant lesions. Additionally, we employ a pressure mapping kit to create a 3D flexible printing file, providing tactile feedback for accurate diagnosis.

Utilizing Digital & Physical Simulations to Investigate
Early detection of genital skin cancer is hindered by factors such as privacy concerns, social barriers, and discomfort. Traditional biopsy methods, though accurate, can cause pain and infection in the genital region. Our engineering objective is to develop a non-invasive screening method using machine learning. We created a mobile app that processes lesion images through a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN), achieving an 83% accuracy in classifying malignant lesions. Additionally, we employ a pressure mapping kit to create a 3D flexible printing file, providing tactile feedback for accurate diagnosis.

Creating a Haptic 4D Model Along With Machine Learning Analysis by Developing a Non- Invasive Pressure Mapping Method to Screen for Genital Skin Cancer
Early detection of genital skin cancer is hindered by factors such as privacy concerns, social barriers, and discomfort. Traditional biopsy methods, though accurate, can cause pain and infection in the genital region. Our engineering objective is to develop a non-invasive screening method using machine learning. We created a mobile app that processes lesion images through a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN), achieving an 83% accuracy in classifying malignant lesions. Additionally, we employ a pressure mapping kit to create a 3D flexible printing file, providing tactile feedback for accurate diagnosis.
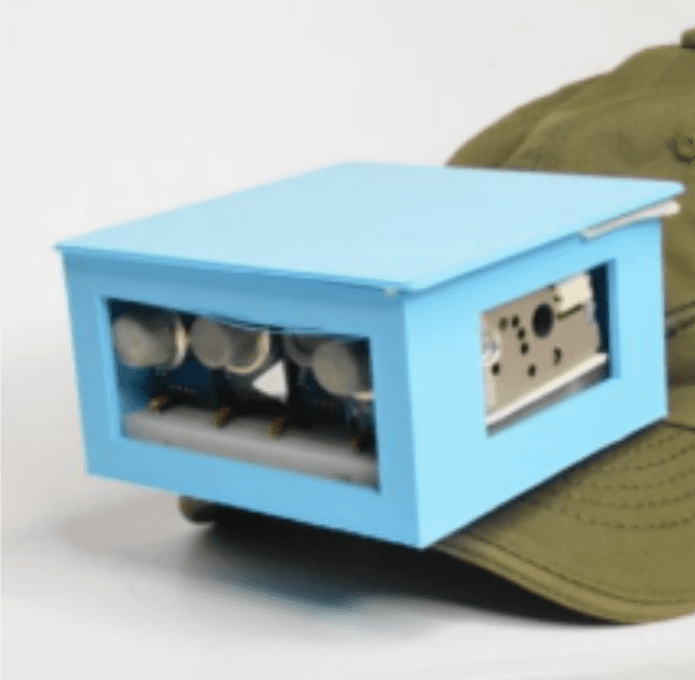

Environmental Technology or Environmental Safety
Sewage disposal cleanup is a hazardous job, exposing workers to harmful gases, infections, and health risks like musculoskeletal disorders and respiratory problems. SEWER GUARD is a project aimed at developing an information and communication ecosystem to monitor and alert workers about dangerous gas levels in sewers. It uses MQ series sensors to measure gas levels and sends alerts if they exceed safe thresholds. The system correlates gas intensity, depth, and exposure time, enabling workers to evacuate before conditions become life-threatening. An Android app and cloud storage are integrated for monitoring and data storage. Authorities can also be notified via SMS if sewage overflow is likely. SEWER GUARD aims to improve the safety and working conditions of sanitary workers engaged in sewer cleanup operations.

Environmental Technology or Environmental Safety
Sewage disposal cleanup is a hazardous job, exposing workers to harmful gases, infections, and health risks like musculoskeletal disorders and respiratory problems. SEWER GUARD is a project aimed at developing an information and communication ecosystem to monitor and alert workers about dangerous gas levels in sewers. It uses MQ series sensors to measure gas levels and sends alerts if they exceed safe thresholds. The system correlates gas intensity, depth, and exposure time, enabling workers to evacuate before conditions become life-threatening. An Android app and cloud storage are integrated for monitoring and data storage. Authorities can also be notified via SMS if sewage overflow is likely. SEWER GUARD aims to improve the safety and working conditions of sanitary workers engaged in sewer cleanup operations.

Environmental Technology or Environmental Safety
The research presented here looks into the vibration properties of 3D-printed airless tires, which have the potential to revolutionize tire design and transportation efficiency. Through extensive experimentation and vibration research, three distinct tire constructions were investigated. Because of its good damping and deformation qualities, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) was chosen as the 3D printing material. The experimental arrangement was designed to simulate real-world road conditions, and an MPU6050 sensor captured tire vibrations in three axes. The vibrational properties of the tire structures were revealed using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) analysis, allowing for a comparative assessment of their stability. Structure 1 was found to be the most vibration-stable, followed by Structures 3 and 2.
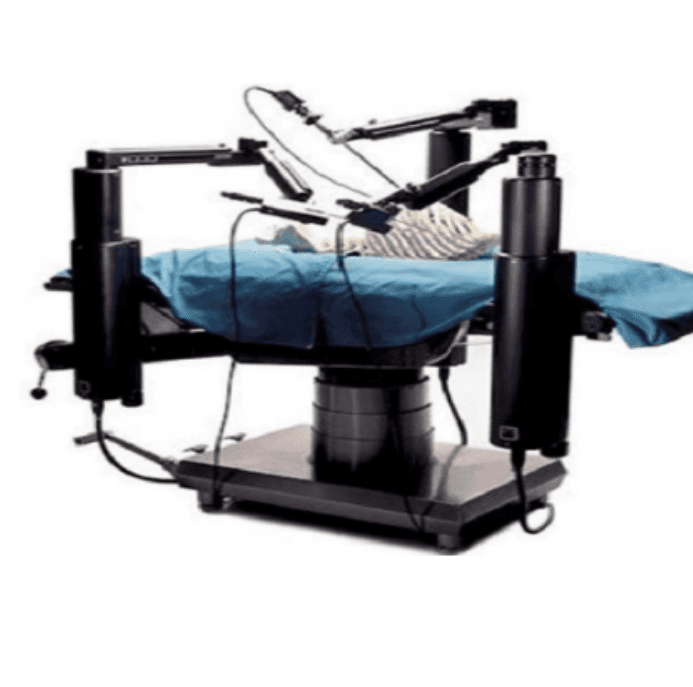
A Review on RoboticsA Review on Robotics Used in Biomedical Surgery
In terms of advancing surgical techniques, robotic surgery, which has been around for more than 20 years is a revolutionary development. The last ten years have seen a rise in the usage of robotics in medical treatments. In an effort to develop smaller, more effective, and less expensive equipment, researchers are ready to achieve record heights as robotic surgery becomes more and more common. Robotic surgery has been successfully used in many hospitals throughout the world and is gaining recognition on a global scale. In this article, we examine robotic surgery's development and progression, current robotic systems, limitations as well as current statistics, and current roles of robotics in surgery, and finally, we discuss the possible roles of robotic surgery in the future.

A Review on RoboticsA Review on Robotics Used in Biomedical Surgery
In terms of advancing surgical techniques, robotic surgery, which has been around for more than 20 years is a revolutionary development. The last ten years have seen a rise in the usage of robotics in medical treatments. In an effort to develop smaller, more effective, and less expensive equipment, researchers are ready to achieve record heights as robotic surgery becomes more and more common. Robotic surgery has been successfully used in many hospitals throughout the world and is gaining recognition on a global scale. In this article, we examine robotic surgery's development and progression, current robotic systems, limitations as well as current statistics, and current roles of robotics in surgery, and finally, we discuss the possible roles of robotic surgery in the future.

A Review on RoboticsA Review on Robotics Used in Biomedical Surgery
In terms of advancing surgical techniques, robotic surgery, which has been around for more than 20 years is a revolutionary development. The last ten years have seen a rise in the usage of robotics in medical treatments. In an effort to develop smaller, more effective, and less expensive equipment, researchers are ready to achieve record heights as robotic surgery becomes more and more common. Robotic surgery has been successfully used in many hospitals throughout the world and is gaining recognition on a global scale. In this article, we examine robotic surgery's development and progression, current robotic systems, limitations as well as current statistics, and current roles of robotics in surgery, and finally, we discuss the possible roles of robotic surgery in the future.
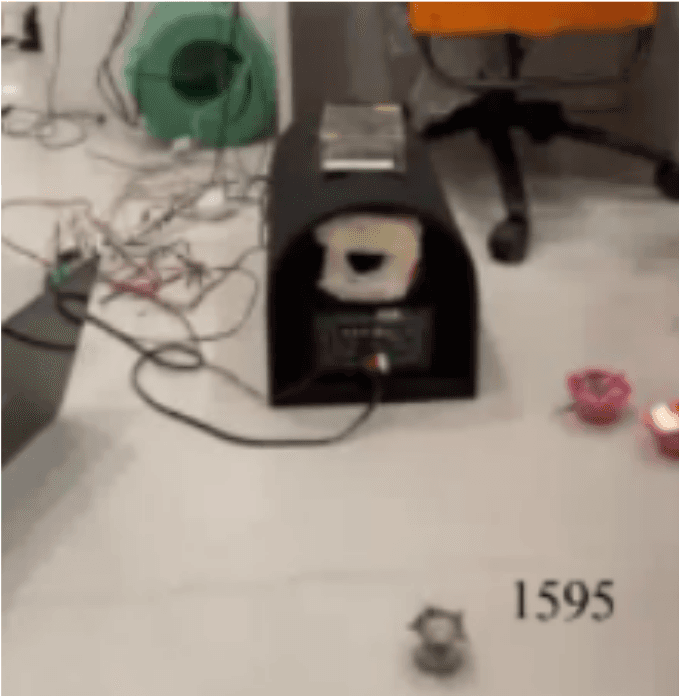

Targeted Extinguishing of Fire Through the Propagation of Acoustic Waves
This research explores the use of sound pressure waves as an innovative method for extinguishing fires. Through theoretical analysis and experiments, it confirms that directed longitudinal sound waves can effectively cool and extinguish fires by depriving them of heat. The study optimizes the process using frequency generator circuits, acoustic lensing, and vortex tubes to concentrate the sound toward the fire source. Computer vision algorithms are implemented to detect fires and align the sound waves accordingly. This acoustic fire extinguishing technique offers a cheaper, environmentally friendly alternative to traditional methods, with the potential to save numerous lives.

Targeted Extinguishing of Fire Through the Propagation of Acoustic Waves
This research explores the use of sound pressure waves as an innovative method for extinguishing fires. Through theoretical analysis and experiments, it confirms that directed longitudinal sound waves can effectively cool and extinguish fires by depriving them of heat. The study optimizes the process using frequency generator circuits, acoustic lensing, and vortex tubes to concentrate the sound toward the fire source. Computer vision algorithms are implemented to detect fires and align the sound waves accordingly. This acoustic fire extinguishing technique offers a cheaper, environmentally friendly alternative to traditional methods, with the potential to save numerous lives.

Targeted Extinguishing of Fire Through the Propagation of Acoustic Waves
This research explores the use of sound pressure waves as an innovative method for extinguishing fires. Through theoretical analysis and experiments, it confirms that directed longitudinal sound waves can effectively cool and extinguish fires by depriving them of heat. The study optimizes the process using frequency generator circuits, acoustic lensing, and vortex tubes to concentrate the sound toward the fire source. Computer vision algorithms are implemented to detect fires and align the sound waves accordingly. This acoustic fire extinguishing technique offers a cheaper, environmentally friendly alternative to traditional methods, with the potential to save numerous lives.
Statistical Scrutiny of the Prediction Capability of Different Time Series Machine Learning Models in Forecasting Bitcoin Prices
Cryptocurrencies (CTC) are decentralised digital currency. In the past decade, there has been a massive increase in its usage due to the advancement made in the field of blockchain. Bitcoin (BTC) is the first decentralised CTC which garnered a lot of attention from the media as well as the public due to its ability to sustain the momentum in the market. However, investing in BTC is not the first choice of the investor due to the market's erratic behaviour, price volatility and lack of a model that could be used to predict its price. For this purpose three machine learning (ML) models namely Long Short Term Memory (LSTM), Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average method (ARIMA) and Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated MovingAverage method (SARIMA) models have been employed which are statistically scrutinised on the basis of the performance metrics namely Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) and coefficient of determination (R2 ).

Statistical Scrutiny of the Prediction Capability of Different Time Series Machine Learning Models in Forecasting Bitcoin Prices
Cryptocurrencies (CTC) are decentralised digital currency. In the past decade, there has been a massive increase in its usage due to the advancement made in the field of blockchain. Bitcoin (BTC) is the first decentralised CTC which garnered a lot of attention from the media as well as the public due to its ability to sustain the momentum in the market. However, investing in BTC is not the first choice of the investor due to the market's erratic behaviour, price volatility and lack of a model that could be used to predict its price. For this purpose three machine learning (ML) models namely Long Short Term Memory (LSTM), Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average method (ARIMA) and Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated MovingAverage method (SARIMA) models have been employed which are statistically scrutinised on the basis of the performance metrics namely Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) and coefficient of determination (R2 ).

Statistical Scrutiny of the Prediction Capability of Different Time Series Machine Learning Models in Forecasting Bitcoin Prices
Cryptocurrencies (CTC) are decentralised digital currency. In the past decade, there has been a massive increase in its usage due to the advancement made in the field of blockchain. Bitcoin (BTC) is the first decentralised CTC which garnered a lot of attention from the media as well as the public due to its ability to sustain the momentum in the market. However, investing in BTC is not the first choice of the investor due to the market's erratic behaviour, price volatility and lack of a model that could be used to predict its price. For this purpose three machine learning (ML) models namely Long Short Term Memory (LSTM), Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average method (ARIMA) and Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated MovingAverage method (SARIMA) models have been employed which are statistically scrutinised on the basis of the performance metrics namely Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) and coefficient of determination (R2 ).
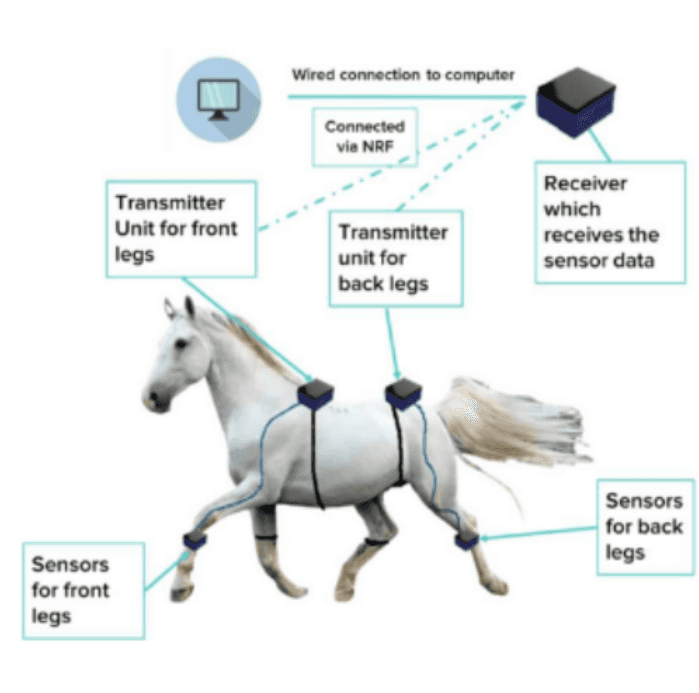
A Novel Approach to Quantify and Compute Gait Analysis Parameters of Quadrupeds
Gait analysis is the study of human and animal locomotion. Analysis of gait is particularly prevalent in developed countries, owing to extensive capital and resources. However, in developing countries such as India, gait analysis devices and instruments are restricted solely to metropolitan cities. Even in Metropolitan Cities, the analysis of human gait is costly. An analysis of quadruped gait is notably absent in developing countries and, if present, is extremely expensive. This creates a financial disparity, in which those in poverty are unable to have a veterinarian kinematically check their Quadruped's gait, while the wealthy are able to do so. The solution presented aims to analyze the gait of all quadrupeds. This mechanism correlates the usage of a Gyroscope, 3-axis accelerometer, and Digital Motion Processor along with graphs plotted using Python's MatPlotLib Library and three-dimensional simulations with an AutoCAD model and simulated using the library Panda3D in a portable, wearable device.

A Novel Approach to Quantify and Compute Gait Analysis Parameters of Quadrupeds
Gait analysis is the study of human and animal locomotion. Analysis of gait is particularly prevalent in developed countries, owing to extensive capital and resources. However, in developing countries such as India, gait analysis devices and instruments are restricted solely to metropolitan cities. Even in Metropolitan Cities, the analysis of human gait is costly. An analysis of quadruped gait is notably absent in developing countries and, if present, is extremely expensive. This creates a financial disparity, in which those in poverty are unable to have a veterinarian kinematically check their Quadruped's gait, while the wealthy are able to do so. The solution presented aims to analyze the gait of all quadrupeds. This mechanism correlates the usage of a Gyroscope, 3-axis accelerometer, and Digital Motion Processor along with graphs plotted using Python's MatPlotLib Library and three-dimensional simulations with an AutoCAD model and simulated using the library Panda3D in a portable, wearable device.

A Novel Approach to Quantify and Compute Gait Analysis Parameters of Quadrupeds
Gait analysis is the study of human and animal locomotion. Analysis of gait is particularly prevalent in developed countries, owing to extensive capital and resources. However, in developing countries such as India, gait analysis devices and instruments are restricted solely to metropolitan cities. Even in Metropolitan Cities, the analysis of human gait is costly. An analysis of quadruped gait is notably absent in developing countries and, if present, is extremely expensive. This creates a financial disparity, in which those in poverty are unable to have a veterinarian kinematically check their Quadruped's gait, while the wealthy are able to do so. The solution presented aims to analyze the gait of all quadrupeds. This mechanism correlates the usage of a Gyroscope, 3-axis accelerometer, and Digital Motion Processor along with graphs plotted using Python's MatPlotLib Library and three-dimensional simulations with an AutoCAD model and simulated using the library Panda3D in a portable, wearable device.
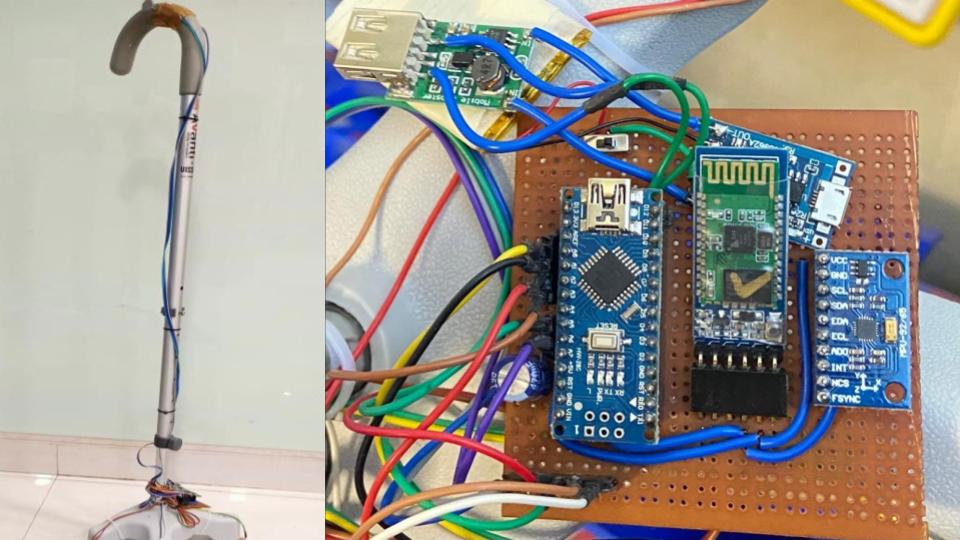
WalkFit
This project presents a smart walking stick designed to improve safety for the elderly by predicting fall risks. The lightweight, user-friendly prototype integrates sensors to monitor tilt angles and pressure distribution in real-time. By collaborating with physiotherapists and leveraging machine learning algorithms, the system analyzes the collected data to anticipate potential falls. This innovative solution provides valuable insights for families and healthcare professionals, demonstrating applications in physiology, neurology, and orthopedics. With its comprehensive approach and adaptability, the smart walking stick offers a promising avenue to enhance the well-being and overall safety of the aging population.

WalkFit
This project presents a smart walking stick designed to improve safety for the elderly by predicting fall risks. The lightweight, user-friendly prototype integrates sensors to monitor tilt angles and pressure distribution in real-time. By collaborating with physiotherapists and leveraging machine learning algorithms, the system analyzes the collected data to anticipate potential falls. This innovative solution provides valuable insights for families and healthcare professionals, demonstrating applications in physiology, neurology, and orthopedics. With its comprehensive approach and adaptability, the smart walking stick offers a promising avenue to enhance the well-being and overall safety of the aging population.

WalkFit
This project presents a smart walking stick designed to improve safety for the elderly by predicting fall risks. The lightweight, user-friendly prototype integrates sensors to monitor tilt angles and pressure distribution in real-time. By collaborating with physiotherapists and leveraging machine learning algorithms, the system analyzes the collected data to anticipate potential falls. This innovative solution provides valuable insights for families and healthcare professionals, demonstrating applications in physiology, neurology, and orthopedics. With its comprehensive approach and adaptability, the smart walking stick offers a promising avenue to enhance the well-being and overall safety of the aging population.

An Artificial Intelligence Integrated Technique for Screening Neurological Diseases with Sound as a Biomarker
This project aims to develop a machine learning-based system for detecting neurological disorders like Parkinson's disease (PD) and paralysis through voice analysis. Researchers recorded speech samples from patients and healthy individuals, extracting features using Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC). K-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) models were trained on this dataset to classify voices into PD, paralysis, or normal categories. With an overall accuracy rate comparable to human laryngologists (60.1% and 56.1%), this system can assist clinicians in accurately identifying the presence and stage of neurological disorders, enabling appropriate treatment recommendations through therapy, medication, or a combination thereof

An Artificial Intelligence Integrated Technique for Screening Neurological Diseases with Sound as a Biomarker
This project aims to develop a machine learning-based system for detecting neurological disorders like Parkinson's disease (PD) and paralysis through voice analysis. Researchers recorded speech samples from patients and healthy individuals, extracting features using Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC). K-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) models were trained on this dataset to classify voices into PD, paralysis, or normal categories. With an overall accuracy rate comparable to human laryngologists (60.1% and 56.1%), this system can assist clinicians in accurately identifying the presence and stage of neurological disorders, enabling appropriate treatment recommendations through therapy, medication, or a combination thereof

An Artificial Intelligence Integrated Technique for Screening Neurological Diseases with Sound as a Biomarker
This project aims to develop a machine learning-based system for detecting neurological disorders like Parkinson's disease (PD) and paralysis through voice analysis. Researchers recorded speech samples from patients and healthy individuals, extracting features using Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC). K-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) models were trained on this dataset to classify voices into PD, paralysis, or normal categories. With an overall accuracy rate comparable to human laryngologists (60.1% and 56.1%), this system can assist clinicians in accurately identifying the presence and stage of neurological disorders, enabling appropriate treatment recommendations through therapy, medication, or a combination thereof
A Model to Identify the Impairment Caused by Smoking to the Oral Cavity
This project addresses the detection and classification of oral mucosal impairments caused by smoking or other factors using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). The CNN model is trained and tested on a dataset of 1,788 images categorized into three classes: healthy mucosa, impairments due to smoking, and impairments due to other factors. The dataset is split into 70% for training and 30% for validation. The developed CNN model achieves remarkable training and test accuracies of 99.95% and 100%, respectively, with training and test loss values of 0.0151 and 0.0023. This intelligent system enables accurate detection and differentiation of oral mucosal impairments, providing valuable diagnostic support for healthcare professionals.

A Model to Identify the Impairment Caused by Smoking to the Oral Cavity
This project addresses the detection and classification of oral mucosal impairments caused by smoking or other factors using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). The CNN model is trained and tested on a dataset of 1,788 images categorized into three classes: healthy mucosa, impairments due to smoking, and impairments due to other factors. The dataset is split into 70% for training and 30% for validation. The developed CNN model achieves remarkable training and test accuracies of 99.95% and 100%, respectively, with training and test loss values of 0.0151 and 0.0023. This intelligent system enables accurate detection and differentiation of oral mucosal impairments, providing valuable diagnostic support for healthcare professionals.

A Model to Identify the Impairment Caused by Smoking to the Oral Cavity
This project addresses the detection and classification of oral mucosal impairments caused by smoking or other factors using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). The CNN model is trained and tested on a dataset of 1,788 images categorized into three classes: healthy mucosa, impairments due to smoking, and impairments due to other factors. The dataset is split into 70% for training and 30% for validation. The developed CNN model achieves remarkable training and test accuracies of 99.95% and 100%, respectively, with training and test loss values of 0.0151 and 0.0023. This intelligent system enables accurate detection and differentiation of oral mucosal impairments, providing valuable diagnostic support for healthcare professionals.
Development of a Robust Model to Predict the Sales of Tickets Employing Fuzzy IF- THEN Rules Based Algorithm
This study presents a robust model for predicting ticket sales of football matches based on game demand using a fuzzy IF-THEN rules-based algorithm. The proposed two-level simulation model first simulates the demand for a football match, and then simulates ticket sales by computing the Multi-Point Characteristics Index (MPCI) value. Factors influencing demand are categorized and expressed as linguistic terms, with uncertainties modeled using triangular fuzzy numbers (TFNs). The TFNs are converted to crisp values using the center of gravity method, and the properties and operations of TFNs are defined. The developed fuzzy IF-THEN rules-based algorithm, built on TFNs, provides an effective approach to forecasting ticket sales in the sports industry, considering the complex dynamics of game demand.

Development of a Robust Model to Predict the Sales of Tickets Employing Fuzzy IF- THEN Rules Based Algorithm
This study presents a robust model for predicting ticket sales of football matches based on game demand using a fuzzy IF-THEN rules-based algorithm. The proposed two-level simulation model first simulates the demand for a football match, and then simulates ticket sales by computing the Multi-Point Characteristics Index (MPCI) value. Factors influencing demand are categorized and expressed as linguistic terms, with uncertainties modeled using triangular fuzzy numbers (TFNs). The TFNs are converted to crisp values using the center of gravity method, and the properties and operations of TFNs are defined. The developed fuzzy IF-THEN rules-based algorithm, built on TFNs, provides an effective approach to forecasting ticket sales in the sports industry, considering the complex dynamics of game demand.

Development of a Robust Model to Predict the Sales of Tickets Employing Fuzzy IF- THEN Rules Based Algorithm
This study presents a robust model for predicting ticket sales of football matches based on game demand using a fuzzy IF-THEN rules-based algorithm. The proposed two-level simulation model first simulates the demand for a football match, and then simulates ticket sales by computing the Multi-Point Characteristics Index (MPCI) value. Factors influencing demand are categorized and expressed as linguistic terms, with uncertainties modeled using triangular fuzzy numbers (TFNs). The TFNs are converted to crisp values using the center of gravity method, and the properties and operations of TFNs are defined. The developed fuzzy IF-THEN rules-based algorithm, built on TFNs, provides an effective approach to forecasting ticket sales in the sports industry, considering the complex dynamics of game demand.

Microplastic Classification and Quantification in Aqueous Systems
This study tackles microplastic contamination in Mumbai's aquatic ecosystems, using advanced analytical techniques and a trained CNN model for accurate identification and quantification. Results, with a high accuracy of 97%, provide vital insights into distribution, and ecological impact, and offer a robust method for responsible environmental monitoring in compliance with evolving global standards. Microplastic contamination in aquatic ecosystems poses a severe threat to environmental health and public well-being. This study addresses the urgent need for accurate identification and quantification of microplastics in water bodies using advanced analytical techniques and machine learning. The pervasive issue of microplastic pollution demands innovative approaches to understanding its extent, sources, and impact on aquatic environments.

Microplastic Classification and Quantification in Aqueous Systems
This study tackles microplastic contamination in Mumbai's aquatic ecosystems, using advanced analytical techniques and a trained CNN model for accurate identification and quantification. Results, with a high accuracy of 97%, provide vital insights into distribution, and ecological impact, and offer a robust method for responsible environmental monitoring in compliance with evolving global standards. Microplastic contamination in aquatic ecosystems poses a severe threat to environmental health and public well-being. This study addresses the urgent need for accurate identification and quantification of microplastics in water bodies using advanced analytical techniques and machine learning. The pervasive issue of microplastic pollution demands innovative approaches to understanding its extent, sources, and impact on aquatic environments.

Microplastic Classification and Quantification in Aqueous Systems
This study tackles microplastic contamination in Mumbai's aquatic ecosystems, using advanced analytical techniques and a trained CNN model for accurate identification and quantification. Results, with a high accuracy of 97%, provide vital insights into distribution, and ecological impact, and offer a robust method for responsible environmental monitoring in compliance with evolving global standards. Microplastic contamination in aquatic ecosystems poses a severe threat to environmental health and public well-being. This study addresses the urgent need for accurate identification and quantification of microplastics in water bodies using advanced analytical techniques and machine learning. The pervasive issue of microplastic pollution demands innovative approaches to understanding its extent, sources, and impact on aquatic environments.
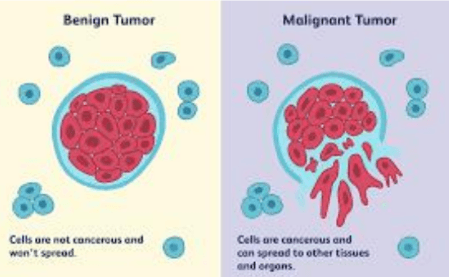
CancerEase: A New Approach Towards Early Prediction of Breast Cancer Using MRI Scan Data.
Breast cancer is a significant health concern, affecting 1 in 8 women and posing challenges for healthcare systems. To aid in early diagnosis, we present CancerEase, a machine learning software that uses MRI scan data to classify breast cancer as malignant or benign. CancerEase employs three models: Neural Networks, Logistic Regression, and K-Nearest Neighbors Classifier, and selects the most accurate model for diagnosis. Trained on Kaggle's MRI data contributed by professionals, the Neural Network Model achieved the highest accuracy of approximately 92.98%. CancerEase shows promising results as an effective tool for tackling the global breast cancer problem.

CancerEase: A New Approach Towards Early Prediction of Breast Cancer Using MRI Scan Data.
Breast cancer is a significant health concern, affecting 1 in 8 women and posing challenges for healthcare systems. To aid in early diagnosis, we present CancerEase, a machine learning software that uses MRI scan data to classify breast cancer as malignant or benign. CancerEase employs three models: Neural Networks, Logistic Regression, and K-Nearest Neighbors Classifier, and selects the most accurate model for diagnosis. Trained on Kaggle's MRI data contributed by professionals, the Neural Network Model achieved the highest accuracy of approximately 92.98%. CancerEase shows promising results as an effective tool for tackling the global breast cancer problem.

CancerEase: A New Approach Towards Early Prediction of Breast Cancer Using MRI Scan Data.
Breast cancer is a significant health concern, affecting 1 in 8 women and posing challenges for healthcare systems. To aid in early diagnosis, we present CancerEase, a machine learning software that uses MRI scan data to classify breast cancer as malignant or benign. CancerEase employs three models: Neural Networks, Logistic Regression, and K-Nearest Neighbors Classifier, and selects the most accurate model for diagnosis. Trained on Kaggle's MRI data contributed by professionals, the Neural Network Model achieved the highest accuracy of approximately 92.98%. CancerEase shows promising results as an effective tool for tackling the global breast cancer problem.
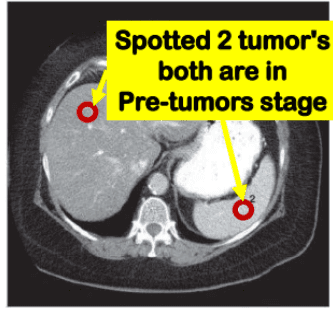
Screening Liver tumor with 3D-IRCAD, ResUNet Model
Our project focuses on liver tumor screening, addressing the limitations of current methods such as manual interpretation of CT scans and the expense and side effects of MRI. Leveraging Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), specifically the 3D-IRCAD ResUNet Model, our solution detects liver tumors early and efficiently. Using machine learning models trained on a dataset from IRCAD Research Institute, our approach achieves high accuracy in tumor detection. The CNN's performance surpasses human expertise in radiology, providing promising results for early tumor detection.

Screening Liver tumor with 3D-IRCAD, ResUNet Model
Our project focuses on liver tumor screening, addressing the limitations of current methods such as manual interpretation of CT scans and the expense and side effects of MRI. Leveraging Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), specifically the 3D-IRCAD ResUNet Model, our solution detects liver tumors early and efficiently. Using machine learning models trained on a dataset from IRCAD Research Institute, our approach achieves high accuracy in tumor detection. The CNN's performance surpasses human expertise in radiology, providing promising results for early tumor detection.

Screening Liver tumor with 3D-IRCAD, ResUNet Model
Our project focuses on liver tumor screening, addressing the limitations of current methods such as manual interpretation of CT scans and the expense and side effects of MRI. Leveraging Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), specifically the 3D-IRCAD ResUNet Model, our solution detects liver tumors early and efficiently. Using machine learning models trained on a dataset from IRCAD Research Institute, our approach achieves high accuracy in tumor detection. The CNN's performance surpasses human expertise in radiology, providing promising results for early tumor detection.
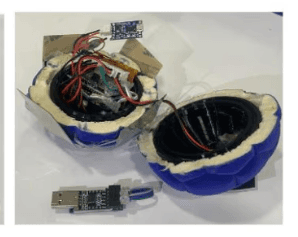
Stress Ball with Embedded Sensor for Exercise and Muscle Strength Assessment in Autistic Children
This study describes the construction and testing of a ball with built-in sensors that are intended to evaluate muscular strength and promote exercise in autistic youngsters. To measure the throwing force and the squeezing strength, the ball has in built accelerometers and force sensors. This research highlights how technology-assisted therapy can benefit autistic children's physical health and development. The data collected by the stress ball included force data from the FSR sensor, timestamps, and acceleration data from the MPU6050 sensor. The stress ball uses the Bluetooth module to transmit data wirelessly to a remote device running Python script which stores the data for later analysis. The pressure data and the acceleration data generated during the squeezing action and the throwing action were collected across 6 weeks. The average of the peak force and the acceleration data were plotted for multiple weeks.

Stress Ball with Embedded Sensor for Exercise and Muscle Strength Assessment in Autistic Children
This study describes the construction and testing of a ball with built-in sensors that are intended to evaluate muscular strength and promote exercise in autistic youngsters. To measure the throwing force and the squeezing strength, the ball has in built accelerometers and force sensors. This research highlights how technology-assisted therapy can benefit autistic children's physical health and development. The data collected by the stress ball included force data from the FSR sensor, timestamps, and acceleration data from the MPU6050 sensor. The stress ball uses the Bluetooth module to transmit data wirelessly to a remote device running Python script which stores the data for later analysis. The pressure data and the acceleration data generated during the squeezing action and the throwing action were collected across 6 weeks. The average of the peak force and the acceleration data were plotted for multiple weeks.

Stress Ball with Embedded Sensor for Exercise and Muscle Strength Assessment in Autistic Children
This study describes the construction and testing of a ball with built-in sensors that are intended to evaluate muscular strength and promote exercise in autistic youngsters. To measure the throwing force and the squeezing strength, the ball has in built accelerometers and force sensors. This research highlights how technology-assisted therapy can benefit autistic children's physical health and development. The data collected by the stress ball included force data from the FSR sensor, timestamps, and acceleration data from the MPU6050 sensor. The stress ball uses the Bluetooth module to transmit data wirelessly to a remote device running Python script which stores the data for later analysis. The pressure data and the acceleration data generated during the squeezing action and the throwing action were collected across 6 weeks. The average of the peak force and the acceleration data were plotted for multiple weeks.
Application of deep learning neural network to create a multi-class identifier to Detect and categorize periodontal diseases
Periodontal diseases is the major cause of bad breath and loss of tooth in adults worldwide. The comprehensive intention of the present study is to detect and categorize the type of periodontal diseases. In order to achieve the objective a Convolution Neural Network (CNN) model is proposed in the study. The proposed CNN model is built using the Tensorflow framework which is coded in Python 3.8. The proposed model is trained using 3241 images of periodontal and non-periodontal diseases. The CNN model is tested using 90 images. The training and testing accuracy of the CNN model is 97.82% and 73.61% respectively whereas the loss computed by Mean Squre Error (MSE) for training and testing is 0.07 and 0.006 respectively.

Application of deep learning neural network to create a multi-class identifier to Detect and categorize periodontal diseases
Periodontal diseases is the major cause of bad breath and loss of tooth in adults worldwide. The comprehensive intention of the present study is to detect and categorize the type of periodontal diseases. In order to achieve the objective a Convolution Neural Network (CNN) model is proposed in the study. The proposed CNN model is built using the Tensorflow framework which is coded in Python 3.8. The proposed model is trained using 3241 images of periodontal and non-periodontal diseases. The CNN model is tested using 90 images. The training and testing accuracy of the CNN model is 97.82% and 73.61% respectively whereas the loss computed by Mean Squre Error (MSE) for training and testing is 0.07 and 0.006 respectively.

Application of deep learning neural network to create a multi-class identifier to Detect and categorize periodontal diseases
Periodontal diseases is the major cause of bad breath and loss of tooth in adults worldwide. The comprehensive intention of the present study is to detect and categorize the type of periodontal diseases. In order to achieve the objective a Convolution Neural Network (CNN) model is proposed in the study. The proposed CNN model is built using the Tensorflow framework which is coded in Python 3.8. The proposed model is trained using 3241 images of periodontal and non-periodontal diseases. The CNN model is tested using 90 images. The training and testing accuracy of the CNN model is 97.82% and 73.61% respectively whereas the loss computed by Mean Squre Error (MSE) for training and testing is 0.07 and 0.006 respectively.
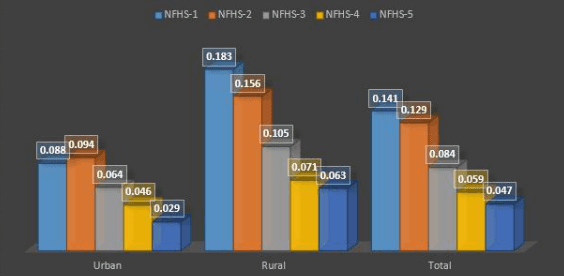
Projecting Teenage Pregnancy and Motherhood and Fertility Rates: An Analytical and Machine Learning Study of Maharashtra, India
Adolescent pregnancy poses significant challenges with long-term physical, mental, and economic implications for both teenage mothers and their babies. This paper, focusing on Maharashtra, is divided into two sections: fertility trends and teenage pregnancy and motherhood. Data from the NFHS surveys were analyzed using Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) to investigate variables such as residency, age, marital status, education, and more. The findings indicate that higher pregnancy rates are associated with rural residency, lower income, limited education, and specific demographic backgrounds. Additionally, machine learning techniques, specifically the Linear Regression algorithm, were applied to the data, demonstrating the model's accuracy in predicting pregnancy trends.

Projecting Teenage Pregnancy and Motherhood and Fertility Rates: An Analytical and Machine Learning Study of Maharashtra, India
Adolescent pregnancy poses significant challenges with long-term physical, mental, and economic implications for both teenage mothers and their babies. This paper, focusing on Maharashtra, is divided into two sections: fertility trends and teenage pregnancy and motherhood. Data from the NFHS surveys were analyzed using Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) to investigate variables such as residency, age, marital status, education, and more. The findings indicate that higher pregnancy rates are associated with rural residency, lower income, limited education, and specific demographic backgrounds. Additionally, machine learning techniques, specifically the Linear Regression algorithm, were applied to the data, demonstrating the model's accuracy in predicting pregnancy trends.

Projecting Teenage Pregnancy and Motherhood and Fertility Rates: An Analytical and Machine Learning Study of Maharashtra, India
Adolescent pregnancy poses significant challenges with long-term physical, mental, and economic implications for both teenage mothers and their babies. This paper, focusing on Maharashtra, is divided into two sections: fertility trends and teenage pregnancy and motherhood. Data from the NFHS surveys were analyzed using Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) to investigate variables such as residency, age, marital status, education, and more. The findings indicate that higher pregnancy rates are associated with rural residency, lower income, limited education, and specific demographic backgrounds. Additionally, machine learning techniques, specifically the Linear Regression algorithm, were applied to the data, demonstrating the model's accuracy in predicting pregnancy trends.
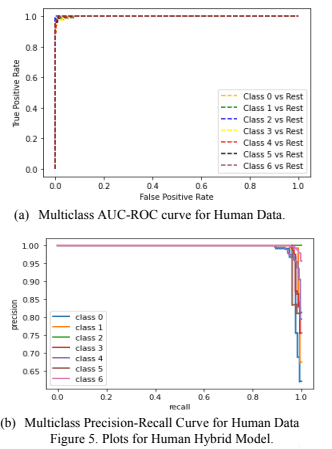
Development of a Robust DNA Sequencing Multiclass Hybrid Classifier Employing Machine Learning and NLP For Automated Gene Classification
DNA sequencing determines the order of chemical bases in DNA molecules, revealing genetic information crucial for understanding gene function and disease. This study presents a hybrid ensemble machine learning model, utilizing eleven classifiers, to develop a genomic classifier for DNA sequences. By employing NLP and machine learning techniques, the model enhances gene classification in biomedical research. Performance evaluation demonstrates high accuracy across human, chimpanzee, and dog datasets, with the model achieving 98.08% accuracy for human data, 90.75% for chimpanzee data, and 70% for dog data. The study transcends species boundaries, offering insights into genome classifications and paving the way for further advancements in genetic analysis.

Development of a Robust DNA Sequencing Multiclass Hybrid Classifier Employing Machine Learning and NLP For Automated Gene Classification
DNA sequencing determines the order of chemical bases in DNA molecules, revealing genetic information crucial for understanding gene function and disease. This study presents a hybrid ensemble machine learning model, utilizing eleven classifiers, to develop a genomic classifier for DNA sequences. By employing NLP and machine learning techniques, the model enhances gene classification in biomedical research. Performance evaluation demonstrates high accuracy across human, chimpanzee, and dog datasets, with the model achieving 98.08% accuracy for human data, 90.75% for chimpanzee data, and 70% for dog data. The study transcends species boundaries, offering insights into genome classifications and paving the way for further advancements in genetic analysis.

Development of a Robust DNA Sequencing Multiclass Hybrid Classifier Employing Machine Learning and NLP For Automated Gene Classification
DNA sequencing determines the order of chemical bases in DNA molecules, revealing genetic information crucial for understanding gene function and disease. This study presents a hybrid ensemble machine learning model, utilizing eleven classifiers, to develop a genomic classifier for DNA sequences. By employing NLP and machine learning techniques, the model enhances gene classification in biomedical research. Performance evaluation demonstrates high accuracy across human, chimpanzee, and dog datasets, with the model achieving 98.08% accuracy for human data, 90.75% for chimpanzee data, and 70% for dog data. The study transcends species boundaries, offering insights into genome classifications and paving the way for further advancements in genetic analysis.
Find your nearest innovation lab
These awards reflect projects that pushed my boundaries, told deeper stories, and caught the attention of people who care about what visuals can say.
Find your nearest innovation lab
These awards reflect projects that pushed my boundaries, told deeper stories, and caught the attention of people who care about what visuals can say.