
Data Science & AI/ML
Use data and machine intelligence to crack real-world challenges and drive smarter decisions.
Data Science & AI/ML
Use data and machine intelligence to crack real-world challenges and drive smarter decisions.

Data Science & AI/ML
Use data and machine intelligence to crack real-world challenges and drive smarter decisions.
Data Science & AI/ML
Use data and machine intelligence to crack real-world challenges and drive smarter decisions.
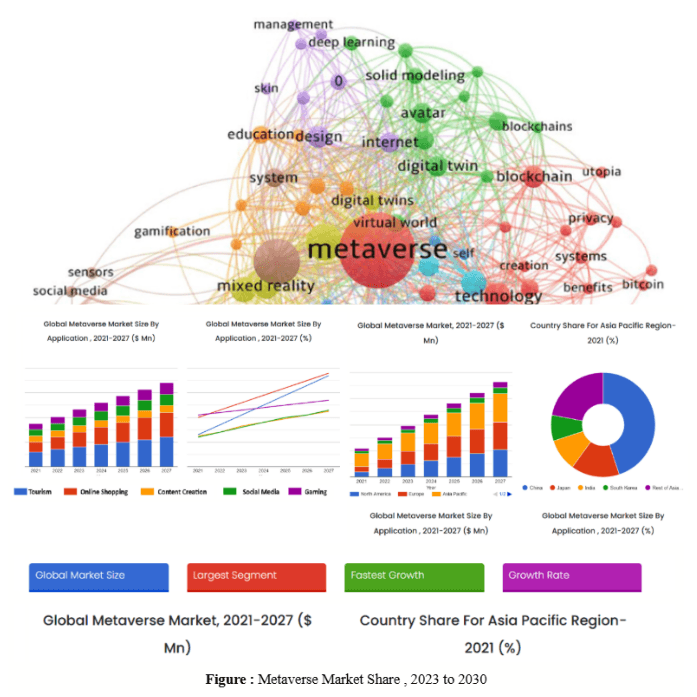
The Future of Travel: Assessing the Transformative Effects of Metaverse Travel on Tourism Industry
The main objective of this financial analysis project is to evaluate how virtual metaverse adoption could impact different aspects of the tourism industry. It aims to study areas such as revenue generation, employment opportunities, investment patterns, and overall economic growth within the tourism sector. To achieve this, the study will employ a rigorous research methodology that encompasses data collection from various sources, thorough data analysis, and financial modelling techniques. The analysis will involve studying real-world data from existing virtual metaverse platforms, tourism industry reports, and economic indicators to project potential outcomes. This project investigates the financial ramifications of incorporating virtual metaverse technologies into the tourism industry.

The Future of Travel: Assessing the Transformative Effects of Metaverse Travel on Tourism Industry
The main objective of this financial analysis project is to evaluate how virtual metaverse adoption could impact different aspects of the tourism industry. It aims to study areas such as revenue generation, employment opportunities, investment patterns, and overall economic growth within the tourism sector. To achieve this, the study will employ a rigorous research methodology that encompasses data collection from various sources, thorough data analysis, and financial modelling techniques. The analysis will involve studying real-world data from existing virtual metaverse platforms, tourism industry reports, and economic indicators to project potential outcomes. This project investigates the financial ramifications of incorporating virtual metaverse technologies into the tourism industry.

The Future of Travel: Assessing the Transformative Effects of Metaverse Travel on Tourism Industry
The main objective of this financial analysis project is to evaluate how virtual metaverse adoption could impact different aspects of the tourism industry. It aims to study areas such as revenue generation, employment opportunities, investment patterns, and overall economic growth within the tourism sector. To achieve this, the study will employ a rigorous research methodology that encompasses data collection from various sources, thorough data analysis, and financial modelling techniques. The analysis will involve studying real-world data from existing virtual metaverse platforms, tourism industry reports, and economic indicators to project potential outcomes. This project investigates the financial ramifications of incorporating virtual metaverse technologies into the tourism industry.
Statistical Scrutiny of the Prediction Capability of Different Time Series Machine Learning Models in Forecasting Bitcoin Prices
Cryptocurrencies (CTC) are decentralised digital currency. In the past decade, there has been a massive increase in its usage due to the advancement made in the field of blockchain. Bitcoin (BTC) is the first decentralised CTC which garnered a lot of attention from the media as well as the public due to its ability to sustain the momentum in the market. However, investing in BTC is not the first choice of the investor due to the market's erratic behaviour, price volatility and lack of a model that could be used to predict its price. In this direction, the present study aims in developing a time-series forecasting model that can efficiently as well as effectively predict the price of Bitcoins. For this purpose three machine learning (ML) models namely Long Short Term Memory (LSTM), Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average method (ARIMA) and Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated

Statistical Scrutiny of the Prediction Capability of Different Time Series Machine Learning Models in Forecasting Bitcoin Prices
Cryptocurrencies (CTC) are decentralised digital currency. In the past decade, there has been a massive increase in its usage due to the advancement made in the field of blockchain. Bitcoin (BTC) is the first decentralised CTC which garnered a lot of attention from the media as well as the public due to its ability to sustain the momentum in the market. However, investing in BTC is not the first choice of the investor due to the market's erratic behaviour, price volatility and lack of a model that could be used to predict its price. In this direction, the present study aims in developing a time-series forecasting model that can efficiently as well as effectively predict the price of Bitcoins. For this purpose three machine learning (ML) models namely Long Short Term Memory (LSTM), Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average method (ARIMA) and Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated

Statistical Scrutiny of the Prediction Capability of Different Time Series Machine Learning Models in Forecasting Bitcoin Prices
The research presented here looks into the vibration properties of 3D-printed airless tires, which have the potential to revolutionize tire design and transportation efficiency. Through extensive experimentation and vibration research, three distinct tire constructions were investigated. Because of its good damping and deformation qualities, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) was chosen as the 3D printing material. The experimental arrangement was designed to simulate real-world road conditions, and an MPU6050 sensor captured tire vibrations in three axes. The vibrational properties of the tire structures were revealed using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) analysis, allowing for a comparative assessment of their stability. Structure 1 was found to be the most vibration-stable, followed by Structures 3 and 2.
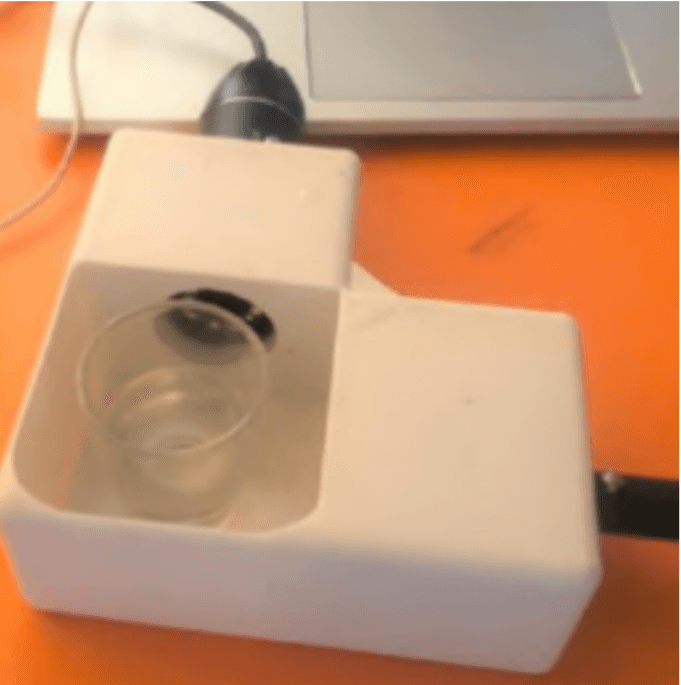

Quantification of Microplastic in Domestic Greywater Using Image Processing and Machine Learning at Microscopic Level
The abstract discusses the issue of microplastics released from washing synthetic textiles, which contribute significantly to ocean pollution. It highlights the need for innovative methods to detect microplastics in wastewater. The aim of the project is to create a prototype for real-time monitoring of microplastics in greywater released from household washing machines. The prototype includes monitoring using a camera, analyzing and storing data in the cloud, and employing computer vision and machine learning techniques for microplastic detection in the images. It also includes a system for logging and monitoring microplastics in greywater. The prototype can be used by the government to regulate the amount and type of microplastics released by various types of clothes.

Quantification of Microplastic in Domestic Greywater Using Image Processing and Machine Learning at Microscopic Level
The abstract discusses the issue of microplastics released from washing synthetic textiles, which contribute significantly to ocean pollution. It highlights the need for innovative methods to detect microplastics in wastewater. The aim of the project is to create a prototype for real-time monitoring of microplastics in greywater released from household washing machines. The prototype includes monitoring using a camera, analyzing and storing data in the cloud, and employing computer vision and machine learning techniques for microplastic detection in the images. It also includes a system for logging and monitoring microplastics in greywater. The prototype can be used by the government to regulate the amount and type of microplastics released by various types of clothes.

Quantification of Microplastic in Domestic Greywater Using Image Processing and Machine Learning at Microscopic Level
The abstract discusses the issue of microplastics released from washing synthetic textiles, which contribute significantly to ocean pollution. It highlights the need for innovative methods to detect microplastics in wastewater. The aim of the project is to create a prototype for real-time monitoring of microplastics in greywater released from household washing machines. The prototype includes monitoring using a camera, analyzing and storing data in the cloud, and employing computer vision and machine learning techniques for microplastic detection in the images. It also includes a system for logging and monitoring microplastics in greywater. The prototype can be used by the government to regulate the amount and type of microplastics released by various types of clothes.
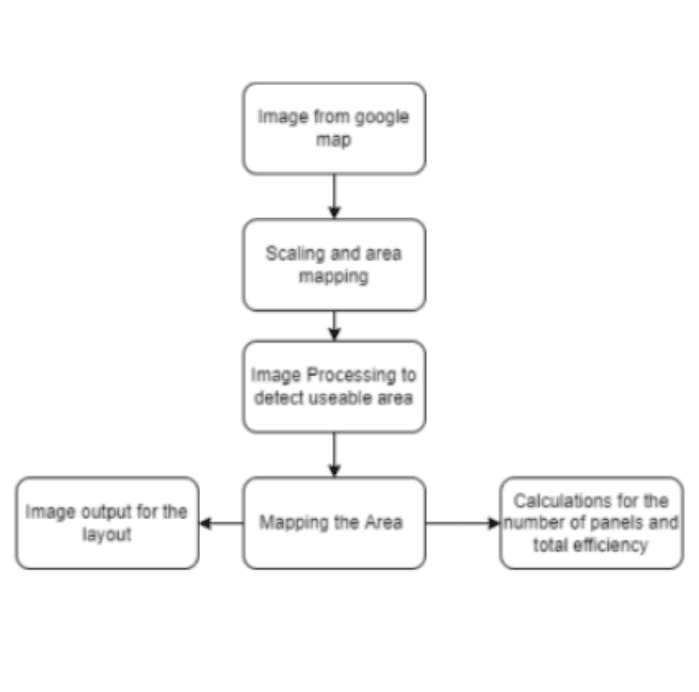
Calculating Maximum Power Generation Capacity of The Roof Space Through Solar Panels Using Image Processing and Satellite Images
The program uses satellite images and image processing techniques with Python libraries like OpenCV and NumPy. It collects satellite images from Google Maps, scales them based on the distance scale in the image, crops the roof area, and detects the usable space. The program then provides the maximum number of panels that can be installed on the roof, along with a blueprint for their location and orientation. The solution aims to address the space constraints of solar panel installation, allowing efficient energy production without dedicating land space for large solar farms, especially in urban areas with limited space.

Calculating Maximum Power Generation Capacity of The Roof Space Through Solar Panels Using Image Processing and Satellite Images
The program uses satellite images and image processing techniques with Python libraries like OpenCV and NumPy. It collects satellite images from Google Maps, scales them based on the distance scale in the image, crops the roof area, and detects the usable space. The program then provides the maximum number of panels that can be installed on the roof, along with a blueprint for their location and orientation. The solution aims to address the space constraints of solar panel installation, allowing efficient energy production without dedicating land space for large solar farms, especially in urban areas with limited space.

Calculating Maximum Power Generation Capacity of The Roof Space Through Solar Panels Using Image Processing and Satellite Images
The program uses satellite images and image processing techniques with Python libraries like OpenCV and NumPy. It collects satellite images from Google Maps, scales them based on the distance scale in the image, crops the roof area, and detects the usable space. The program then provides the maximum number of panels that can be installed on the roof, along with a blueprint for their location and orientation. The solution aims to address the space constraints of solar panel installation, allowing efficient energy production without dedicating land space for large solar farms, especially in urban areas with limited space.
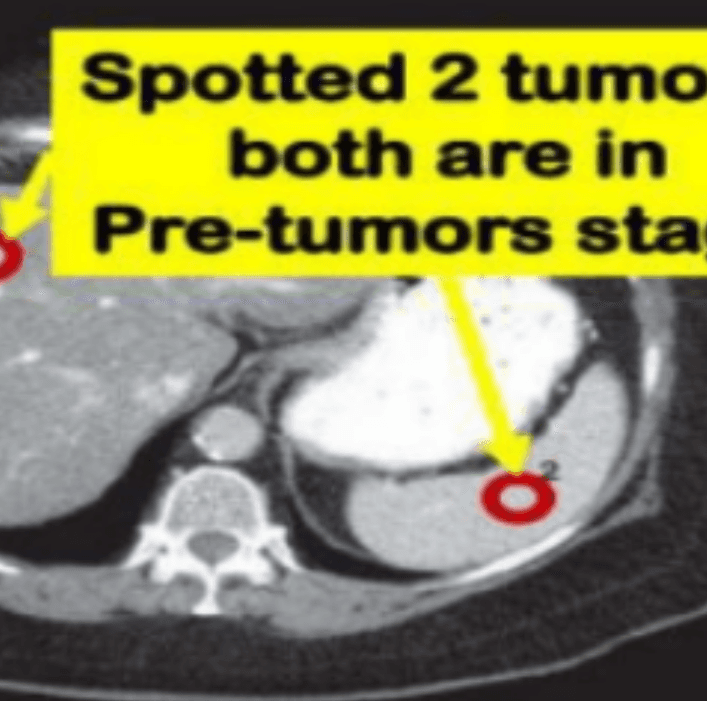
Screening Liver tumor with 3D-IRCAD, ResUNet Model
Our project focuses on liver tumor screening, addressing the limitations of current methods such as manual interpretation of CT scans and the expense and side effects of MRI. Leveraging Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), specifically the 3D-IRCAD ResUNet Model, our solution detects liver tumors early and efficiently. Using machine learning models trained on a dataset from IRCAD Research Institute, our approach achieves high accuracy in tumor detection. The CNN's performance surpasses human expertise in radiology, providing promising results for early tumor detection.

Screening Liver tumor with 3D-IRCAD, ResUNet Model
Our project focuses on liver tumor screening, addressing the limitations of current methods such as manual interpretation of CT scans and the expense and side effects of MRI. Leveraging Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), specifically the 3D-IRCAD ResUNet Model, our solution detects liver tumors early and efficiently. Using machine learning models trained on a dataset from IRCAD Research Institute, our approach achieves high accuracy in tumor detection. The CNN's performance surpasses human expertise in radiology, providing promising results for early tumor detection.

Screening Liver tumor with 3D-IRCAD, ResUNet Model
Our project focuses on liver tumor screening, addressing the limitations of current methods such as manual interpretation of CT scans and the expense and side effects of MRI. Leveraging Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), specifically the 3D-IRCAD ResUNet Model, our solution detects liver tumors early and efficiently. Using machine learning models trained on a dataset from IRCAD Research Institute, our approach achieves high accuracy in tumor detection. The CNN's performance surpasses human expertise in radiology, providing promising results for early tumor detection.
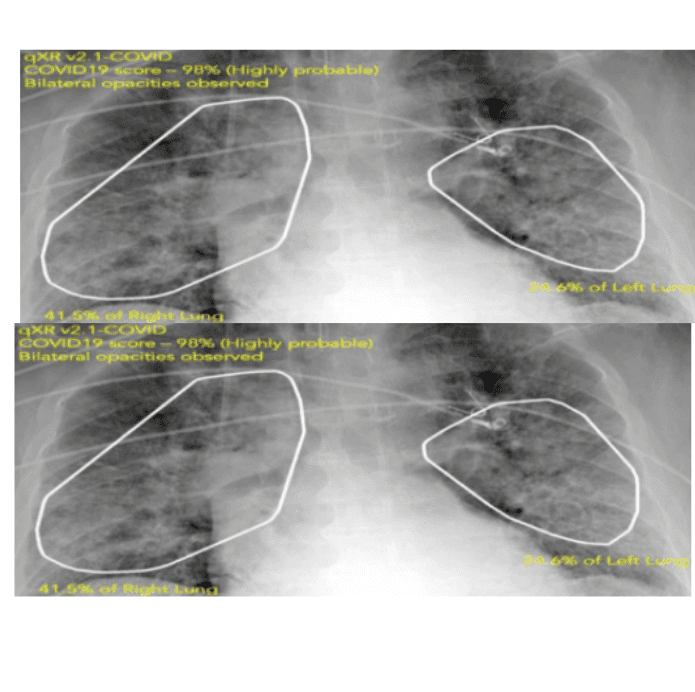
Projecting Teenage Pregnancy and Motherhood and Fertility Rates: An Analytical and Machine Learning Study of Maharashtra, India
Adolescent pregnancy poses significant challenges with long-term physical, mental, and economic implications for both teenage mothers and their babies. This paper, focusing on Maharashtra, is divided into two sections: fertility trends and teenage pregnancy and motherhood. Data from the NFHS surveys were analyzed using Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) to investigate variables such as residency, age, marital status, education, and more. The findings indicate that higher pregnancy rates are associated with rural residency, lower income, limited education, and specific demographic backgrounds. Additionally, machine learning techniques, specifically the Linear Regression algorithm, were applied to the data, demonstrating the model's accuracy in predicting pregnancy trends.

Projecting Teenage Pregnancy and Motherhood and Fertility Rates: An Analytical and Machine Learning Study of Maharashtra, India
Adolescent pregnancy poses significant challenges with long-term physical, mental, and economic implications for both teenage mothers and their babies. This paper, focusing on Maharashtra, is divided into two sections: fertility trends and teenage pregnancy and motherhood. Data from the NFHS surveys were analyzed using Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) to investigate variables such as residency, age, marital status, education, and more. The findings indicate that higher pregnancy rates are associated with rural residency, lower income, limited education, and specific demographic backgrounds. Additionally, machine learning techniques, specifically the Linear Regression algorithm, were applied to the data, demonstrating the model's accuracy in predicting pregnancy trends.

Projecting Teenage Pregnancy and Motherhood and Fertility Rates: An Analytical and Machine Learning Study of Maharashtra, India
Adolescent pregnancy poses significant challenges with long-term physical, mental, and economic implications for both teenage mothers and their babies. This paper, focusing on Maharashtra, is divided into two sections: fertility trends and teenage pregnancy and motherhood. Data from the NFHS surveys were analyzed using Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) to investigate variables such as residency, age, marital status, education, and more. The findings indicate that higher pregnancy rates are associated with rural residency, lower income, limited education, and specific demographic backgrounds. Additionally, machine learning techniques, specifically the Linear Regression algorithm, were applied to the data, demonstrating the model's accuracy in predicting pregnancy trends.

Development of a Robust DNA Sequencing Multiclass Hybrid Classifier Employing Machine Learning and NLP For Automated Gene Classification
DNA sequencing determines the order of chemical bases in DNA molecules, revealing genetic information crucial for understanding gene function and disease. This study presents a hybrid ensemble machine learning model, utilizing eleven classifiers, to develop a genomic classifier for DNA sequences. By employing NLP and machine learning techniques, the model enhances gene classification in biomedical research. Performance evaluation demonstrates high accuracy across human, chimpanzee, and dog datasets, with the model achieving 98.08% accuracy for human data, 90.75% for chimpanzee data, and 70% for dog data. The study transcends species boundaries, offering insights into genome classifications and paving the way for further advancements in genetic analysis.

Development of a Robust DNA Sequencing Multiclass Hybrid Classifier Employing Machine Learning and NLP For Automated Gene Classification
DNA sequencing determines the order of chemical bases in DNA molecules, revealing genetic information crucial for understanding gene function and disease. This study presents a hybrid ensemble machine learning model, utilizing eleven classifiers, to develop a genomic classifier for DNA sequences. By employing NLP and machine learning techniques, the model enhances gene classification in biomedical research. Performance evaluation demonstrates high accuracy across human, chimpanzee, and dog datasets, with the model achieving 98.08% accuracy for human data, 90.75% for chimpanzee data, and 70% for dog data. The study transcends species boundaries, offering insights into genome classifications and paving the way for further advancements in genetic analysis.

Development of a Robust DNA Sequencing Multiclass Hybrid Classifier Employing Machine Learning and NLP For Automated Gene Classification
DNA sequencing determines the order of chemical bases in DNA molecules, revealing genetic information crucial for understanding gene function and disease. This study presents a hybrid ensemble machine learning model, utilizing eleven classifiers, to develop a genomic classifier for DNA sequences. By employing NLP and machine learning techniques, the model enhances gene classification in biomedical research. Performance evaluation demonstrates high accuracy across human, chimpanzee, and dog datasets, with the model achieving 98.08% accuracy for human data, 90.75% for chimpanzee data, and 70% for dog data. The study transcends species boundaries, offering insights into genome classifications and paving the way for further advancements in genetic analysis.

An Integrated Approach to Select the Dream Team for a Cricket Match
This paper proposes an integrated approach for selecting the best fantasy cricket team based on player performance. The approach combines the cross-entropy method, weighted sum method (WSM), and goal programming problem (GPP). It extracts player performance data through web scraping and computes points using cross-entropy and WSM, giving higher weightage to recent games. The GPP part selects players by using binary decision variables, where 1 indicates a player's inclusion in the team. The proposed algorithm dynamically adjusts factor weights based on recent performance. The approach is applied to select the dream team for an India-New Zealand cricket match, demonstrating its practicality.

An Integrated Approach to Select the Dream Team for a Cricket Match
This paper proposes an integrated approach for selecting the best fantasy cricket team based on player performance. The approach combines the cross-entropy method, weighted sum method (WSM), and goal programming problem (GPP). It extracts player performance data through web scraping and computes points using cross-entropy and WSM, giving higher weightage to recent games. The GPP part selects players by using binary decision variables, where 1 indicates a player's inclusion in the team. The proposed algorithm dynamically adjusts factor weights based on recent performance. The approach is applied to select the dream team for an India-New Zealand cricket match, demonstrating its practicality.

An Integrated Approach to Select the Dream Team for a Cricket Match
This paper proposes an integrated approach for selecting the best fantasy cricket team based on player performance. The approach combines the cross-entropy method, weighted sum method (WSM), and goal programming problem (GPP). It extracts player performance data through web scraping and computes points using cross-entropy and WSM, giving higher weightage to recent games. The GPP part selects players by using binary decision variables, where 1 indicates a player's inclusion in the team. The proposed algorithm dynamically adjusts factor weights based on recent performance. The approach is applied to select the dream team for an India-New Zealand cricket match, demonstrating its practicality.
Novel Approach to Analyse Structures to Predict Earthquake Impact in Urban Areas
Recent decades have seen a rise in earthquake risks in urban areas due to urbanization, poor planning, infrastructure issues, and environmental degradation. Urban centers need robust preparedness and emergency plans, including quantifying earthquake effects, especially building losses, correlated with casualties and emergency response. My project aims to predict and assess earthquake impact in urban areas by analyzing building structures, using Google Maps images to calculate dimensions and safe areas. Our algorithm employs image processing and Machine Learning to predict seismic wave effects and determine optimal building distances, reducing risk. With high accuracy and scalability, this model could revolutionize infrastructure planning worldwide.

Novel Approach to Analyse Structures to Predict Earthquake Impact in Urban Areas
Recent decades have seen a rise in earthquake risks in urban areas due to urbanization, poor planning, infrastructure issues, and environmental degradation. Urban centers need robust preparedness and emergency plans, including quantifying earthquake effects, especially building losses, correlated with casualties and emergency response. My project aims to predict and assess earthquake impact in urban areas by analyzing building structures, using Google Maps images to calculate dimensions and safe areas. Our algorithm employs image processing and Machine Learning to predict seismic wave effects and determine optimal building distances, reducing risk. With high accuracy and scalability, this model could revolutionize infrastructure planning worldwide.

Novel Approach to Analyse Structures to Predict Earthquake Impact in Urban Areas
Recent decades have seen a rise in earthquake risks in urban areas due to urbanization, poor planning, infrastructure issues, and environmental degradation. Urban centers need robust preparedness and emergency plans, including quantifying earthquake effects, especially building losses, correlated with casualties and emergency response. My project aims to predict and assess earthquake impact in urban areas by analyzing building structures, using Google Maps images to calculate dimensions and safe areas. Our algorithm employs image processing and Machine Learning to predict seismic wave effects and determine optimal building distances, reducing risk. With high accuracy and scalability, this model could revolutionize infrastructure planning worldwide.

Experiment on a novel approach toward quantifying the toxicity level of the soil around the Yamuna River and checking the impact of polluted water on the soil
The abstract discusses an experiment aimed at quantifying the toxic effect of the polluted Yamuna River on the soil in the Mayur Vihar region of Delhi, India. Soil samples were collected at various distances from the river bank, and the decomposition of cotton pieces placed in these samples was observed over time. Image processing and a convolutional neural network model were applied to calculate the level of decomposition and fertility coefficient, indicating the impact of the river water on soil. The results were validated through chemical laboratory tests. Additionally, holy basil seeds were sown in the soil samples, and their growth patterns were observed to assess soil fertility at different distances from the river bank.

Experiment on a novel approach toward quantifying the toxicity level of the soil around the Yamuna River and checking the impact of polluted water on the soil
The abstract discusses an experiment aimed at quantifying the toxic effect of the polluted Yamuna River on the soil in the Mayur Vihar region of Delhi, India. Soil samples were collected at various distances from the river bank, and the decomposition of cotton pieces placed in these samples was observed over time. Image processing and a convolutional neural network model were applied to calculate the level of decomposition and fertility coefficient, indicating the impact of the river water on soil. The results were validated through chemical laboratory tests. Additionally, holy basil seeds were sown in the soil samples, and their growth patterns were observed to assess soil fertility at different distances from the river bank.

Experiment on a novel approach toward quantifying the toxicity level of the soil around the Yamuna River and checking the impact of polluted water on the soil
The abstract discusses an experiment aimed at quantifying the toxic effect of the polluted Yamuna River on the soil in the Mayur Vihar region of Delhi, India. Soil samples were collected at various distances from the river bank, and the decomposition of cotton pieces placed in these samples was observed over time. Image processing and a convolutional neural network model were applied to calculate the level of decomposition and fertility coefficient, indicating the impact of the river water on soil. The results were validated through chemical laboratory tests. Additionally, holy basil seeds were sown in the soil samples, and their growth patterns were observed to assess soil fertility at different distances from the river bank.
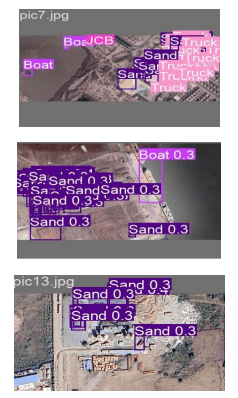
Sand Mining Prediction Using Satellite Images
This research paper focuses on the prediction of sand mining in different areas using satellite images. Illegal sand mining has emerged as a major environmental issue, affecting numerous regions worldwide. Sand mining nowadays has become a curse for society. It should be stopped before it creates a drastic problem for the universe. Some areas are widely affected by illegal sand mining resulting in floods and scarcity of resources. In this paper, YOLOv5( you only look once) is used to train the model. The collection of data is a major problem one is going to face at the start of the project, in the case of a satellite-based image. To feed the algorithm, a dataset is taken that clearly demonstrates the difference between legal and illegal sand mining. After collecting the data, the next step is to label the data and for labeling, several platforms can be used. In this research paper, LabelImg is used for the labeling part.

Sand Mining Prediction Using Satellite Images
This research paper focuses on the prediction of sand mining in different areas using satellite images. Illegal sand mining has emerged as a major environmental issue, affecting numerous regions worldwide. Sand mining nowadays has become a curse for society. It should be stopped before it creates a drastic problem for the universe. Some areas are widely affected by illegal sand mining resulting in floods and scarcity of resources. In this paper, YOLOv5( you only look once) is used to train the model. The collection of data is a major problem one is going to face at the start of the project, in the case of a satellite-based image. To feed the algorithm, a dataset is taken that clearly demonstrates the difference between legal and illegal sand mining. After collecting the data, the next step is to label the data and for labeling, several platforms can be used. In this research paper, LabelImg is used for the labeling part.

Sand Mining Prediction Using Satellite Images
This research paper focuses on the prediction of sand mining in different areas using satellite images. Illegal sand mining has emerged as a major environmental issue, affecting numerous regions worldwide. Sand mining nowadays has become a curse for society. It should be stopped before it creates a drastic problem for the universe. Some areas are widely affected by illegal sand mining resulting in floods and scarcity of resources. In this paper, YOLOv5( you only look once) is used to train the model. The collection of data is a major problem one is going to face at the start of the project, in the case of a satellite-based image. To feed the algorithm, a dataset is taken that clearly demonstrates the difference between legal and illegal sand mining. After collecting the data, the next step is to label the data and for labeling, several platforms can be used. In this research paper, LabelImg is used for the labeling part.

Comparative Analysis of Traffic Classification Algorithms in Deep Learning
Aging roads and poor road-maintenance systems resulted many potholes, whose numbers increase over time. Potholes jeopardize road safety and transportation efficiency. Moreover, they are often a contributing factor to car accidents. To address the problems associated with potholes, the locations and size of potholes must be determined quickly to find the location a data base as to be developed, which requires a specific pothole-detection system that can collect pothole information at low cost and over a wide area. However, pothole repair has long relied on manual detection efforts causing loss of time and money to government. Thus, in this paper, we introduced a pothole-detection system using a commercial “Road sepoy”. The proposed system detects potholes using vision-based tracking system and MATLAB algorithm specifically designed to work with road sepoy camera giving us accurately in real-time environment. Geo-mapping the pothole in google maps helps the exact location.

Comparative Analysis of Traffic Classification Algorithms in Deep Learning
Aging roads and poor road-maintenance systems resulted many potholes, whose numbers increase over time. Potholes jeopardize road safety and transportation efficiency. Moreover, they are often a contributing factor to car accidents. To address the problems associated with potholes, the locations and size of potholes must be determined quickly to find the location a data base as to be developed, which requires a specific pothole-detection system that can collect pothole information at low cost and over a wide area. However, pothole repair has long relied on manual detection efforts causing loss of time and money to government. Thus, in this paper, we introduced a pothole-detection system using a commercial “Road sepoy”. The proposed system detects potholes using vision-based tracking system and MATLAB algorithm specifically designed to work with road sepoy camera giving us accurately in real-time environment. Geo-mapping the pothole in google maps helps the exact location.

Comparative Analysis of Traffic Classification Algorithms in Deep Learning
Aging roads and poor road-maintenance systems resulted many potholes, whose numbers increase over time. Potholes jeopardize road safety and transportation efficiency. Moreover, they are often a contributing factor to car accidents. To address the problems associated with potholes, the locations and size of potholes must be determined quickly to find the location a data base as to be developed, which requires a specific pothole-detection system that can collect pothole information at low cost and over a wide area. However, pothole repair has long relied on manual detection efforts causing loss of time and money to government. Thus, in this paper, we introduced a pothole-detection system using a commercial “Road sepoy”. The proposed system detects potholes using vision-based tracking system and MATLAB algorithm specifically designed to work with road sepoy camera giving us accurately in real-time environment. Geo-mapping the pothole in google maps helps the exact location.
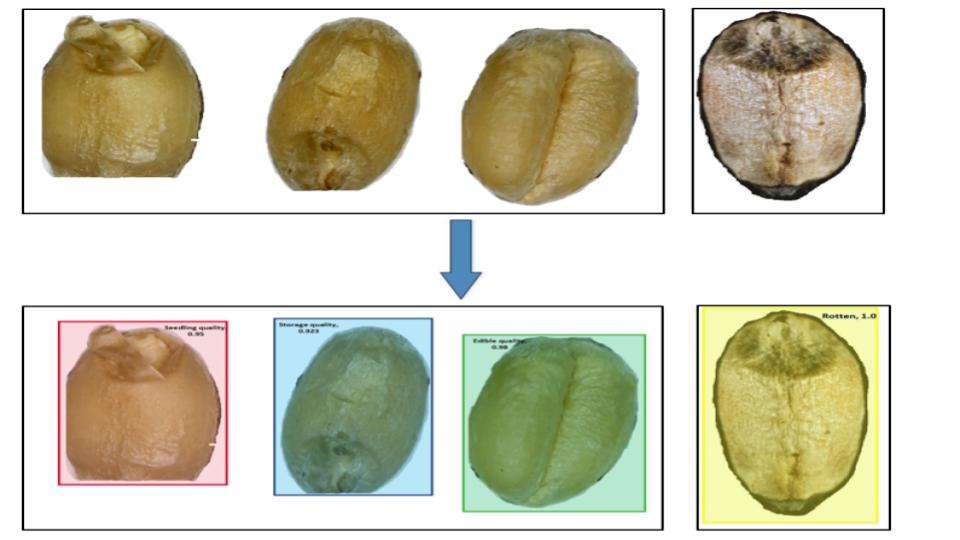
Assessment of Quality of The Wheat Grain Using Image Processing and Mask R-CNN
The study develops a Mask Regional Convolutional Neural Network (Mask RCNN) model to classify the quality of wheat grains into four categories: storage quality, edible, seeding quality, or rotten. The model is trained on 122 images created from 2,000 grains, using image processing to extract grain texture. The wheat grains are annotated with VGG Image Annotator, and the JSON files are used for training and testing the Mask RCNN model. The trained model achieves low training and validation losses and demonstrates high accuracy in classifying the grain quality when tested on a new image with all four classes.

Assessment of Quality of The Wheat Grain Using Image Processing and Mask R-CNN
The study develops a Mask Regional Convolutional Neural Network (Mask RCNN) model to classify the quality of wheat grains into four categories: storage quality, edible, seeding quality, or rotten. The model is trained on 122 images created from 2,000 grains, using image processing to extract grain texture. The wheat grains are annotated with VGG Image Annotator, and the JSON files are used for training and testing the Mask RCNN model. The trained model achieves low training and validation losses and demonstrates high accuracy in classifying the grain quality when tested on a new image with all four classes.

Assessment of Quality of The Wheat Grain Using Image Processing and Mask R-CNN
The study develops a Mask Regional Convolutional Neural Network (Mask RCNN) model to classify the quality of wheat grains into four categories: storage quality, edible, seeding quality, or rotten. The model is trained on 122 images created from 2,000 grains, using image processing to extract grain texture. The wheat grains are annotated with VGG Image Annotator, and the JSON files are used for training and testing the Mask RCNN model. The trained model achieves low training and validation losses and demonstrates high accuracy in classifying the grain quality when tested on a new image with all four classes.
Autonomous Assistance in Guitar Tutoring for Uninterrupted Self Learning and Practice
Guitar Tutor is a software that guides users in playing the right guitar notes by comparing the real tune with the notes played and pointing out differences. It uses a database of chords created from audio files in WAV format. The software employs a Feed Forward Neural Network model to extract and classify notes from the audio input. It detects audio events, filters noise, and analyzes specific frequency patterns to predict the note played, comparing it with the base dataset with an accuracy of 85%.

Autonomous Assistance in Guitar Tutoring for Uninterrupted Self Learning and Practice
Guitar Tutor is a software that guides users in playing the right guitar notes by comparing the real tune with the notes played and pointing out differences. It uses a database of chords created from audio files in WAV format. The software employs a Feed Forward Neural Network model to extract and classify notes from the audio input. It detects audio events, filters noise, and analyzes specific frequency patterns to predict the note played, comparing it with the base dataset with an accuracy of 85%.

Autonomous Assistance in Guitar Tutoring for Uninterrupted Self Learning and Practice
Guitar Tutor is a software that guides users in playing the right guitar notes by comparing the real tune with the notes played and pointing out differences. It uses a database of chords created from audio files in WAV format. The software employs a Feed Forward Neural Network model to extract and classify notes from the audio input. It detects audio events, filters noise, and analyzes specific frequency patterns to predict the note played, comparing it with the base dataset with an accuracy of 85%.
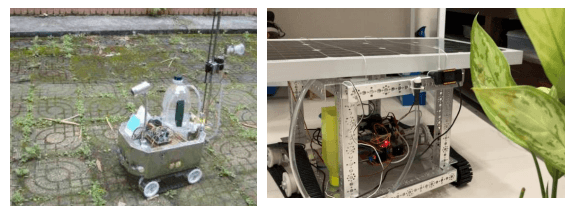
Smart Robotic Pythomedic and Pesticide Sprayer using Image Processing and machine learning
Plant diseases pose a significant global and Indian agricultural challenge, resulting in crop yield reduction and financial losses for farmers. While existing solutions like smart disease detection using machine learning offer promise, they often present cost or implementation barriers. Our solution introduces a user-friendly Smart Spraying robot equipped with a front camera and machine learning algorithm to identify and address plant diseases efficiently. Tested with over 3000 images across three vegetable plants, the model demonstrates 100% accuracy in detecting specific leaf diseases. However, its applicability is currently limited to these plants. Future iterations can expand its scope to encompass a broader range of crops.

Smart Robotic Pythomedic and Pesticide Sprayer using Image Processing and machine learning
Plant diseases pose a significant global and Indian agricultural challenge, resulting in crop yield reduction and financial losses for farmers. While existing solutions like smart disease detection using machine learning offer promise, they often present cost or implementation barriers. Our solution introduces a user-friendly Smart Spraying robot equipped with a front camera and machine learning algorithm to identify and address plant diseases efficiently. Tested with over 3000 images across three vegetable plants, the model demonstrates 100% accuracy in detecting specific leaf diseases. However, its applicability is currently limited to these plants. Future iterations can expand its scope to encompass a broader range of crops.

Smart Robotic Pythomedic and Pesticide Sprayer using Image Processing and machine learning
Plant diseases pose a significant global and Indian agricultural challenge, resulting in crop yield reduction and financial losses for farmers. While existing solutions like smart disease detection using machine learning offer promise, they often present cost or implementation barriers. Our solution introduces a user-friendly Smart Spraying robot equipped with a front camera and machine learning algorithm to identify and address plant diseases efficiently. Tested with over 3000 images across three vegetable plants, the model demonstrates 100% accuracy in detecting specific leaf diseases. However, its applicability is currently limited to these plants. Future iterations can expand its scope to encompass a broader range of crops.
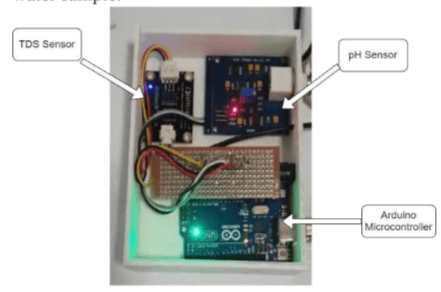
A Novel Approach Towards Calculating The Reusability Coefficient Of Water From Nearby Water Bodies Using Artificial Intelligence
Most water bodies are polluted, but there is limited data on the level of pollution. This project proposes a solution to assess water quality by collecting samples from various sources like sewage, rivers, and farms. The solution has three parts: 1) detecting turbidity using image processing, 2) measuring TDS and pH using an Arduino-based prototype, and 3) determining a quality coefficient through machine learning. All components are integrated into a 3D-printed device. The model achieves an accuracy of 89% in estimating water quality, while the circuit accurately measures TDS and pH. This real-time solution enables the detection of water body quality and potential usage after appropriate treatment.

A Novel Approach Towards Calculating The Reusability Coefficient Of Water From Nearby Water Bodies Using Artificial Intelligence
Most water bodies are polluted, but there is limited data on the level of pollution. This project proposes a solution to assess water quality by collecting samples from various sources like sewage, rivers, and farms. The solution has three parts: 1) detecting turbidity using image processing, 2) measuring TDS and pH using an Arduino-based prototype, and 3) determining a quality coefficient through machine learning. All components are integrated into a 3D-printed device. The model achieves an accuracy of 89% in estimating water quality, while the circuit accurately measures TDS and pH. This real-time solution enables the detection of water body quality and potential usage after appropriate treatment.

A Novel Approach Towards Calculating The Reusability Coefficient Of Water From Nearby Water Bodies Using Artificial Intelligence
Most water bodies are polluted, but there is limited data on the level of pollution. This project proposes a solution to assess water quality by collecting samples from various sources like sewage, rivers, and farms. The solution has three parts: 1) detecting turbidity using image processing, 2) measuring TDS and pH using an Arduino-based prototype, and 3) determining a quality coefficient through machine learning. All components are integrated into a 3D-printed device. The model achieves an accuracy of 89% in estimating water quality, while the circuit accurately measures TDS and pH. This real-time solution enables the detection of water body quality and potential usage after appropriate treatment.
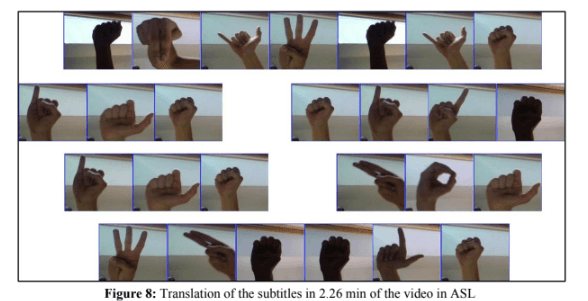
Converting Youtube Video to American Sign Language Translation Using Convolution Neural Network and Video Processing
Sign language is a vital mode of communication for the deaf, comprising around 5% of the global population. Despite the availability of subtitles in various languages, YouTube lacks sign language-based subtitles. This study aims to develop American Sign Language (ASL) subtitles for YouTube videos. The proposed method involves a three-phase framework integrating deep learning-based Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and image/video processing techniques. A torch-based CNN model achieved high accuracy in training and testing (99.982% and 98% respectively). The study demonstrates the practical application of the integrated method by extracting a random YouTube video.

Converting Youtube Video to American Sign Language Translation Using Convolution Neural Network and Video Processing
Sign language is a vital mode of communication for the deaf, comprising around 5% of the global population. Despite the availability of subtitles in various languages, YouTube lacks sign language-based subtitles. This study aims to develop American Sign Language (ASL) subtitles for YouTube videos. The proposed method involves a three-phase framework integrating deep learning-based Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and image/video processing techniques. A torch-based CNN model achieved high accuracy in training and testing (99.982% and 98% respectively). The study demonstrates the practical application of the integrated method by extracting a random YouTube video.

Converting Youtube Video to American Sign Language Translation Using Convolution Neural Network and Video Processing
Sign language is a vital mode of communication for the deaf, comprising around 5% of the global population. Despite the availability of subtitles in various languages, YouTube lacks sign language-based subtitles. This study aims to develop American Sign Language (ASL) subtitles for YouTube videos. The proposed method involves a three-phase framework integrating deep learning-based Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and image/video processing techniques. A torch-based CNN model achieved high accuracy in training and testing (99.982% and 98% respectively). The study demonstrates the practical application of the integrated method by extracting a random YouTube video.
Computational Analysis of Awareness, Usage, and Effectiveness of MOOCS With Special Focus on Acceptance of Design Courses
The internet has revolutionized education, enabling the rise of Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) that provide widespread access to diverse academic content. Platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and EdX offer free and paid online courses, empowering learners with self-paced, flexible, and dynamic educational opportunities. These certifications can significantly boost careers by facilitating easier access to information, tailored learning experiences, and enhanced convenience. As the popularity of MOOCs continues to grow, a robust recommendation system is crucial to help learners navigate the wealth of educational resources available.

Computational Analysis of Awareness, Usage, and Effectiveness of MOOCS With Special Focus on Acceptance of Design Courses
The internet has revolutionized education, enabling the rise of Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) that provide widespread access to diverse academic content. Platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and EdX offer free and paid online courses, empowering learners with self-paced, flexible, and dynamic educational opportunities. These certifications can significantly boost careers by facilitating easier access to information, tailored learning experiences, and enhanced convenience. As the popularity of MOOCs continues to grow, a robust recommendation system is crucial to help learners navigate the wealth of educational resources available.

Computational Analysis of Awareness, Usage, and Effectiveness of MOOCS With Special Focus on Acceptance of Design Courses
The internet has revolutionized education, enabling the rise of Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) that provide widespread access to diverse academic content. Platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and EdX offer free and paid online courses, empowering learners with self-paced, flexible, and dynamic educational opportunities. These certifications can significantly boost careers by facilitating easier access to information, tailored learning experiences, and enhanced convenience. As the popularity of MOOCs continues to grow, a robust recommendation system is crucial to help learners navigate the wealth of educational resources available.
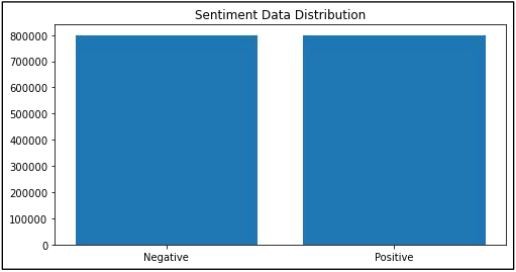
Hybrid Machine Learning Applications in Classifying the Sentiment by Analyzing the Political Tweets
The study proposes a hybrid machine learning algorithm combining natural language processing (NLP) and long short-term memory (LSTM) for sentiment analysis of political tweets. The NLP part extracts keywords summarizing the tweets and correlates them with positive or negative sentiments, while the LSTM part classifies the keywords into positive or negative sentiments. The model was applied to a dataset of 1.6 million political tweets and achieved 78% accuracy, 0.456 loss, 79% precision, and 0.78 F1 score. The aim is to analyze public sentiment from tweets to detect early crises and strategize political moves.

Hybrid Machine Learning Applications in Classifying the Sentiment by Analyzing the Political Tweets
The study proposes a hybrid machine learning algorithm combining natural language processing (NLP) and long short-term memory (LSTM) for sentiment analysis of political tweets. The NLP part extracts keywords summarizing the tweets and correlates them with positive or negative sentiments, while the LSTM part classifies the keywords into positive or negative sentiments. The model was applied to a dataset of 1.6 million political tweets and achieved 78% accuracy, 0.456 loss, 79% precision, and 0.78 F1 score. The aim is to analyze public sentiment from tweets to detect early crises and strategize political moves.

Hybrid Machine Learning Applications in Classifying the Sentiment by Analyzing the Political Tweets
The study proposes a hybrid machine learning algorithm combining natural language processing (NLP) and long short-term memory (LSTM) for sentiment analysis of political tweets. The NLP part extracts keywords summarizing the tweets and correlates them with positive or negative sentiments, while the LSTM part classifies the keywords into positive or negative sentiments. The model was applied to a dataset of 1.6 million political tweets and achieved 78% accuracy, 0.456 loss, 79% precision, and 0.78 F1 score. The aim is to analyze public sentiment from tweets to detect early crises and strategize political moves.
Find your nearest innovation lab
These awards reflect projects that pushed my boundaries, told deeper stories, and caught the attention of people who care about what visuals can say.
Find your nearest innovation lab
These awards reflect projects that pushed my boundaries, told deeper stories, and caught the attention of people who care about what visuals can say.