
Elderly Care & Wellness
Reimagine aging with smart home sensors, AI companions and health-tracking wearables for dignified living.
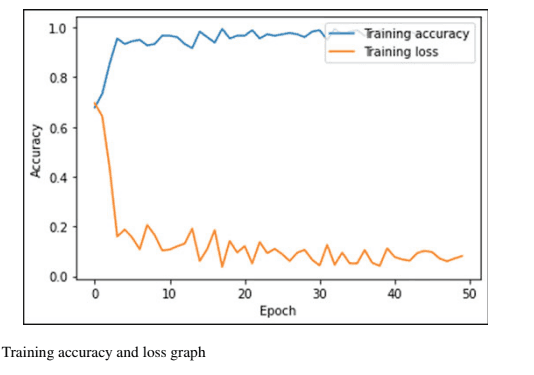
An Artificial Intelligence Integrated Technique for Screening Neurological Diseases with Sound as a Biomarker
This project aims to develop a machine learning-based system for detecting neurological disorders like Parkinson's disease (PD) and paralysis through voice analysis. Researchers recorded speech samples from patients and healthy individuals, extracting features using Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC). K-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) models were trained on this dataset to classify voices into PD, paralysis, or normal categories. With an overall accuracy rate comparable to human laryngologists (60.1% and 56.1%), this system can assist clinicians in accurately identifying the presence and stage of neurological disorders, enabling appropriate treatment recommendations through therapy, medication, or a combination thereof

An Artificial Intelligence Integrated Technique for Screening Neurological Diseases with Sound as a Biomarker
This project aims to develop a machine learning-based system for detecting neurological disorders like Parkinson's disease (PD) and paralysis through voice analysis. Researchers recorded speech samples from patients and healthy individuals, extracting features using Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC). K-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) models were trained on this dataset to classify voices into PD, paralysis, or normal categories. With an overall accuracy rate comparable to human laryngologists (60.1% and 56.1%), this system can assist clinicians in accurately identifying the presence and stage of neurological disorders, enabling appropriate treatment recommendations through therapy, medication, or a combination thereof

An Artificial Intelligence Integrated Technique for Screening Neurological Diseases with Sound as a Biomarker
This project aims to develop a machine learning-based system for detecting neurological disorders like Parkinson's disease (PD) and paralysis through voice analysis. Researchers recorded speech samples from patients and healthy individuals, extracting features using Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC). K-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) models were trained on this dataset to classify voices into PD, paralysis, or normal categories. With an overall accuracy rate comparable to human laryngologists (60.1% and 56.1%), this system can assist clinicians in accurately identifying the presence and stage of neurological disorders, enabling appropriate treatment recommendations through therapy, medication, or a combination thereof
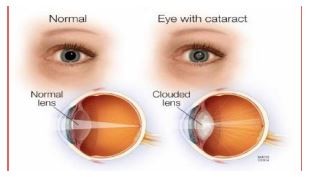
An Autonomous way to detect and quantify Cataracts using Computer Vision
The project focuses on detecting cataracts using Python, aiming to address limitations in current detection methods. Cataracts, a leading cause of blindness in older individuals, pose challenges for diagnosis, especially in rural areas with limited access to ophthalmologists. To overcome these challenges, we developed a program using Python libraries such as OpenCV, NumPy, and FPDF. This program analyzes patient information and eye images to generate a PDF report indicating the presence and severity of cataracts. By creating color masks and incorporating range checks, our program accurately detects cataracts and provides essential information for quantifying the severity of the condition. This solution facilitates early detection and intervention by providing doctors with comprehensive reports for efficient diagnosis.

An Autonomous way to detect and quantify Cataracts using Computer Vision
The project focuses on detecting cataracts using Python, aiming to address limitations in current detection methods. Cataracts, a leading cause of blindness in older individuals, pose challenges for diagnosis, especially in rural areas with limited access to ophthalmologists. To overcome these challenges, we developed a program using Python libraries such as OpenCV, NumPy, and FPDF. This program analyzes patient information and eye images to generate a PDF report indicating the presence and severity of cataracts. By creating color masks and incorporating range checks, our program accurately detects cataracts and provides essential information for quantifying the severity of the condition. This solution facilitates early detection and intervention by providing doctors with comprehensive reports for efficient diagnosis.

An Autonomous way to detect and quantify Cataracts using Computer Vision
The project focuses on detecting cataracts using Python, aiming to address limitations in current detection methods. Cataracts, a leading cause of blindness in older individuals, pose challenges for diagnosis, especially in rural areas with limited access to ophthalmologists. To overcome these challenges, we developed a program using Python libraries such as OpenCV, NumPy, and FPDF. This program analyzes patient information and eye images to generate a PDF report indicating the presence and severity of cataracts. By creating color masks and incorporating range checks, our program accurately detects cataracts and provides essential information for quantifying the severity of the condition. This solution facilitates early detection and intervention by providing doctors with comprehensive reports for efficient diagnosis.
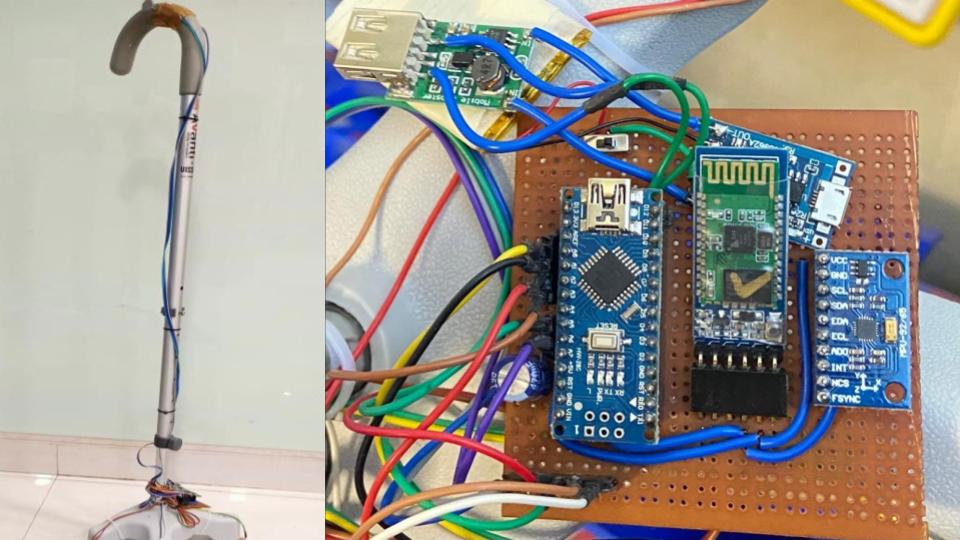
WalkFit
This project presents a smart walking stick designed to improve safety for the elderly by predicting fall risks. The lightweight, user-friendly prototype integrates sensors to monitor tilt angles and pressure distribution in real-time. By collaborating with physiotherapists and leveraging machine learning algorithms, the system analyzes the collected data to anticipate potential falls. This innovative solution provides valuable insights for families and healthcare professionals, demonstrating applications in physiology, neurology, and orthopedics. With its comprehensive approach and adaptability, the smart walking stick offers a promising avenue to enhance the well-being and overall safety of the aging population.

WalkFit
This project presents a smart walking stick designed to improve safety for the elderly by predicting fall risks. The lightweight, user-friendly prototype integrates sensors to monitor tilt angles and pressure distribution in real-time. By collaborating with physiotherapists and leveraging machine learning algorithms, the system analyzes the collected data to anticipate potential falls. This innovative solution provides valuable insights for families and healthcare professionals, demonstrating applications in physiology, neurology, and orthopedics. With its comprehensive approach and adaptability, the smart walking stick offers a promising avenue to enhance the well-being and overall safety of the aging population.

WalkFit
This project presents a smart walking stick designed to improve safety for the elderly by predicting fall risks. The lightweight, user-friendly prototype integrates sensors to monitor tilt angles and pressure distribution in real-time. By collaborating with physiotherapists and leveraging machine learning algorithms, the system analyzes the collected data to anticipate potential falls. This innovative solution provides valuable insights for families and healthcare professionals, demonstrating applications in physiology, neurology, and orthopedics. With its comprehensive approach and adaptability, the smart walking stick offers a promising avenue to enhance the well-being and overall safety of the aging population.
Averting Frustration in Geriatric Patients through Identification, 2D Mapping and Navigation Using Machine Learning
This project presents MemoryMap, an assistive system designed for elderly patients in the early stages of Alzheimer’s. The device uses a camera-equipped wearable to perform real-time object and facial recognition through OpenCV and machine learning. It maps the locations of important items, stores them in a database, and provides visual and audio navigation to guide the user back to misplaced objects. By combining live video analysis, automated mapping, and intuitive feedback, the system reduces agitation caused by memory loss and supports greater independence in daily activities.

Averting Frustration in Geriatric Patients through Identification, 2D Mapping and Navigation Using Machine Learning
This project presents MemoryMap, an assistive system designed for elderly patients in the early stages of Alzheimer’s. The device uses a camera-equipped wearable to perform real-time object and facial recognition through OpenCV and machine learning. It maps the locations of important items, stores them in a database, and provides visual and audio navigation to guide the user back to misplaced objects. By combining live video analysis, automated mapping, and intuitive feedback, the system reduces agitation caused by memory loss and supports greater independence in daily activities.

Averting Frustration in Geriatric Patients through Identification, 2D Mapping and Navigation Using Machine Learning
This project presents MemoryMap, an assistive system designed for elderly patients in the early stages of Alzheimer’s. The device uses a camera-equipped wearable to perform real-time object and facial recognition through OpenCV and machine learning. It maps the locations of important items, stores them in a database, and provides visual and audio navigation to guide the user back to misplaced objects. By combining live video analysis, automated mapping, and intuitive feedback, the system reduces agitation caused by memory loss and supports greater independence in daily activities.
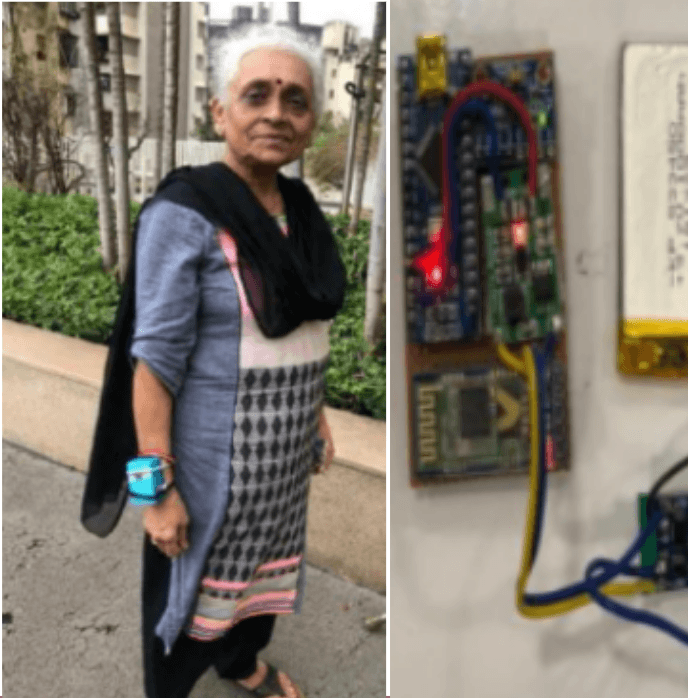
SAATHI – Your Fitness Companion
Our project addresses the lack of regular physical exercise among the elderly by providing a simple and social solution. Through our research, we discovered that many seniors struggle with technology but prefer exercising in groups. To tackle this, we developed an exercise wristband and a mobile app that allows users to track their steps, set goals, and form exercise groups. The app is designed to be user-friendly with clear icons and minimal pages. By connecting with others in the app, users can find motivation and companionship, encouraging them to stay active.

SAATHI – Your Fitness Companion
Our project addresses the lack of regular physical exercise among the elderly by providing a simple and social solution. Through our research, we discovered that many seniors struggle with technology but prefer exercising in groups. To tackle this, we developed an exercise wristband and a mobile app that allows users to track their steps, set goals, and form exercise groups. The app is designed to be user-friendly with clear icons and minimal pages. By connecting with others in the app, users can find motivation and companionship, encouraging them to stay active.

SAATHI – Your Fitness Companion
Our project addresses the lack of regular physical exercise among the elderly by providing a simple and social solution. Through our research, we discovered that many seniors struggle with technology but prefer exercising in groups. To tackle this, we developed an exercise wristband and a mobile app that allows users to track their steps, set goals, and form exercise groups. The app is designed to be user-friendly with clear icons and minimal pages. By connecting with others in the app, users can find motivation and companionship, encouraging them to stay active.
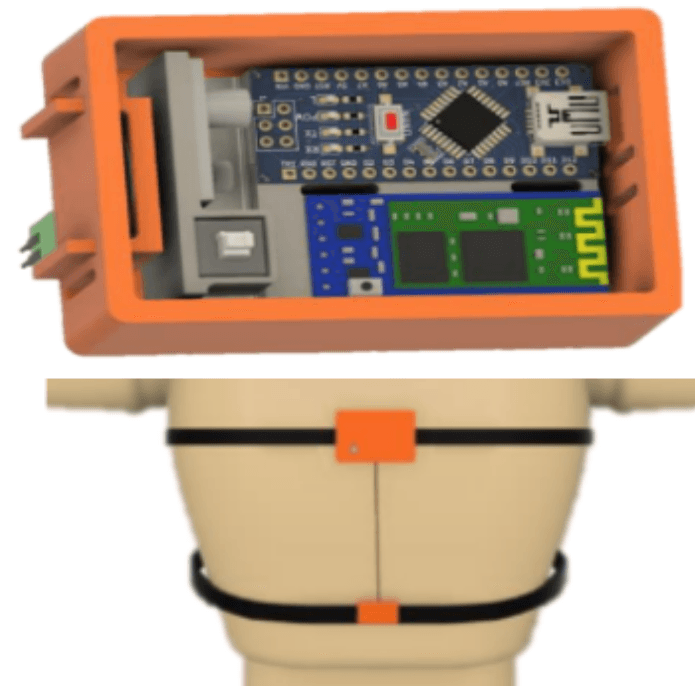
Breath Free – Screening stress and Anxiety from breathing pattern
The product aims to detect early stress and anxiety by measuring breathing patterns as a vital sign. It uses two 3D-printed box-like structures fitted with FSR sensors to measure chest and belly expansion in a non-invasive way. The wireless device connects to a computer via Bluetooth and sends data serially. A Python program collects the data and generates an A4-size infographic report on breathing, including chest and belly breathing patterns, consistency and flow, breathing rate, and the number of deep, shallow, and normal breaths. Testing revealed that the breathing patterns of working professionals in stressful jobs differ from those of school-going children. The device was also tested for gaming activities to assess excitement and stress, which can affect breathing. The product can potentially help control stress and anxiety by monitoring breathing patterns and implementing proper physical practices.

Breath Free – Screening stress and Anxiety from breathing pattern
The product aims to detect early stress and anxiety by measuring breathing patterns as a vital sign. It uses two 3D-printed box-like structures fitted with FSR sensors to measure chest and belly expansion in a non-invasive way. The wireless device connects to a computer via Bluetooth and sends data serially. A Python program collects the data and generates an A4-size infographic report on breathing, including chest and belly breathing patterns, consistency and flow, breathing rate, and the number of deep, shallow, and normal breaths. Testing revealed that the breathing patterns of working professionals in stressful jobs differ from those of school-going children. The device was also tested for gaming activities to assess excitement and stress, which can affect breathing. The product can potentially help control stress and anxiety by monitoring breathing patterns and implementing proper physical practices.

Breath Free – Screening stress and Anxiety from breathing pattern
The product aims to detect early stress and anxiety by measuring breathing patterns as a vital sign. It uses two 3D-printed box-like structures fitted with FSR sensors to measure chest and belly expansion in a non-invasive way. The wireless device connects to a computer via Bluetooth and sends data serially. A Python program collects the data and generates an A4-size infographic report on breathing, including chest and belly breathing patterns, consistency and flow, breathing rate, and the number of deep, shallow, and normal breaths. Testing revealed that the breathing patterns of working professionals in stressful jobs differ from those of school-going children. The device was also tested for gaming activities to assess excitement and stress, which can affect breathing. The product can potentially help control stress and anxiety by monitoring breathing patterns and implementing proper physical practices.
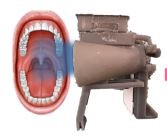
Mouthscope: Autonomous Detection of Oral Precancerous
Lesions By Fluorescent Imaging
Oral cancer (OC), highly treatable in early stages, is often diagnosed late in rural India due to lack of accessible screening. MouthScope uses AI to automate OC screening, making it more accessible. It scans the oral cavity for potentially cancerous lesions without professional intervention. The portable device works on auto-fluorescence principle, capturing color differences with a phone camera, which are analyzed by machine learning models (ResNet_v2 and YOLOv5) with 96% accuracy. It allows real-time self-detection and mass screening, enabling self-checkups. Tested on 24 patients, MouthScope clearly distinguished malignant from normal tissue. By using smartphones and machine learning, MouthScope eliminates the need for extensive infrastructure, making mass OC screening more attainable for rural India.

Mouthscope: Autonomous Detection of Oral Precancerous
Lesions By Fluorescent Imaging
Oral cancer (OC), highly treatable in early stages, is often diagnosed late in rural India due to lack of accessible screening. MouthScope uses AI to automate OC screening, making it more accessible. It scans the oral cavity for potentially cancerous lesions without professional intervention. The portable device works on auto-fluorescence principle, capturing color differences with a phone camera, which are analyzed by machine learning models (ResNet_v2 and YOLOv5) with 96% accuracy. It allows real-time self-detection and mass screening, enabling self-checkups. Tested on 24 patients, MouthScope clearly distinguished malignant from normal tissue. By using smartphones and machine learning, MouthScope eliminates the need for extensive infrastructure, making mass OC screening more attainable for rural India.

Mouthscope: Autonomous Detection of Oral Precancerous
Lesions By Fluorescent Imaging
Oral cancer (OC), highly treatable in early stages, is often diagnosed late in rural India due to lack of accessible screening. MouthScope uses AI to automate OC screening, making it more accessible. It scans the oral cavity for potentially cancerous lesions without professional intervention. The portable device works on auto-fluorescence principle, capturing color differences with a phone camera, which are analyzed by machine learning models (ResNet_v2 and YOLOv5) with 96% accuracy. It allows real-time self-detection and mass screening, enabling self-checkups. Tested on 24 patients, MouthScope clearly distinguished malignant from normal tissue. By using smartphones and machine learning, MouthScope eliminates the need for extensive infrastructure, making mass OC screening more attainable for rural India.
A Computational Approach To Learning Music
Learning the guitar is not an easy task, several people have tried methods like online lessons and even physical ones, yet progress is slow. Due to the above, most quit whilst others find marginal levels of success. Research has been conducted to design a different approach to learning and practicing the guitar. Its purpose is to establish a system in which a user can create music without having to explore the intricacies of music theory, making the task easier and thus more achievable for the general population. By doing so, it strives to make music a more approachable domain for those who wish to explore it. In the process, I devised a unique way of approaching the instrument; one that avoids theory and draws focus on musical sense. Using open CV and python, I designed a program that takes scales as inputs and provides a harmonious sequence of notes as an output. Although based on the guitar, the theory explored in the project can be applied to any fretted instrument that holds a discrete set of notes. Using this program, general users can have access to instruments and consequently the benefits associated with playing music.
A Computational Approach To Learning Music
Learning the guitar is not an easy task, several people have tried methods like online lessons and even physical ones, yet progress is slow. Due to the above, most quit whilst others find marginal levels of success. Research has been conducted to design a different approach to learning and practicing the guitar. Its purpose is to establish a system in which a user can create music without having to explore the intricacies of music theory, making the task easier and thus more achievable for the general population. By doing so, it strives to make music a more approachable domain for those who wish to explore it. In the process, I devised a unique way of approaching the instrument; one that avoids theory and draws focus on musical sense. Using open CV and python, I designed a program that takes scales as inputs and provides a harmonious sequence of notes as an output. Although based on the guitar, the theory explored in the project can be applied to any fretted instrument that holds a discrete set of notes. Using this program, general users can have access to instruments and consequently the benefits associated with playing music.
A Computational Approach To Learning Music
Learning the guitar is not an easy task, several people have tried methods like online lessons and even physical ones, yet progress is slow. Due to the above, most quit whilst others find marginal levels of success. Research has been conducted to design a different approach to learning and practicing the guitar. Its purpose is to establish a system in which a user can create music without having to explore the intricacies of music theory, making the task easier and thus more achievable for the general population. By doing so, it strives to make music a more approachable domain for those who wish to explore it. In the process, I devised a unique way of approaching the instrument; one that avoids theory and draws focus on musical sense. Using open CV and python, I designed a program that takes scales as inputs and provides a harmonious sequence of notes as an output. Although based on the guitar, the theory explored in the project can be applied to any fretted instrument that holds a discrete set of notes. Using this program, general users can have access to instruments and consequently the benefits associated with playing music.
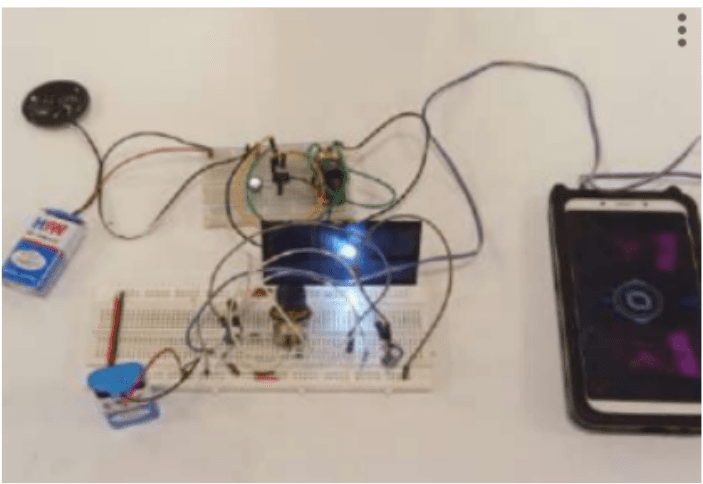
The Future of LiFi Technology to Transfer the Data
A Li-Fi network is a novel wireless technology that provides connection within a network. Li-Fi is an abbreviation for light-fidelity, which was proposed by German physicist Herald Haas. It transmits data via illumination by delivering data through an LED light bulb whose intensity fluctuates quicker than the human eye can follow. Practically LiFi is interference-free and safer than radio technology such as Wi-Fi or cellular networks. It involves the use of light instead of radio frequencies to transmit data. Radio frequency communication requires complex radio circuitry, antennas, and receivers, while LiFi is much simpler and uses direct modulation techniques.

The Future of LiFi Technology to Transfer the Data
A Li-Fi network is a novel wireless technology that provides connection within a network. Li-Fi is an abbreviation for light-fidelity, which was proposed by German physicist Herald Haas. It transmits data via illumination by delivering data through an LED light bulb whose intensity fluctuates quicker than the human eye can follow. Practically LiFi is interference-free and safer than radio technology such as Wi-Fi or cellular networks. It involves the use of light instead of radio frequencies to transmit data. Radio frequency communication requires complex radio circuitry, antennas, and receivers, while LiFi is much simpler and uses direct modulation techniques.

The Future of LiFi Technology to Transfer the Data
A Li-Fi network is a novel wireless technology that provides connection within a network. Li-Fi is an abbreviation for light-fidelity, which was proposed by German physicist Herald Haas. It transmits data via illumination by delivering data through an LED light bulb whose intensity fluctuates quicker than the human eye can follow. Practically LiFi is interference-free and safer than radio technology such as Wi-Fi or cellular networks. It involves the use of light instead of radio frequencies to transmit data. Radio frequency communication requires complex radio circuitry, antennas, and receivers, while LiFi is much simpler and uses direct modulation techniques.
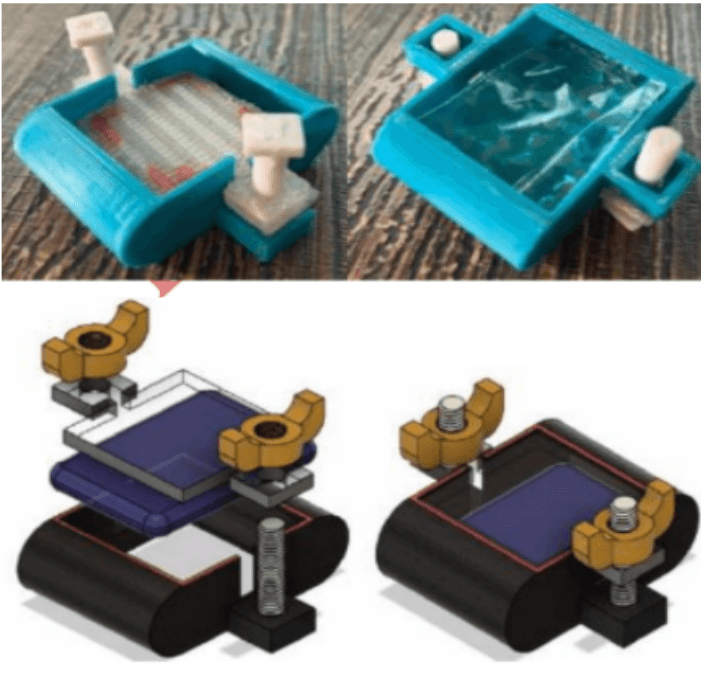
Creating a Haptic 4D Model Along With Machine Learning Analysis by Developing a Non- Invasive Pressure Mapping Method to Screen for Genital Skin Cancer
Early detection of genital skin cancer is hindered by factors such as privacy concerns, social barriers, and discomfort. Traditional biopsy methods, though accurate, can cause pain and infection in the genital region. Our engineering objective is to develop a non-invasive screening method using machine learning. We created a mobile app that processes lesion images through a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN), achieving an 83% accuracy in classifying malignant lesions. Additionally, we employ a pressure mapping kit to create a 3D flexible printing file, providing tactile feedback for accurate diagnosis.

Creating a Haptic 4D Model Along With Machine Learning Analysis by Developing a Non- Invasive Pressure Mapping Method to Screen for Genital Skin Cancer
Early detection of genital skin cancer is hindered by factors such as privacy concerns, social barriers, and discomfort. Traditional biopsy methods, though accurate, can cause pain and infection in the genital region. Our engineering objective is to develop a non-invasive screening method using machine learning. We created a mobile app that processes lesion images through a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN), achieving an 83% accuracy in classifying malignant lesions. Additionally, we employ a pressure mapping kit to create a 3D flexible printing file, providing tactile feedback for accurate diagnosis.

Creating a Haptic 4D Model Along With Machine Learning Analysis by Developing a Non- Invasive Pressure Mapping Method to Screen for Genital Skin Cancer
Early detection of genital skin cancer is hindered by factors such as privacy concerns, social barriers, and discomfort. Traditional biopsy methods, though accurate, can cause pain and infection in the genital region. Our engineering objective is to develop a non-invasive screening method using machine learning. We created a mobile app that processes lesion images through a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN), achieving an 83% accuracy in classifying malignant lesions. Additionally, we employ a pressure mapping kit to create a 3D flexible printing file, providing tactile feedback for accurate diagnosis.
Find your nearest innovation lab
These awards reflect projects that pushed my boundaries, told deeper stories, and caught the attention of people who care about what visuals can say.
Find your nearest innovation lab
These awards reflect projects that pushed my boundaries, told deeper stories, and caught the attention of people who care about what visuals can say.