
Space & Aerospace Tech
Pioneer satellite systems, space robotics, and AI-driven missions to explore the final frontier.

Bathymetric Scanner for Underwater Terrain Survey using
Embedded System and TF Mini LiDAR Sensor
Marine Geology and OceanographyExisting methods for mapping deep-sea terrains are inefficient, expensive, and time-consuming. The current multi-beam echo-sounder technique requires a specialized submarine, making it risky and inaccessible. To address these issues, we have developed a remote LiDAR scanning device that can efficiently and cost-effectively map deep-sea environments. Our solution utilizes a 3D-printed, remotely controlled scanner to build detailed 3D models of seafloor terrains. This innovative approach revolutionizes the field of deep-sea mapping, enabling enhanced understanding of the Earth's environment and improved disaster response capabilities.

Bathymetric Scanner for Underwater Terrain Survey using
Embedded System and TF Mini LiDAR Sensor
Marine Geology and OceanographyExisting methods for mapping deep-sea terrains are inefficient, expensive, and time-consuming. The current multi-beam echo-sounder technique requires a specialized submarine, making it risky and inaccessible. To address these issues, we have developed a remote LiDAR scanning device that can efficiently and cost-effectively map deep-sea environments. Our solution utilizes a 3D-printed, remotely controlled scanner to build detailed 3D models of seafloor terrains. This innovative approach revolutionizes the field of deep-sea mapping, enabling enhanced understanding of the Earth's environment and improved disaster response capabilities.

Bathymetric Scanner for Underwater Terrain Survey using
Embedded System and TF Mini LiDAR Sensor
The research presented here looks into the vibration properties of 3D-printed airless tires, which have the potential to revolutionize tire design and transportation efficiency. Through extensive experimentation and vibration research, three distinct tire constructions were investigated. Because of its good damping and deformation qualities, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) was chosen as the 3D printing material. The experimental arrangement was designed to simulate real-world road conditions, and an MPU6050 sensor captured tire vibrations in three axes. The vibrational properties of the tire structures were revealed using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) analysis, allowing for a comparative assessment of their stability. Structure 1 was found to be the most vibration-stable, followed by Structures 3 and 2.

An Empirical Study of Performance Variations: 3D Printed Toroidal Propeller vs. Traditional Propeller
This empirical study compares the performance variations of 3D-printed toroidal propellers and standard propellers, with a focus on the implications for drone propulsion systems. The project seeks to learn more about thrust efficiency, noise levels, and current consumption. The results show that toroidal propellers, particularly those with three blades, generate more thrust with the same or less current consumption as conventional propellers. Toroidal designs' distinctive blade curvature improves aerodynamics by decreasing turbulence and noise. These discoveries have important implications for improving drone motor efficiency, battery consumption, and environmental sustainability.

An Empirical Study of Performance Variations: 3D Printed Toroidal Propeller vs. Traditional Propeller
This empirical study compares the performance variations of 3D-printed toroidal propellers and standard propellers, with a focus on the implications for drone propulsion systems. The project seeks to learn more about thrust efficiency, noise levels, and current consumption. The results show that toroidal propellers, particularly those with three blades, generate more thrust with the same or less current consumption as conventional propellers. Toroidal designs' distinctive blade curvature improves aerodynamics by decreasing turbulence and noise. These discoveries have important implications for improving drone motor efficiency, battery consumption, and environmental sustainability.

An Empirical Study of Performance Variations: 3D Printed Toroidal Propeller vs. Traditional Propeller
The research presented here looks into the vibration properties of 3D-printed airless tires, which have the potential to revolutionize tire design and transportation efficiency. Through extensive experimentation and vibration research, three distinct tire constructions were investigated. Because of its good damping and deformation qualities, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) was chosen as the 3D printing material. The experimental arrangement was designed to simulate real-world road conditions, and an MPU6050 sensor captured tire vibrations in three axes. The vibrational properties of the tire structures were revealed using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) analysis, allowing for a comparative assessment of their stability. Structure 1 was found to be the most vibration-stable, followed by Structures 3 and 2.
Computational Analysis of Awareness, Usage, and Effectiveness of MOOCS With Special Focus on Acceptance of Design Courses
The internet has revolutionized education, enabling the rise of Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) that provide widespread access to diverse academic content. Platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and EdX offer free and paid online courses, empowering learners with self-paced, flexible, and dynamic educational opportunities. These certifications can significantly boost careers by facilitating easier access to information, tailored learning experiences, and enhanced convenience. As the popularity of MOOCs continues to grow, a robust recommendation system is crucial to help learners navigate the wealth of educational resources available.

Computational Analysis of Awareness, Usage, and Effectiveness of MOOCS With Special Focus on Acceptance of Design Courses
The internet has revolutionized education, enabling the rise of Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) that provide widespread access to diverse academic content. Platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and EdX offer free and paid online courses, empowering learners with self-paced, flexible, and dynamic educational opportunities. These certifications can significantly boost careers by facilitating easier access to information, tailored learning experiences, and enhanced convenience. As the popularity of MOOCs continues to grow, a robust recommendation system is crucial to help learners navigate the wealth of educational resources available.

Computational Analysis of Awareness, Usage, and Effectiveness of MOOCS With Special Focus on Acceptance of Design Courses
The internet has revolutionized education, enabling the rise of Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) that provide widespread access to diverse academic content. Platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and EdX offer free and paid online courses, empowering learners with self-paced, flexible, and dynamic educational opportunities. These certifications can significantly boost careers by facilitating easier access to information, tailored learning experiences, and enhanced convenience. As the popularity of MOOCs continues to grow, a robust recommendation system is crucial to help learners navigate the wealth of educational resources available.
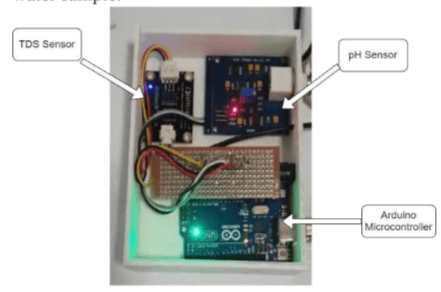
A Novel Approach Towards Calculating The Reusability Coefficient Of Water From Nearby Water Bodies Using Artificial Intelligence
Most water bodies are polluted, but there is limited data on the level of pollution. This project proposes a solution to assess water quality by collecting samples from various sources like sewage, rivers, and farms. The solution has three parts: 1) detecting turbidity using image processing, 2) measuring TDS and pH using an Arduino-based prototype, and 3) determining a quality coefficient through machine learning. All components are integrated into a 3D-printed device. The model achieves an accuracy of 89% in estimating water quality, while the circuit accurately measures TDS and pH. This real-time solution enables the detection of water body quality and potential usage after appropriate treatment

A Novel Approach Towards Calculating The Reusability Coefficient Of Water From Nearby Water Bodies Using Artificial Intelligence
Most water bodies are polluted, but there is limited data on the level of pollution. This project proposes a solution to assess water quality by collecting samples from various sources like sewage, rivers, and farms. The solution has three parts: 1) detecting turbidity using image processing, 2) measuring TDS and pH using an Arduino-based prototype, and 3) determining a quality coefficient through machine learning. All components are integrated into a 3D-printed device. The model achieves an accuracy of 89% in estimating water quality, while the circuit accurately measures TDS and pH. This real-time solution enables the detection of water body quality and potential usage after appropriate treatment

A Novel Approach Towards Calculating The Reusability Coefficient Of Water From Nearby Water Bodies Using Artificial Intelligence
Most water bodies are polluted, but there is limited data on the level of pollution. This project proposes a solution to assess water quality by collecting samples from various sources like sewage, rivers, and farms. The solution has three parts: 1) detecting turbidity using image processing, 2) measuring TDS and pH using an Arduino-based prototype, and 3) determining a quality coefficient through machine learning. All components are integrated into a 3D-printed device. The model achieves an accuracy of 89% in estimating water quality, while the circuit accurately measures TDS and pH. This real-time solution enables the detection of water body quality and potential usage after appropriate treatment

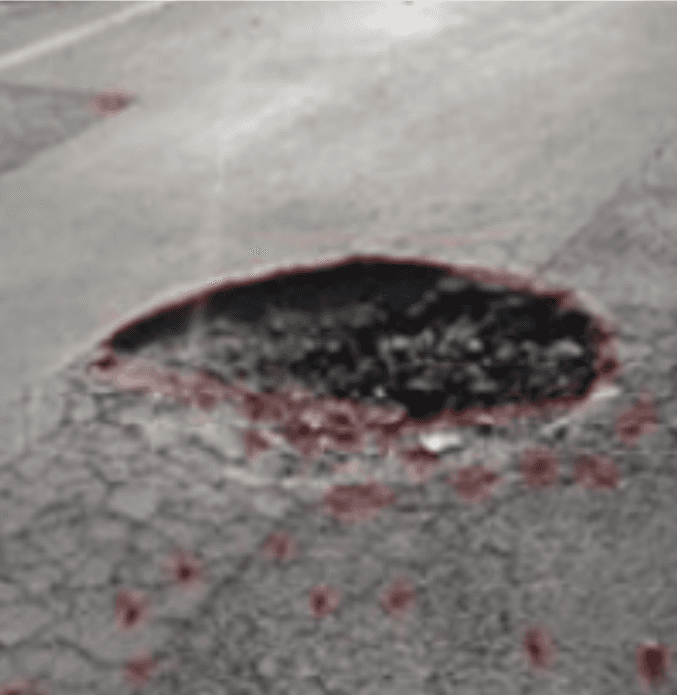
Comparative Analysis of Traffic Classification Algorithms in Deep Learning
Aging roads and poor road-maintenance systems resulted many potholes, whose numbers increase over time. Potholes jeopardize road safety and transportation efficiency. Moreover, they are often a contributing factor to car accidents. To address the problems associated with potholes, the locations and size of potholes must be determined quickly to find the location a data base as to be developed, which requires a specific pothole-detection system that can collect pothole information at low cost and over a wide area. However, pothole repair has long relied on manual detection efforts causing loss of time and money to government. Thus, in this paper, we introduced a pothole-detection system using a commercial “Road sepoy”. The proposed system detects potholes using vision-based tracking system and MATLAB algorithm specifically designed to work with road sepoy camera giving us accurately in real-time environment. Geo-mapping the pothole in google maps helps the exact location.

Comparative Analysis of Traffic Classification Algorithms in Deep Learning
Aging roads and poor road-maintenance systems resulted many potholes, whose numbers increase over time. Potholes jeopardize road safety and transportation efficiency. Moreover, they are often a contributing factor to car accidents. To address the problems associated with potholes, the locations and size of potholes must be determined quickly to find the location a data base as to be developed, which requires a specific pothole-detection system that can collect pothole information at low cost and over a wide area. However, pothole repair has long relied on manual detection efforts causing loss of time and money to government. Thus, in this paper, we introduced a pothole-detection system using a commercial “Road sepoy”. The proposed system detects potholes using vision-based tracking system and MATLAB algorithm specifically designed to work with road sepoy camera giving us accurately in real-time environment. Geo-mapping the pothole in google maps helps the exact location.

Comparative Analysis of Traffic Classification Algorithms in Deep Learning
Aging roads and poor road-maintenance systems resulted many potholes, whose numbers increase over time. Potholes jeopardize road safety and transportation efficiency. Moreover, they are often a contributing factor to car accidents. To address the problems associated with potholes, the locations and size of potholes must be determined quickly to find the location a data base as to be developed, which requires a specific pothole-detection system that can collect pothole information at low cost and over a wide area. However, pothole repair has long relied on manual detection efforts causing loss of time and money to government. Thus, in this paper, we introduced a pothole-detection system using a commercial “Road sepoy”. The proposed system detects potholes using vision-based tracking system and MATLAB algorithm specifically designed to work with road sepoy camera giving us accurately in real-time environment. Geo-mapping the pothole in google maps helps the exact location.

Experiment on a novel approach toward quantifying the toxicity level of the soil around the Yamuna River and checking the impact of polluted water on the soil
The abstract discusses an experiment aimed at quantifying the toxic effect of the polluted Yamuna River on the soil in the Mayur Vihar region of Delhi, India. Soil samples were collected at various distances from the river bank, and the decomposition of cotton pieces placed in these samples was observed over time. Image processing and a convolutional neural network model were applied to calculate the level of decomposition and fertility coefficient, indicating the impact of the river water on soil. The results were validated through chemical laboratory tests. Additionally, holy basil seeds were sown in the soil samples, and their growth patterns were observed to assess soil fertility at different distances from the river bank.

Experiment on a novel approach toward quantifying the toxicity level of the soil around the Yamuna River &
The abstract discusses an experiment aimed at quantifying the toxic effect of the polluted Yamuna River on the soil in the Mayur Vihar region of Delhi, India. Soil samples were collected at various distances from the river bank, and the decomposition of cotton pieces placed in these samples was observed over time. Image processing and a convolutional neural network model were applied to calculate the level of decomposition and fertility coefficient, indicating the impact of the river water on soil. The results were validated through chemical laboratory tests. Additionally, holy basil seeds were sown in the soil samples, and their growth patterns were observed to assess soil fertility at different distances from the river bank.

Experiment on a novel approach toward quantifying the toxicity level of the soil around the Yamuna River and checking the impact of polluted water on the soil
The abstract discusses an experiment aimed at quantifying the toxic effect of the polluted Yamuna River on the soil in the Mayur Vihar region of Delhi, India. Soil samples were collected at various distances from the river bank, and the decomposition of cotton pieces placed in these samples was observed over time. Image processing and a convolutional neural network model were applied to calculate the level of decomposition and fertility coefficient, indicating the impact of the river water on soil. The results were validated through chemical laboratory tests. Additionally, holy basil seeds were sown in the soil samples, and their growth patterns were observed to assess soil fertility at different distances from the river bank.
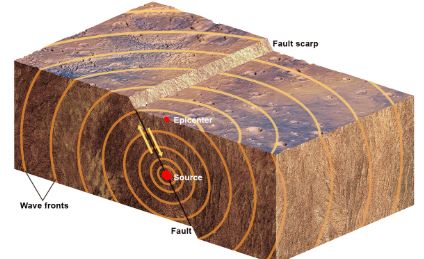
Novel Approach to Analyse Structures to Predict Earthquake Impact in Urban Areas
Recent decades have seen a rise in earthquake risks in urban areas due to urbanization, poor planning, infrastructure issues, and environmental degradation. Urban centers need robust preparedness and emergency plans, including quantifying earthquake effects, especially building losses, correlated with casualties and emergency response. My project aims to predict and assess earthquake impact in urban areas by analyzing building structures, using Google Maps images to calculate dimensions and safe areas. Our algorithm employs image processing and Machine Learning to predict seismic wave effects and determine optimal building distances, reducing risk. With high accuracy and scalability, this model could revolutionize infrastructure planning worldwide.

Novel Approach to Analyse Structures to Predict Earthquake Impact in Urban Areas
Recent decades have seen a rise in earthquake risks in urban areas due to urbanization, poor planning, infrastructure issues, and environmental degradation. Urban centers need robust preparedness and emergency plans, including quantifying earthquake effects, especially building losses, correlated with casualties and emergency response. My project aims to predict and assess earthquake impact in urban areas by analyzing building structures, using Google Maps images to calculate dimensions and safe areas. Our algorithm employs image processing and Machine Learning to predict seismic wave effects and determine optimal building distances, reducing risk. With high accuracy and scalability, this model could revolutionize infrastructure planning worldwide.

Novel Approach to Analyse Structures to Predict Earthquake Impact in Urban Areas
Recent decades have seen a rise in earthquake risks in urban areas due to urbanization, poor planning, infrastructure issues, and environmental degradation. Urban centers need robust preparedness and emergency plans, including quantifying earthquake effects, especially building losses, correlated with casualties and emergency response. My project aims to predict and assess earthquake impact in urban areas by analyzing building structures, using Google Maps images to calculate dimensions and safe areas. Our algorithm employs image processing and Machine Learning to predict seismic wave effects and determine optimal building distances, reducing risk. With high accuracy and scalability, this model could revolutionize infrastructure planning worldwide.
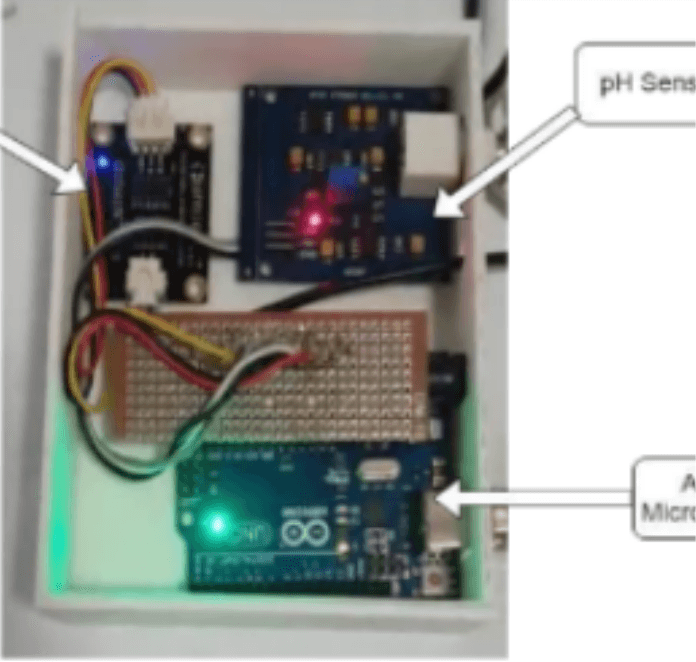
Rapid Approach to Quantify the Industrial Pollution in The Water Bodies Using Machine Learning and Satellite Imaging
Chemical industries often pollute nearby water bodies, affecting water quality and groundwater, which impacts agriculture. There is a need for rapid testing of water from such polluted sources near industries. Our solution tackles this by assessing water quality using satellite images. We collected images of Pune city via the Mapbox API and developed a machine learning model to detect water bodies and assess their quality using image processing. Clean and polluted water bodies are segregated. Polluted bodies are further tested using a sensing device that measures pH and TDS of water samples. The convolutional neural network model achieves over 95% accuracy in water body detection. This solution provides a reliable and rapid method for checking water quality and evaluating the impact of nearby industries on water bodies.

Rapid Approach to Quantify the Industrial Pollution in The Water Bodies Using Machine Learning and Satellite Imaging
Chemical industries often pollute nearby water bodies, affecting water quality and groundwater, which impacts agriculture. There is a need for rapid testing of water from such polluted sources near industries. Our solution tackles this by assessing water quality using satellite images. We collected images of Pune city via the Mapbox API and developed a machine learning model to detect water bodies and assess their quality using image processing. Clean and polluted water bodies are segregated. Polluted bodies are further tested using a sensing device that measures pH and TDS of water samples. The convolutional neural network model achieves over 95% accuracy in water body detection. This solution provides a reliable and rapid method for checking water quality and evaluating the impact of nearby industries on water bodies.

Rapid Approach to Quantify the Industrial Pollution in The Water Bodies Using Machine Learning and Satellite Imaging
Chemical industries often pollute nearby water bodies, affecting water quality and groundwater, which impacts agriculture. There is a need for rapid testing of water from such polluted sources near industries. Our solution tackles this by assessing water quality using satellite images. We collected images of Pune city via the Mapbox API and developed a machine learning model to detect water bodies and assess their quality using image processing. Clean and polluted water bodies are segregated. Polluted bodies are further tested using a sensing device that measures pH and TDS of water samples. The convolutional neural network model achieves over 95% accuracy in water body detection. This solution provides a reliable and rapid method for checking water quality and evaluating the impact of nearby industries on water bodies.

Application of Data Analysis and Soft Computation to Model the Need of Crop Insurance for the Indian Farmers
A very high level of uncertainty is associated with agriculture in the form of natural, social, and human-related actions. Farmers incur heavy losses whenever their farmlands are affected. Crop insurance is the answer to such losses that existed as an institutional response to nature-induced risk. Hence, there is a demand to model the need for crop insurance for Indian Farmers. The first part involves applying exploratory data analysis (EDA) to correlate the factors with the farmers' responses. A correlational analysis is also conducted to study the relationship between different factors. The second part involves the application of three machine learning (ML) algorithms, namely, Logistic Regression (LR), Random Forest (RF), and Gradient Boost classifier (GB) to meet the aims and objectives of the paper.

Application of Data Analysis and Soft Computation to Model the Need of Crop Insurance for the Indian Farmers
A very high level of uncertainty is associated with agriculture in the form of natural, social, and human-related actions. Farmers incur heavy losses whenever their farmlands are affected. Crop insurance is the answer to such losses that existed as an institutional response to nature-induced risk. Hence, there is a demand to model the need for crop insurance for Indian Farmers. The first part involves applying exploratory data analysis (EDA) to correlate the factors with the farmers' responses. A correlational analysis is also conducted to study the relationship between different factors. The second part involves the application of three machine learning (ML) algorithms, namely, Logistic Regression (LR), Random Forest (RF), and Gradient Boost classifier (GB) to meet the aims and objectives of the paper.

Application of Data Analysis and Soft Computation to Model the Need of Crop Insurance for the Indian Farmers
A very high level of uncertainty is associated with agriculture in the form of natural, social, and human-related actions. Farmers incur heavy losses whenever their farmlands are affected. Crop insurance is the answer to such losses that existed as an institutional response to nature-induced risk. Hence, there is a demand to model the need for crop insurance for Indian Farmers. The first part involves applying exploratory data analysis (EDA) to correlate the factors with the farmers' responses. A correlational analysis is also conducted to study the relationship between different factors. The second part involves the application of three machine learning (ML) algorithms, namely, Logistic Regression (LR), Random Forest (RF), and Gradient Boost classifier (GB) to meet the aims and objectives of the paper.
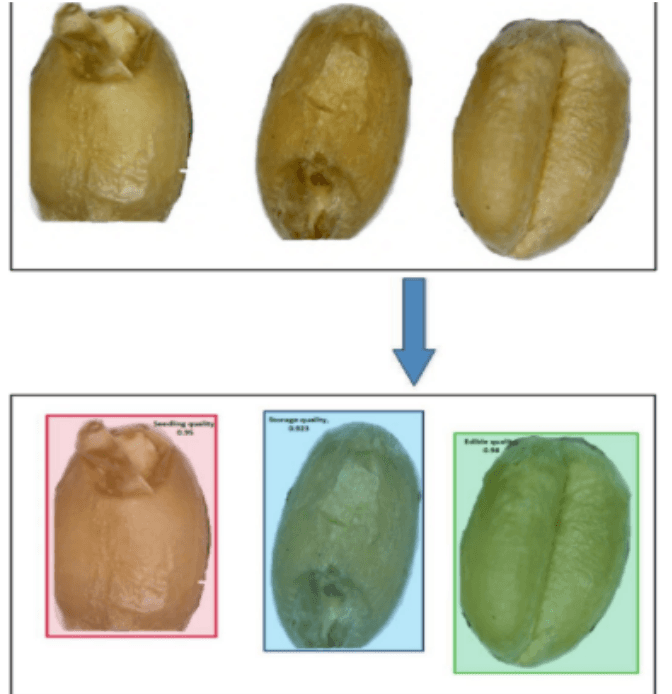
Assessment of Quality of The Wheat Grain Using
Image Processing and Mask R-CNN
The study develops a Mask Regional Convolutional Neural Network (Mask RCNN) model to classify the quality of wheat grains into four categories: storage quality, edible, seeding quality, or rotten. The model is trained on 122 images created from 2,000 grains, using image processing to extract grain texture. The wheat grains are annotated with VGG Image Annotator, and the JSON files are used for training and testing the Mask RCNN model. The trained model achieves low training and validation losses and demonstrates high accuracy in classifying the grain quality when tested on a new image with all four classes.

Assessment of Quality of The Wheat Grain Using
Image Processing and Mask R-CNN
The study develops a Mask Regional Convolutional Neural Network (Mask RCNN) model to classify the quality of wheat grains into four categories: storage quality, edible, seeding quality, or rotten. The model is trained on 122 images created from 2,000 grains, using image processing to extract grain texture. The wheat grains are annotated with VGG Image Annotator, and the JSON files are used for training and testing the Mask RCNN model. The trained model achieves low training and validation losses and demonstrates high accuracy in classifying the grain quality when tested on a new image with all four classes.

Assessment of Quality of The Wheat Grain Using
Image Processing and Mask R-CNN
The study develops a Mask Regional Convolutional Neural Network (Mask RCNN) model to classify the quality of wheat grains into four categories: storage quality, edible, seeding quality, or rotten. The model is trained on 122 images created from 2,000 grains, using image processing to extract grain texture. The wheat grains are annotated with VGG Image Annotator, and the JSON files are used for training and testing the Mask RCNN model. The trained model achieves low training and validation losses and demonstrates high accuracy in classifying the grain quality when tested on a new image with all four classes.

Calculating Maximum Power Generation Capacity of The Roof Space Through Solar Panels Using Image Processing and Satellite Images
The program uses satellite images and image processing techniques with Python libraries like OpenCV and NumPy. It collects satellite images from Google Maps, scales them based on the distance scale in the image, crops the roof area, and detects the usable space. The program then provides the maximum number of panels that can be installed on the roof, along with a blueprint for their location and orientation. The solution aims to address the space constraints of solar panel installation, allowing efficient energy production without dedicating land space for large solar farms, especially in urban areas with limited space.

Calculating Maximum Power Generation Capacity of The Roof Space Through Solar Panels Using Image Processing and Satellite Images
The program uses satellite images and image processing techniques with Python libraries like OpenCV and NumPy. It collects satellite images from Google Maps, scales them based on the distance scale in the image, crops the roof area, and detects the usable space. The program then provides the maximum number of panels that can be installed on the roof, along with a blueprint for their location and orientation. The solution aims to address the space constraints of solar panel installation, allowing efficient energy production without dedicating land space for large solar farms, especially in urban areas with limited space.

Calculating Maximum Power Generation Capacity of The Roof Space Through Solar Panels Using Image Processing and Satellite Images
The program uses satellite images and image processing techniques with Python libraries like OpenCV and NumPy. It collects satellite images from Google Maps, scales them based on the distance scale in the image, crops the roof area, and detects the usable space. The program then provides the maximum number of panels that can be installed on the roof, along with a blueprint for their location and orientation. The solution aims to address the space constraints of solar panel installation, allowing efficient energy production without dedicating land space for large solar farms, especially in urban areas with limited space.

An Artificial Intelligence Integrated Technique for Screening
Neurological Diseases with Sound as a Biomarker
This project aims to develop a machine learning-based system for detecting neurological disorders like Parkinson's disease (PD) and paralysis through voice analysis. Researchers recorded speech samples from patients and healthy individuals, extracting features using Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC). K-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) models were trained on this dataset to classify voices into PD, paralysis, or normal categories. With an overall accuracy rate comparable to human laryngologists (60.1% and 56.1%), this system can assist clinicians in accurately identifying the presence and stage of neurological disorders, enabling appropriate treatment recommendations through therapy, medication, or a combination thereof

An Artificial Intelligence Integrated Technique for Screening
Neurological Diseases with Sound as a Biomarker
This project aims to develop a machine learning-based system for detecting neurological disorders like Parkinson's disease (PD) and paralysis through voice analysis. Researchers recorded speech samples from patients and healthy individuals, extracting features using Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC). K-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) models were trained on this dataset to classify voices into PD, paralysis, or normal categories. With an overall accuracy rate comparable to human laryngologists (60.1% and 56.1%), this system can assist clinicians in accurately identifying the presence and stage of neurological disorders, enabling appropriate treatment recommendations through therapy, medication, or a combination thereof

An Artificial Intelligence Integrated Technique for Screening
Neurological Diseases with Sound as a Biomarker
This project aims to develop a machine learning-based system for detecting neurological disorders like Parkinson's disease (PD) and paralysis through voice analysis. Researchers recorded speech samples from patients and healthy individuals, extracting features using Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC). K-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) models were trained on this dataset to classify voices into PD, paralysis, or normal categories. With an overall accuracy rate comparable to human laryngologists (60.1% and 56.1%), this system can assist clinicians in accurately identifying the presence and stage of neurological disorders, enabling appropriate treatment recommendations through therapy, medication, or a combination thereof
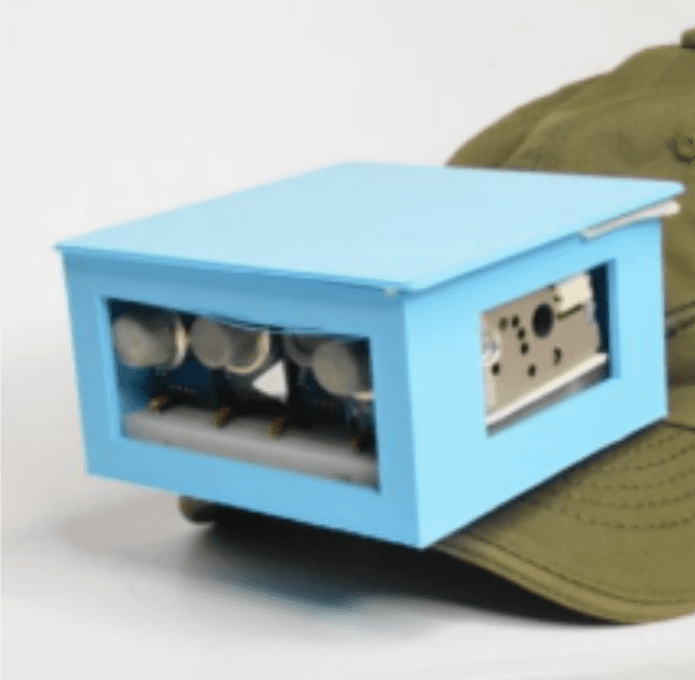

Environmental Technology or Environmental Safety
Sewage disposal cleanup is a hazardous job, exposing workers to harmful gases, infections, and health risks like musculoskeletal disorders and respiratory problems. SEWER GUARD is a project aimed at developing an information and communication ecosystem to monitor and alert workers about dangerous gas levels in sewers. It uses MQ series sensors to measure gas levels and sends alerts if they exceed safe thresholds. The system correlates gas intensity, depth, and exposure time, enabling workers to evacuate before conditions become life-threatening. An Android app and cloud storage are integrated for monitoring and data storage. Authorities can also be notified via SMS if sewage overflow is likely. SEWER GUARD aims to improve the safety and working conditions of sanitary workers engaged in sewer cleanup operations.

Environmental Technology or Environmental Safety
Sewage disposal cleanup is a hazardous job, exposing workers to harmful gases, infections, and health risks like musculoskeletal disorders and respiratory problems. SEWER GUARD is a project aimed at developing an information and communication ecosystem to monitor and alert workers about dangerous gas levels in sewers. It uses MQ series sensors to measure gas levels and sends alerts if they exceed safe thresholds. The system correlates gas intensity, depth, and exposure time, enabling workers to evacuate before conditions become life-threatening. An Android app and cloud storage are integrated for monitoring and data storage. Authorities can also be notified via SMS if sewage overflow is likely. SEWER GUARD aims to improve the safety and working conditions of sanitary workers engaged in sewer cleanup operations.

Environmental Technology or Environmental Safety
The research presented here looks into the vibration properties of 3D-printed airless tires, which have the potential to revolutionize tire design and transportation efficiency. Through extensive experimentation and vibration research, three distinct tire constructions were investigated. Because of its good damping and deformation qualities, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) was chosen as the 3D printing material. The experimental arrangement was designed to simulate real-world road conditions, and an MPU6050 sensor captured tire vibrations in three axes. The vibrational properties of the tire structures were revealed using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) analysis, allowing for a comparative assessment of their stability. Structure 1 was found to be the most vibration-stable, followed by Structures 3 and 2.
Find your nearest innovation lab
These awards reflect projects that pushed my boundaries, told deeper stories, and caught the attention of people who care about what visuals can say.
Find your nearest innovation lab
These awards reflect projects that pushed my boundaries, told deeper stories, and caught the attention of people who care about what visuals can say.