
Sustainable Tech & Environment
Design breakthrough technologies to combat climate change, cut pollution, and power the planet with renewables.
Sustainable Tech & Environment
Design breakthrough technologies to combat climate change, cut pollution, and power the planet with renewables.

Sustainable Tech & Environment
Design breakthrough technologies to combat climate change, cut pollution, and power the planet with renewables.
Sustainable Tech & Environment
Design breakthrough technologies to combat climate change, cut pollution, and power the planet with renewables.
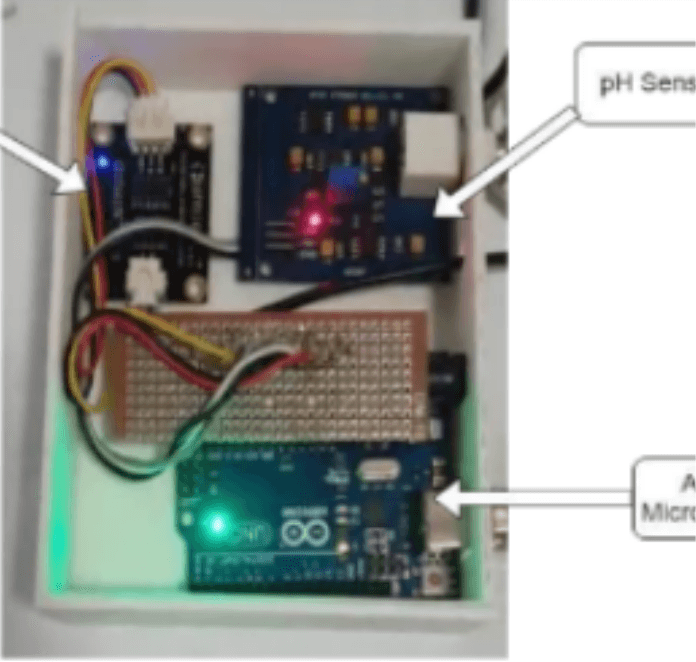
Rapid Approach to Quantify the Industrial Pollution in The Water Bodies Using Machine Learning and Satellite Imaging
Chemical industries often pollute nearby water bodies, affecting water quality and groundwater, which impacts agriculture. There is a need for rapid testing of water from such polluted sources near industries. Our solution tackles this by assessing water quality using satellite images. We collected images of Pune city via the Mapbox API and developed a machine learning model to detect water bodies and assess their quality using image processing. Clean and polluted water bodies are segregated. Polluted bodies are further tested using a sensing device that measures pH and TDS of water samples. The convolutional neural network model achieves over 95% accuracy in water body detection. This solution provides a reliable and rapid method for checking water quality and evaluating the impact of nearby industries on water bodies.

Rapid Approach to Quantify the Industrial Pollution in The Water Bodies Using Machine Learning and Satellite Imaging
Chemical industries often pollute nearby water bodies, affecting water quality and groundwater, which impacts agriculture. There is a need for rapid testing of water from such polluted sources near industries. Our solution tackles this by assessing water quality using satellite images. We collected images of Pune city via the Mapbox API and developed a machine learning model to detect water bodies and assess their quality using image processing. Clean and polluted water bodies are segregated. Polluted bodies are further tested using a sensing device that measures pH and TDS of water samples. The convolutional neural network model achieves over 95% accuracy in water body detection. This solution provides a reliable and rapid method for checking water quality and evaluating the impact of nearby industries on water bodies.

Rapid Approach to Quantify the Industrial Pollution in The Water Bodies Using Machine Learning and Satellite Imaging
Chemical industries often pollute nearby water bodies, affecting water quality and groundwater, which impacts agriculture. There is a need for rapid testing of water from such polluted sources near industries. Our solution tackles this by assessing water quality using satellite images. We collected images of Pune city via the Mapbox API and developed a machine learning model to detect water bodies and assess their quality using image processing. Clean and polluted water bodies are segregated. Polluted bodies are further tested using a sensing device that measures pH and TDS of water samples. The convolutional neural network model achieves over 95% accuracy in water body detection. This solution provides a reliable and rapid method for checking water quality and evaluating the impact of nearby industries on water bodies.
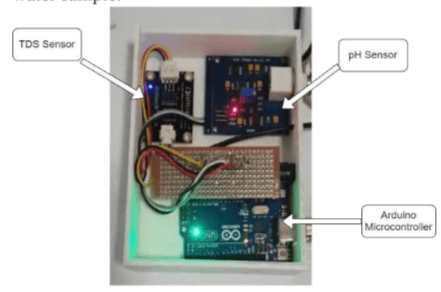
A Novel Approach Towards Calculating The Reusability Coefficient Of Water From Nearby Water Bodies Using Artificial Intelligence
Most water bodies are polluted, but there is limited data on the level of pollution. This project proposes a solution to assess water quality by collecting samples from various sources like sewage, rivers, and farms. The solution has three parts: 1) detecting turbidity using image processing, 2) measuring TDS and pH using an Arduino-based prototype, and 3) determining a quality coefficient through machine learning. All components are integrated into a 3D-printed device. The model achieves an accuracy of 89% in estimating water quality, while the circuit accurately measures TDS and pH. This real-time solution enables the detection of water body quality and potential usage after appropriate treatment

A Novel Approach Towards Calculating The Reusability Coefficient Of Water From Nearby Water Bodies Using Artificial Intelligence
Most water bodies are polluted, but there is limited data on the level of pollution. This project proposes a solution to assess water quality by collecting samples from various sources like sewage, rivers, and farms. The solution has three parts: 1) detecting turbidity using image processing, 2) measuring TDS and pH using an Arduino-based prototype, and 3) determining a quality coefficient through machine learning. All components are integrated into a 3D-printed device. The model achieves an accuracy of 89% in estimating water quality, while the circuit accurately measures TDS and pH. This real-time solution enables the detection of water body quality and potential usage after appropriate treatment

A Novel Approach Towards Calculating The Reusability Coefficient Of Water From Nearby Water Bodies Using Artificial Intelligence
Most water bodies are polluted, but there is limited data on the level of pollution. This project proposes a solution to assess water quality by collecting samples from various sources like sewage, rivers, and farms. The solution has three parts: 1) detecting turbidity using image processing, 2) measuring TDS and pH using an Arduino-based prototype, and 3) determining a quality coefficient through machine learning. All components are integrated into a 3D-printed device. The model achieves an accuracy of 89% in estimating water quality, while the circuit accurately measures TDS and pH. This real-time solution enables the detection of water body quality and potential usage after appropriate treatment

Calculating Maximum Power Generation Capacity of The Roof Space Through Solar Panels Using Image Processing and Satellite Images
The program uses satellite images and image processing techniques with Python libraries like OpenCV and NumPy. It collects satellite images from Google Maps, scales them based on the distance scale in the image, crops the roof area, and detects the usable space. The program then provides the maximum number of panels that can be installed on the roof, along with a blueprint for their location and orientation. The solution aims to address the space constraints of solar panel installation, allowing efficient energy production without dedicating land space for large solar farms, especially in urban areas with limited space.

Calculating Maximum Power Generation Capacity of The Roof Space Through Solar Panels Using Image Processing and Satellite Images
The program uses satellite images and image processing techniques with Python libraries like OpenCV and NumPy. It collects satellite images from Google Maps, scales them based on the distance scale in the image, crops the roof area, and detects the usable space. The program then provides the maximum number of panels that can be installed on the roof, along with a blueprint for their location and orientation. The solution aims to address the space constraints of solar panel installation, allowing efficient energy production without dedicating land space for large solar farms, especially in urban areas with limited space.

Calculating Maximum Power Generation Capacity of The Roof Space Through Solar Panels Using Image Processing and Satellite Images
The program uses satellite images and image processing techniques with Python libraries like OpenCV and NumPy. It collects satellite images from Google Maps, scales them based on the distance scale in the image, crops the roof area, and detects the usable space. The program then provides the maximum number of panels that can be installed on the roof, along with a blueprint for their location and orientation. The solution aims to address the space constraints of solar panel installation, allowing efficient energy production without dedicating land space for large solar farms, especially in urban areas with limited space.
Vacuum Tube-Based Train Waste Collection and Segregation Technique
Proper waste management is critical to ensure a clean environment and public health, and the Indian railways face significant challenges in this area due to inadequate infrastructure, low awareness among commuters, and insufficient recycling facilities. This research paper proposes a solution to these challenges by utilizing vacuum tubes installed along the compartments of each coach and an IoT-based monitoring system to track waste levels. The proposed solution includes the collection, segregation, and storage of waste in designated areas, transportation to processing facilities, and processing in compliance with local regulations while also monitoring and reporting waste management practices. The study evaluates the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed solution, considering its environmental impact and potential benefits for the economy and society. The research findings provide valuable insights into sustainable train waste management and contribute to the long- term development of the railway industry.

Vacuum Tube-Based Train Waste Collection and Segregation Technique
Proper waste management is critical to ensure a clean environment and public health, and the Indian railways face significant challenges in this area due to inadequate infrastructure, low awareness among commuters, and insufficient recycling facilities. This research paper proposes a solution to these challenges by utilizing vacuum tubes installed along the compartments of each coach and an IoT-based monitoring system to track waste levels. The proposed solution includes the collection, segregation, and storage of waste in designated areas, transportation to processing facilities, and processing in compliance with local regulations while also monitoring and reporting waste management practices. The study evaluates the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed solution, considering its environmental impact and potential benefits for the economy and society. The research findings provide valuable insights into sustainable train waste management and contribute to the long- term development of the railway industry.

Vacuum Tube-Based Train Waste Collection and Segregation Technique
Proper waste management is critical to ensure a clean environment and public health, and the Indian railways face significant challenges in this area due to inadequate infrastructure, low awareness among commuters, and insufficient recycling facilities. This research paper proposes a solution to these challenges by utilizing vacuum tubes installed along the compartments of each coach and an IoT-based monitoring system to track waste levels. The proposed solution includes the collection, segregation, and storage of waste in designated areas, transportation to processing facilities, and processing in compliance with local regulations while also monitoring and reporting waste management practices. The study evaluates the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed solution, considering its environmental impact and potential benefits for the economy and society. The research findings provide valuable insights into sustainable train waste management and contribute to the long- term development of the railway industry.
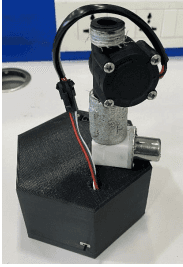
Automatic Water Conservation System
IoT-enabled flow sensor work synergistically with the variable orifice, orifice sensor monitors real-time flow rates, expedite the orifice aperture's adjustment, and optimizes water usage this mortar is attached to the orifice to maintain the flow rate of water. In addition, this sensor provides granular data collection, and continuous monitoring and is essential for subsequent data analysis. Flow sensor data is uploaded to the cloud with a time stamp. The designed prototype was installed in both public washrooms and home-use situations to take measurements of washing hands, vegetables, etc., and determine the most appropriate flow rates for specific household tasks. This prototype’s data was evaluated based on the flow control accuracy, data transmission reliability, efficiency in conservation, and waste reductions. During the present study, data from daily household activities to evaluate the efficiency of the variable orifice system in conjunction with two different modes: Mode1 and Mode 2.

Automatic Water Conservation System
IoT-enabled flow sensor work synergistically with the variable orifice, orifice sensor monitors real-time flow rates, expedite the orifice aperture's adjustment, and optimizes water usage this mortar is attached to the orifice to maintain the flow rate of water. In addition, this sensor provides granular data collection, and continuous monitoring and is essential for subsequent data analysis. Flow sensor data is uploaded to the cloud with a time stamp. The designed prototype was installed in both public washrooms and home-use situations to take measurements of washing hands, vegetables, etc., and determine the most appropriate flow rates for specific household tasks. This prototype’s data was evaluated based on the flow control accuracy, data transmission reliability, efficiency in conservation, and waste reductions. During the present study, data from daily household activities to evaluate the efficiency of the variable orifice system in conjunction with two different modes: Mode1 and Mode 2.

Automatic Water Conservation System
IoT-enabled flow sensor work synergistically with the variable orifice, orifice sensor monitors real-time flow rates, expedite the orifice aperture's adjustment, and optimizes water usage this mortar is attached to the orifice to maintain the flow rate of water. In addition, this sensor provides granular data collection, and continuous monitoring and is essential for subsequent data analysis. Flow sensor data is uploaded to the cloud with a time stamp. The designed prototype was installed in both public washrooms and home-use situations to take measurements of washing hands, vegetables, etc., and determine the most appropriate flow rates for specific household tasks. This prototype’s data was evaluated based on the flow control accuracy, data transmission reliability, efficiency in conservation, and waste reductions. During the present study, data from daily household activities to evaluate the efficiency of the variable orifice system in conjunction with two different modes: Mode1 and Mode 2.

Experiment on a novel approach toward quantifying the toxicity level of the soil around the Yamuna River and checking the impact of polluted water on the soil
The abstract discusses an experiment aimed at quantifying the toxic effect of the polluted Yamuna River on the soil in the Mayur Vihar region of Delhi, India. Soil samples were collected at various distances from the river bank, and the decomposition of cotton pieces placed in these samples was observed over time. Image processing and a convolutional neural network model were applied to calculate the level of decomposition and fertility coefficient, indicating the impact of the river water on soil. The results were validated through chemical laboratory tests. Additionally, holy basil seeds were sown in the soil samples, and their growth patterns were observed to assess soil fertility at different distances from the river bank.

Experiment on a novel approach toward quantifying the toxicity level of the soil around the Yamuna River and checking the impact of polluted water on the soil
The abstract discusses an experiment aimed at quantifying the toxic effect of the polluted Yamuna River on the soil in the Mayur Vihar region of Delhi, India. Soil samples were collected at various distances from the river bank, and the decomposition of cotton pieces placed in these samples was observed over time. Image processing and a convolutional neural network model were applied to calculate the level of decomposition and fertility coefficient, indicating the impact of the river water on soil. The results were validated through chemical laboratory tests. Additionally, holy basil seeds were sown in the soil samples, and their growth patterns were observed to assess soil fertility at different distances from the river bank.

Experiment on a novel approach toward quantifying the toxicity level of the soil around the Yamuna River and checking the impact of polluted water on the soil
The abstract discusses an experiment aimed at quantifying the toxic effect of the polluted Yamuna River on the soil in the Mayur Vihar region of Delhi, India. Soil samples were collected at various distances from the river bank, and the decomposition of cotton pieces placed in these samples was observed over time. Image processing and a convolutional neural network model were applied to calculate the level of decomposition and fertility coefficient, indicating the impact of the river water on soil. The results were validated through chemical laboratory tests. Additionally, holy basil seeds were sown in the soil samples, and their growth patterns were observed to assess soil fertility at different distances from the river bank.
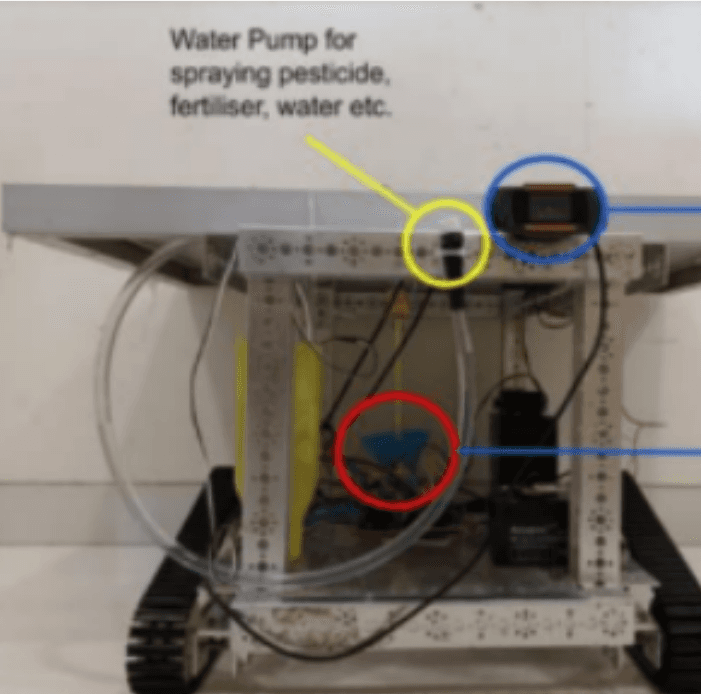
Smart Robotic Pythomedic and Pesticide Sprayer using
Image Processing and machine learning
Plant diseases pose a significant global and Indian agricultural challenge, resulting in crop yield reduction and financial losses for farmers. While existing solutions like smart disease detection using machine learning offer promise, they often present cost or implementation barriers. Our solution introduces a user-friendly Smart Spraying robot equipped with a front camera and machine learning algorithm to identify and address plant diseases efficiently. Tested with over 3000 images across three vegetable plants, the model demonstrates 100% accuracy in detecting specific leaf diseases. However, its applicability is currently limited to these plants. Future iterations can expand its scope to encompass a broader range of crops.

Smart Robotic Pythomedic and Pesticide Sprayer using
Image Processing and machine learning
Plant diseases pose a significant global and Indian agricultural challenge, resulting in crop yield reduction and financial losses for farmers. While existing solutions like smart disease detection using machine learning offer promise, they often present cost or implementation barriers. Our solution introduces a user-friendly Smart Spraying robot equipped with a front camera and machine learning algorithm to identify and address plant diseases efficiently. Tested with over 3000 images across three vegetable plants, the model demonstrates 100% accuracy in detecting specific leaf diseases. However, its applicability is currently limited to these plants. Future iterations can expand its scope to encompass a broader range of crops.

Smart Robotic Pythomedic and Pesticide Sprayer using
Image Processing and machine learning
Plant diseases pose a significant global and Indian agricultural challenge, resulting in crop yield reduction and financial losses for farmers. While existing solutions like smart disease detection using machine learning offer promise, they often present cost or implementation barriers. Our solution introduces a user-friendly Smart Spraying robot equipped with a front camera and machine learning algorithm to identify and address plant diseases efficiently. Tested with over 3000 images across three vegetable plants, the model demonstrates 100% accuracy in detecting specific leaf diseases. However, its applicability is currently limited to these plants. Future iterations can expand its scope to encompass a broader range of crops.
Smart Load Carriers Through IoT Integration: Revolutionizing Aid for the Downtrodden
Load carriers, often underappreciated in logistics, playa crucial role in efficient goods transportation. This project, “Smart Load Carrier,” revolutionizes load transportation by addressing health issues associated with manual handling. Combining a metal base, image processing, and an L298 motor driver, this autonomous carrier navigates efficiently, following human operators and detecting QR codes. Its impact extends to health, economics, and productivity by significantly reducing physical strain, minimizing accidents, and enhancing operational efficiency. The ongoing enhancements focus on increased load capacity and advanced autonomy, positioning the Smart Load Carrier as a transformative solution for diverse load transportation needs. This proposal introduces the implementation of the Smart Load Carrier, a groundbreaking solution aimed at simplifying the handling and transportation of heavy loads. By integrating computer vision and electronics, this project seeks to enhance the overall efficiency of load transportation.

Smart Load Carriers Through IoT Integration: Revolutionizing Aid for the Downtrodden
Load carriers, often underappreciated in logistics, playa crucial role in efficient goods transportation. This project, “Smart Load Carrier,” revolutionizes load transportation by addressing health issues associated with manual handling. Combining a metal base, image processing, and an L298 motor driver, this autonomous carrier navigates efficiently, following human operators and detecting QR codes. Its impact extends to health, economics, and productivity by significantly reducing physical strain, minimizing accidents, and enhancing operational efficiency. The ongoing enhancements focus on increased load capacity and advanced autonomy, positioning the Smart Load Carrier as a transformative solution for diverse load transportation needs. This proposal introduces the implementation of the Smart Load Carrier, a groundbreaking solution aimed at simplifying the handling and transportation of heavy loads. By integrating computer vision and electronics, this project seeks to enhance the overall efficiency of load transportation.

Smart Load Carriers Through IoT Integration: Revolutionizing Aid for the Downtrodden
Load carriers, often underappreciated in logistics, playa crucial role in efficient goods transportation. This project, “Smart Load Carrier,” revolutionizes load transportation by addressing health issues associated with manual handling. Combining a metal base, image processing, and an L298 motor driver, this autonomous carrier navigates efficiently, following human operators and detecting QR codes. Its impact extends to health, economics, and productivity by significantly reducing physical strain, minimizing accidents, and enhancing operational efficiency. The ongoing enhancements focus on increased load capacity and advanced autonomy, positioning the Smart Load Carrier as a transformative solution for diverse load transportation needs. This proposal introduces the implementation of the Smart Load Carrier, a groundbreaking solution aimed at simplifying the handling and transportation of heavy loads. By integrating computer vision and electronics, this project seeks to enhance the overall efficiency of load transportation.
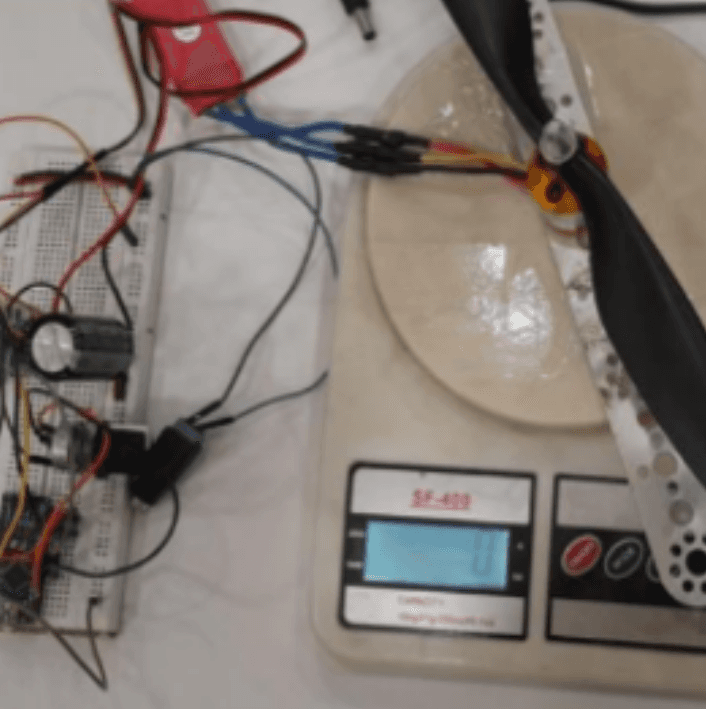
An Empirical Study of Performance Variations: 3D Printed Toroidal Propeller vs. Traditional Propeller
This empirical study compares the performance variations of 3D-printed toroidal propellers and standard propellers, with a focus on the implications for drone propulsion systems. The project seeks to learn more about thrust efficiency, noise levels, and current consumption. The results show that toroidal propellers, particularly those with three blades, generate more thrust with the same or less current consumption as conventional propellers. Toroidal designs' distinctive blade curvature improves aerodynamics by decreasing turbulence and noise. These discoveries have important implications for improving drone motor efficiency, battery consumption, and environmental sustainability.

An Empirical Study of Performance Variations: 3D Printed Toroidal Propeller vs. Traditional Propeller
This empirical study compares the performance variations of 3D-printed toroidal propellers and standard propellers, with a focus on the implications for drone propulsion systems. The project seeks to learn more about thrust efficiency, noise levels, and current consumption. The results show that toroidal propellers, particularly those with three blades, generate more thrust with the same or less current consumption as conventional propellers. Toroidal designs' distinctive blade curvature improves aerodynamics by decreasing turbulence and noise. These discoveries have important implications for improving drone motor efficiency, battery consumption, and environmental sustainability.

An Empirical Study of Performance Variations: 3D Printed Toroidal Propeller vs. Traditional Propeller
This empirical study compares the performance variations of 3D-printed toroidal propellers and standard propellers, with a focus on the implications for drone propulsion systems. The project seeks to learn more about thrust efficiency, noise levels, and current consumption. The results show that toroidal propellers, particularly those with three blades, generate more thrust with the same or less current consumption as conventional propellers. Toroidal designs' distinctive blade curvature improves aerodynamics by decreasing turbulence and noise. These discoveries have important implications for improving drone motor efficiency, battery consumption, and environmental sustainability.
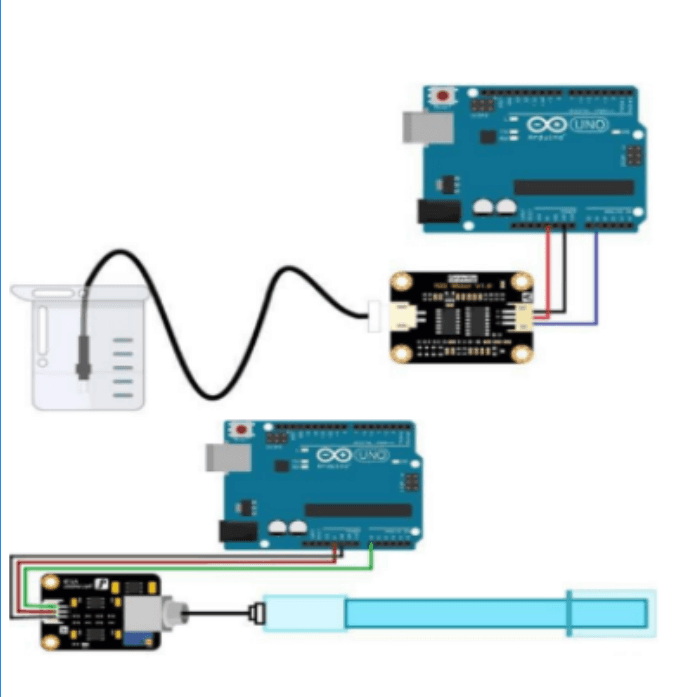
A Novel Approach Towards Calculating The Reusability Coefficient Of Water From Nearby Water Bodies Using Artificial Intelligence
Most water bodies are polluted, but there is limited data on the level of pollution. This project proposes a solution to assess water quality by collecting samples from various sources like sewage, rivers, and farms. The solution has three parts: 1) detecting turbidity using image processing, 2) measuring TDS and pH using an Arduino-based prototype, and 3) determining a quality coefficient through machine learning. All components are integrated into a 3D-printed device. The model achieves an accuracy of 89% in estimating water quality, while the circuit accurately measures TDS and pH. This real-time solution enables the detection of water body quality and potential usage after appropriate treatment

A Novel Approach Towards Calculating The Reusability Coefficient Of Water From Nearby Water Bodies Using Artificial Intelligence
Most water bodies are polluted, but there is limited data on the level of pollution. This project proposes a solution to assess water quality by collecting samples from various sources like sewage, rivers, and farms. The solution has three parts: 1) detecting turbidity using image processing, 2) measuring TDS and pH using an Arduino-based prototype, and 3) determining a quality coefficient through machine learning. All components are integrated into a 3D-printed device. The model achieves an accuracy of 89% in estimating water quality, while the circuit accurately measures TDS and pH. This real-time solution enables the detection of water body quality and potential usage after appropriate treatment

A Novel Approach Towards Calculating The Reusability Coefficient Of Water From Nearby Water Bodies Using Artificial Intelligence
Most water bodies are polluted, but there is limited data on the level of pollution. This project proposes a solution to assess water quality by collecting samples from various sources like sewage, rivers, and farms. The solution has three parts: 1) detecting turbidity using image processing, 2) measuring TDS and pH using an Arduino-based prototype, and 3) determining a quality coefficient through machine learning. All components are integrated into a 3D-printed device. The model achieves an accuracy of 89% in estimating water quality, while the circuit accurately measures TDS and pH. This real-time solution enables the detection of water body quality and potential usage after appropriate treatment
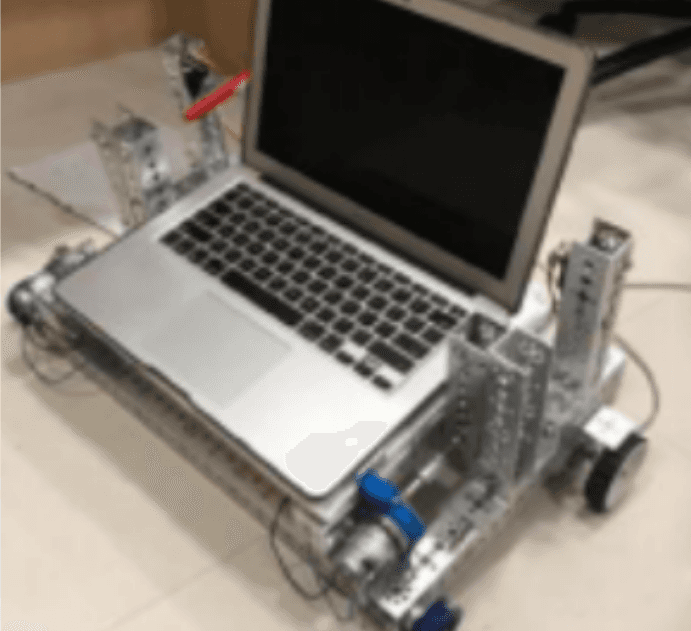

Smart Adaptive Machine Learning Based Laptop Stand (Workbit)
White-collar workers and delivery drivers face different health risks due to their work environments. Office workers often experience issues like poor posture and muscle strain from prolonged sitting at computer terminals. To address this, we propose an intelligent stand called "WorkBit" designed to promote work health by monitoring daily habits and providing preventive measures. The stand, mounted on wheels, adjusts its position based on the user's distance from the laptop, promoting better posture and reducing strain on the eyes and neck.

Smart Adaptive Machine Learning Based Laptop Stand (Workbit)
White-collar workers and delivery drivers face different health risks due to their work environments. Office workers often experience issues like poor posture and muscle strain from prolonged sitting at computer terminals. To address this, we propose an intelligent stand called "WorkBit" designed to promote work health by monitoring daily habits and providing preventive measures. The stand, mounted on wheels, adjusts its position based on the user's distance from the laptop, promoting better posture and reducing strain on the eyes and neck.

Smart Adaptive Machine Learning Based Laptop Stand (Workbit)
White-collar workers and delivery drivers face different health risks due to their work environments. Office workers often experience issues like poor posture and muscle strain from prolonged sitting at computer terminals. To address this, we propose an intelligent stand called "WorkBit" designed to promote work health by monitoring daily habits and providing preventive measures. The stand, mounted on wheels, adjusts its position based on the user's distance from the laptop, promoting better posture and reducing strain on the eyes and neck.
Examination of NPK Values and Their Effects on Soil
Soil health and soil quality are defined as the ability of the soil to perform as an essential living system under the restrictions of land use. This activity maintains the biological productivity of the soil, which benefits both the environment and human health. Soil quality is linked to soil function, whereas soil health portrays the soil as a finite, non-renewable, and dynamic living resource. The notion of soil health, which encompasses interactions between plant inputs and soil in creating a healthy environment, is discussed in this paper.

Examination of NPK Values and Their Effects on Soil
Soil health and soil quality are defined as the ability of the soil to perform as an essential living system under the restrictions of land use. This activity maintains the biological productivity of the soil, which benefits both the environment and human health. Soil quality is linked to soil function, whereas soil health portrays the soil as a finite, non-renewable, and dynamic living resource. The notion of soil health, which encompasses interactions between plant inputs and soil in creating a healthy environment, is discussed in this paper.

Examination of NPK Values and Their Effects on Soil
Soil health and soil quality are defined as the ability of the soil to perform as an essential living system under the restrictions of land use. This activity maintains the biological productivity of the soil, which benefits both the environment and human health. Soil quality is linked to soil function, whereas soil health portrays the soil as a finite, non-renewable, and dynamic living resource. The notion of soil health, which encompasses interactions between plant inputs and soil in creating a healthy environment, is discussed in this paper.
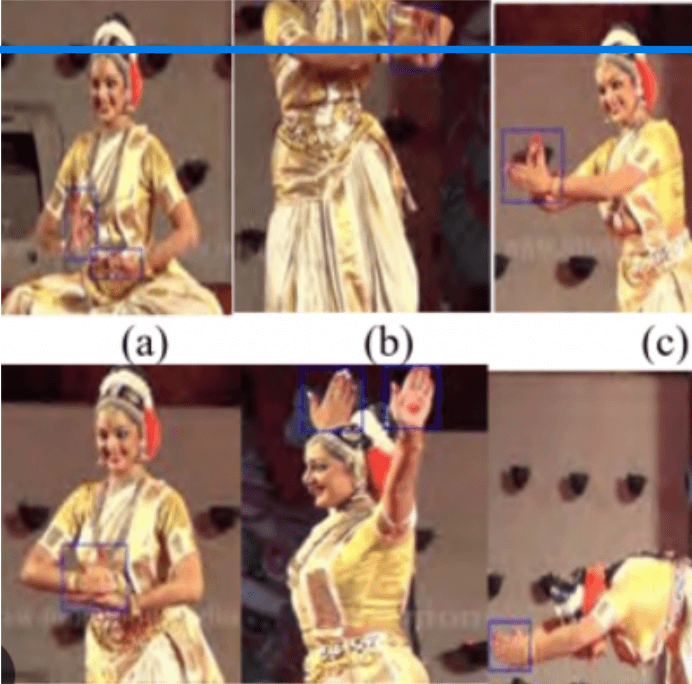

Application of Recurrent Neural Network Application in Identifying the Classical Indian Dance Steps from the Video Inputs
In Indian classical dance, posture is crucial because it enables the dancer to retain equilibrium and control while doing the complicated footwork and hand movements. In classical dance, strong posture enables the dancer to communicate the grace and elegance that are distinctive to this age-old classical dance style. The current work aims to create an intelligent system that can recognize various Indian classical dance positions. Bharatnatyam is taken into account for the study because of how difficult it is to perfect the various postures because of how intricate and similar the gestures are. To differentiate between the various moves, experienced supervision is required. Due to their close resemblance and the significant influence of the rhythmic time cycle on the three, three dance postures—Urdhva Hasta Chakra, Urdhva Kona Suchita, and Ardhaalingan—have been discovered.

Application of Recurrent Neural Network Application in Identifying the Classical Indian Dance Steps from the Video Inputs
In Indian classical dance, posture is crucial because it enables the dancer to retain equilibrium and control while doing the complicated footwork and hand movements. In classical dance, strong posture enables the dancer to communicate the grace and elegance that are distinctive to this age-old classical dance style. The current work aims to create an intelligent system that can recognize various Indian classical dance positions. Bharatnatyam is taken into account for the study because of how difficult it is to perfect the various postures because of how intricate and similar the gestures are. To differentiate between the various moves, experienced supervision is required. Due to their close resemblance and the significant influence of the rhythmic time cycle on the three, three dance postures—Urdhva Hasta Chakra, Urdhva Kona Suchita, and Ardhaalingan—have been discovered.

Application of Recurrent Neural Network Application in Identifying the Classical Indian Dance Steps from the Video Inputs
In Indian classical dance, posture is crucial because it enables the dancer to retain equilibrium and control while doing the complicated footwork and hand movements. In classical dance, strong posture enables the dancer to communicate the grace and elegance that are distinctive to this age-old classical dance style. The current work aims to create an intelligent system that can recognize various Indian classical dance positions. Bharatnatyam is taken into account for the study because of how difficult it is to perfect the various postures because of how intricate and similar the gestures are. To differentiate between the various moves, experienced supervision is required. Due to their close resemblance and the significant influence of the rhythmic time cycle on the three, three dance postures—Urdhva Hasta Chakra, Urdhva Kona Suchita, and Ardhaalingan—have been discovered.
A Machine Learning Approach To Identify The Best Cryptocurrency For Investment
The abstract discusses the development of models to forecast cryptocurrency (CTC) prices and determine the most stable, high-return, and low-risk CTCs for investment purposes. Due to the lack of oversight and uncertainty surrounding cryptocurrencies, investors are often hesitant to invest in them. To address this, Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and Support Vector Machine (SVM) models are developed and trained using time-series data scraped from data.cryptocompare.com. The top five CTCs with the highest average market capitalization are considered for analysis. The ANN model achieved training and testing accuracies of 0.9876 and 0.9198, respectively, while the SVM model achieved 0.796 and 0.7981 for training and testing accuracies. Based on the data from August 1, 2022, the ANN and SVM models predicted Ethereum (ETH) and Dogecoin (DGC) as the best investment options for CTCs.

A Machine Learning Approach To Identify The Best Cryptocurrency For Investment
The abstract discusses the development of models to forecast cryptocurrency (CTC) prices and determine the most stable, high-return, and low-risk CTCs for investment purposes. Due to the lack of oversight and uncertainty surrounding cryptocurrencies, investors are often hesitant to invest in them. To address this, Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and Support Vector Machine (SVM) models are developed and trained using time-series data scraped from data.cryptocompare.com. The top five CTCs with the highest average market capitalization are considered for analysis. The ANN model achieved training and testing accuracies of 0.9876 and 0.9198, respectively, while the SVM model achieved 0.796 and 0.7981 for training and testing accuracies. Based on the data from August 1, 2022, the ANN and SVM models predicted Ethereum (ETH) and Dogecoin (DGC) as the best investment options for CTCs.

A Machine Learning Approach To Identify The Best Cryptocurrency For Investment
The abstract discusses the development of models to forecast cryptocurrency (CTC) prices and determine the most stable, high-return, and low-risk CTCs for investment purposes. Due to the lack of oversight and uncertainty surrounding cryptocurrencies, investors are often hesitant to invest in them. To address this, Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and Support Vector Machine (SVM) models are developed and trained using time-series data scraped from data.cryptocompare.com. The top five CTCs with the highest average market capitalization are considered for analysis. The ANN model achieved training and testing accuracies of 0.9876 and 0.9198, respectively, while the SVM model achieved 0.796 and 0.7981 for training and testing accuracies. Based on the data from August 1, 2022, the ANN and SVM models predicted Ethereum (ETH) and Dogecoin (DGC) as the best investment options for CTCs.
Find your nearest innovation lab
These awards reflect projects that pushed my boundaries, told deeper stories, and caught the attention of people who care about what visuals can say.
Find your nearest innovation lab
These awards reflect projects that pushed my boundaries, told deeper stories, and caught the attention of people who care about what visuals can say.